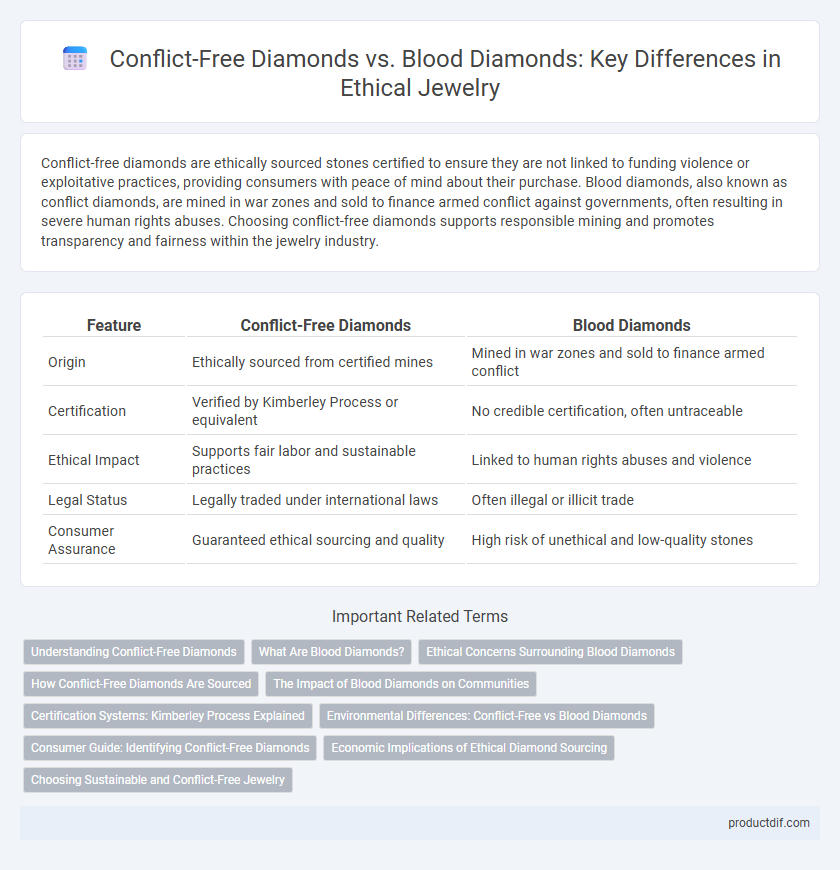
Conflict-free diamonds are ethically sourced stones certified to ensure they are not linked to funding violence or exploitative practices, providing consumers with peace of mind about their purchase. Blood diamonds, also known as conflict diamonds, are mined in war zones and sold to finance armed conflict against governments, often resulting in severe human rights abuses. Choosing conflict-free diamonds supports responsible mining and promotes transparency and fairness within the jewelry industry.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Conflict-Free Diamonds | Blood Diamonds |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Ethically sourced from certified mines | Mined in war zones and sold to finance armed conflict |
| Certification | Verified by Kimberley Process or equivalent | No credible certification, often untraceable |
| Ethical Impact | Supports fair labor and sustainable practices | Linked to human rights abuses and violence |
| Legal Status | Legally traded under international laws | Often illegal or illicit trade |
| Consumer Assurance | Guaranteed ethical sourcing and quality | High risk of unethical and low-quality stones |
Understanding Conflict-Free Diamonds
Conflict-free diamonds are ethically sourced gemstones verified to have no connection to armed conflict or human rights abuses, often certified by the Kimberley Process Certification Scheme (KPCS). These diamonds are mined in regions with transparent supply chains and adhere to strict environmental and labor standards, ensuring sustainable practices. Consumers seeking conflict-free diamonds prioritize transparency, ethical mining, and traceability to avoid supporting violence and exploitation in the diamond trade.
What Are Blood Diamonds?
