Spun glass offers a unique, artisanal texture and lightweight feel ideal for decorative pet water bowls, while molded glass provides uniformity and durability perfect for everyday use. Spun glass's handcrafted nature results in subtle variations, enhancing aesthetic appeal, whereas molded glass ensures consistent shape and thickness for long-lasting performance. Choosing between spun and molded glass depends on whether visual uniqueness or functional reliability is the priority in pet glassware.
Table of Comparison
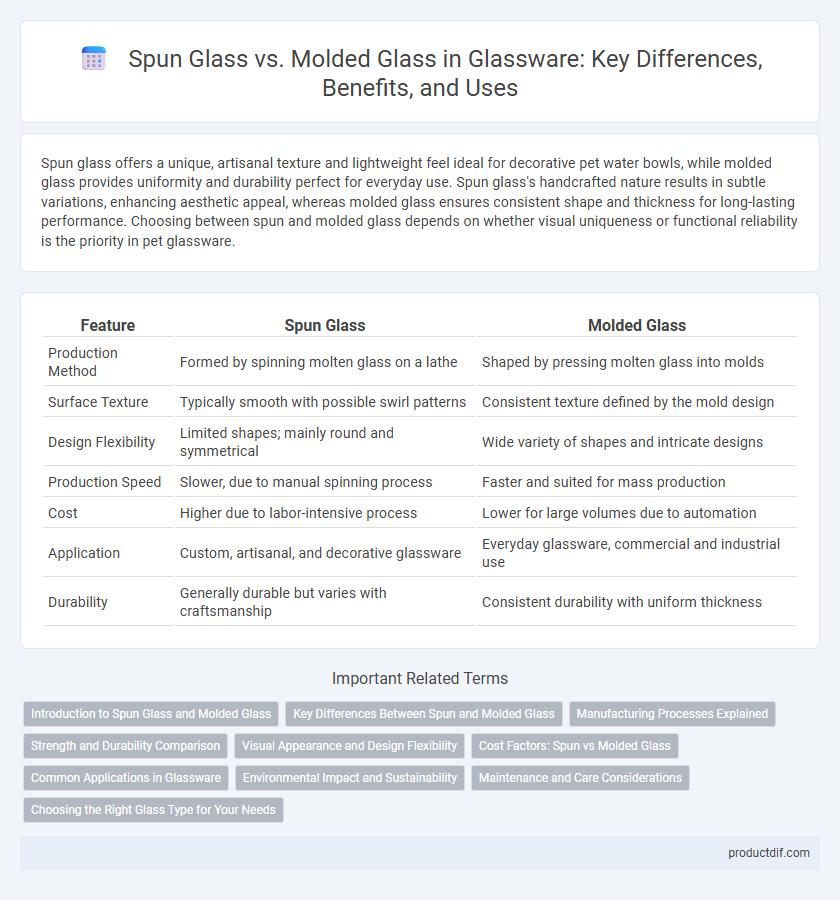
| Feature | Spun Glass | Molded Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Production Method | Formed by spinning molten glass on a lathe | Shaped by pressing molten glass into molds |
| Surface Texture | Typically smooth with possible swirl patterns | Consistent texture defined by the mold design |
| Design Flexibility | Limited shapes; mainly round and symmetrical | Wide variety of shapes and intricate designs |
| Production Speed | Slower, due to manual spinning process | Faster and suited for mass production |
| Cost | Higher due to labor-intensive process | Lower for large volumes due to automation |
| Application | Custom, artisanal, and decorative glassware | Everyday glassware, commercial and industrial use |
| Durability | Generally durable but varies with craftsmanship | Consistent durability with uniform thickness |
Introduction to Spun Glass and Molded Glass
Spun glass is crafted by rotating molten glass at high speeds, creating thin, delicate forms with smooth surface finishes ideal for decorative items. Molded glass involves pouring molten glass into pre-designed molds, allowing for precise shapes and consistent thickness suited for mass production of functional vessels. The manufacturing techniques determine glassware textures, durability, and aesthetic appeal in various applications.