Blood diamonds, also known as conflict diamonds, are diamonds mined in war zones and sold to finance armed conflict against governments, often resulting in severe human rights abuses. These diamonds fuel violence, exploitation, and corruption, causing widespread suffering in affected regions, primarily in parts of Africa like Sierra Leone, Angola, and the Democratic Republic of Congo. Efforts such as the Kimberley Process Certification Scheme aim to prevent blood diamonds from entering the legitimate diamond market, promoting ethical sourcing and consumer awareness.
Ethical Concerns Surrounding Blood Diamonds
Blood diamonds, also known as conflict diamonds, are mined in war zones and sold to finance armed conflict against governments, often involving severe human rights abuses and exploitation. Ethical concerns surrounding blood diamonds highlight the brutal conditions endured by miners, including forced labor, violence, and environmental destruction. Consumers increasingly demand conflict-free diamonds certified by organizations like the Kimberley Process to ensure their jewelry purchases do not fund violence or exploitation.
How Conflict-Free Diamonds Are Sourced
Conflict-free diamonds are sourced through ethical mining practices that ensure the stones are extracted without funding armed conflict or violating human rights. These diamonds undergo rigorous certification processes, such as the Kimberley Process, which tracks the gem from mine to market to guarantee transparency and ethical integrity. By supporting responsible mining companies and adhering to international standards, conflict-free diamonds offer consumers peace of mind and promote sustainable industry practices.
The Impact of Blood Diamonds on Communities
Blood diamonds, also known as conflict diamonds, finance armed conflict and perpetuate violence in mining regions, devastating local communities with forced labor, displacement, and human rights abuses. The extraction of these diamonds often leads to the destruction of local economies and infrastructure, leaving communities impoverished and vulnerable. In contrast, conflict-free diamonds are sourced through ethical supply chains, promoting sustainable development and improving the livelihoods of mining populations.
Certification Systems: Kimberley Process Explained
The Kimberley Process Certification Scheme (KPCS) is an international initiative designed to prevent the trade of conflict diamonds, ensuring that diamonds sold on the market are conflict-free and ethically sourced. By requiring participating countries to certify shipments of rough diamonds as conflict-free, the system aims to reduce funding for armed conflicts in diamond-producing regions. Although effective in promoting transparency, the Kimberley Process faces criticism for limited scope and enforcement challenges, prompting ongoing calls for stronger regulations in the diamond industry.
Environmental Differences: Conflict-Free vs Blood Diamonds
Conflict-free diamonds are mined with strict adherence to environmental regulations, minimizing ecosystem disruption and promoting sustainable practices such as land rehabilitation and water conservation. In contrast, blood diamonds, often sourced from war zones, typically involve unregulated mining that causes severe deforestation, soil erosion, and water contamination. The environmental impact of conflict-free diamonds is significantly lower, supporting ethical sourcing and preservation of biodiversity.
Consumer Guide: Identifying Conflict-Free Diamonds
Consumers seeking conflict-free diamonds should prioritize certifications like the Kimberley Process, which ensures diamonds are sourced without funding armed conflict. Look for reputable jewelers who provide transparent provenance documentation and independent third-party grading reports. Ethical purchasing decisions include verifying diamond origin through traceability programs and supporting brands committed to responsible sourcing standards.
Economic Implications of Ethical Diamond Sourcing
Ethical diamond sourcing, emphasized through conflict-free diamonds, supports local economies by promoting fair labor practices and reinvesting profits into community development. Blood diamonds, or conflict diamonds, finance armed conflict and destabilize regions, causing long-term economic damage and limiting sustainable growth. Consumers increasingly demand transparency in diamond origins, driving the market towards responsible sourcing and benefiting global economic stability.
Choosing Sustainable and Conflict-Free Jewelry
Selecting conflict-free diamonds ensures ethical sourcing by avoiding stones mined in war zones that fund violence, known as blood diamonds. Sustainable jewelry prioritizes transparency, adhering to strict certification like the Kimberley Process to guarantee traceability and fair labor practices. Opting for lab-grown or responsibly mined diamonds reduces environmental impact and supports human rights in the supply chain.
Conflict-Free Diamonds vs Blood Diamonds Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com