Key Differences Between Spun and Molded Glass
Spun glass is created by spinning molten glass at high speeds, resulting in thin, lightweight, and uniformly shaped items, whereas molded glass is formed by pouring molten glass into molds, producing thicker, more complex shapes with detailed textures. Spun glass typically offers greater durability and a smoother surface finish, while molded glass provides more versatility in design and patterns due to the mold's flexibility. The manufacturing process for spun glass allows for faster production rates, making it ideal for mass production of simple glassware, whereas molded glass is preferred for decorative pieces requiring intricate details.
Manufacturing Processes Explained
Spun glass manufacturing involves rotating a molten glass gob rapidly to form thin, uniform discs or fibers through centrifugal force, resulting in lightweight and delicate products. Molded glass is created by pouring molten glass into pre-designed molds, allowing precise shaping and consistent thickness for items like bottles and containers. Differences in these processes affect the texture, strength, and application versatility of the final glassware products.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Spun glass exhibits enhanced strength and durability due to its uniform thickness and lack of seams, which reduces weak points typically found in molded glass. Molded glass, formed by pressing molten glass into a shape, can have variable thickness and internal stresses, potentially leading to increased fragility under impact. The manufacturing process of spun glass results in more resilient glassware suitable for heavy use and greater resistance to cracking and chipping compared to molded glass.
Visual Appearance and Design Flexibility
Spun glass features a distinctive, uniform texture with subtle concentric patterns, offering a handcrafted aesthetic that enhances visual appeal through its organic imperfections. Molded glass provides precise shapes and consistent thickness, enabling intricate designs and sharp details that cater to mass production requirements. The design flexibility of spun glass allows for unique artistic variations, while molded glass supports complex, repeatable forms ideal for functional and decorative uses.
Cost Factors: Spun vs Molded Glass
Spun glass generally incurs higher production costs due to the manual labor and time-intensive process required for shaping each piece individually. Molded glass benefits from automated manufacturing techniques that reduce labor expenses and enable mass production, resulting in lower unit costs. Material waste and energy efficiency also favor molded glass, making it a more cost-effective option for large-scale glassware production.
Common Applications in Glassware
Spun glass is commonly used for decorative and artistic glassware such as bowls, vases, and light fixtures due to its unique texture and handcrafted appearance. Molded glass is preferred for mass-produced items like drinking glasses, bottles, and jars because of its uniform shape and cost-efficient manufacturing process. Both methods offer distinct benefits tailored to specific applications in household and commercial glassware production.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Spun glass production consumes less energy than molded glass, as it involves centrifugal force to shape molten glass without the need for high-pressure molds. Molded glass manufacturing often results in higher material waste due to trimming and mold imperfections, whereas spun glass typically generates minimal scrap, enhancing resource efficiency. Both methods impact sustainability, but spun glass offers a lower carbon footprint and reduced energy consumption, making it a more environmentally friendly option in glassware production.
Maintenance and Care Considerations
Spun glass often features uniform thickness and a smooth surface, making it easier to clean and less prone to harboring dirt or residues, ideal for regular maintenance with mild detergents and soft cloths. Molded glass can possess intricate designs and variable thickness, requiring gentle handling and specialized cleaning tools to avoid scratches or damage, especially around molded patterns or edges. Proper care extends the lifespan of both spun and molded glass, with avoidance of extreme temperature changes and abrasive materials being critical for preserving their clarity and structural integrity.
Choosing the Right Glass Type for Your Needs
Spun glass features a seamless, swirl pattern ideal for decorative items requiring uniform thickness and a vintage aesthetic, while molded glass offers precise shapes and consistent dimensions suited for mass production and functional ware like drinkware or containers. Selecting the right glass type depends on whether the priority is artistic design and uniqueness or durability and replication accuracy in large quantities. Consider the intended use, production scale, and desired visual appeal to determine if spun or molded glass best meets your specific needs.
Spun glass vs Molded glass Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com