Pollinator gardens prioritize planting a diverse range of flowering plants that attract bees, butterflies, and other beneficial insects essential for pollination. Vegetable gardens focus on cultivating edible plants, requiring careful management to optimize soil health and pest control. Both garden types support biodiversity, but pollinator gardens enhance ecosystem balance while vegetable gardens provide fresh, homegrown produce.
Table of Comparison
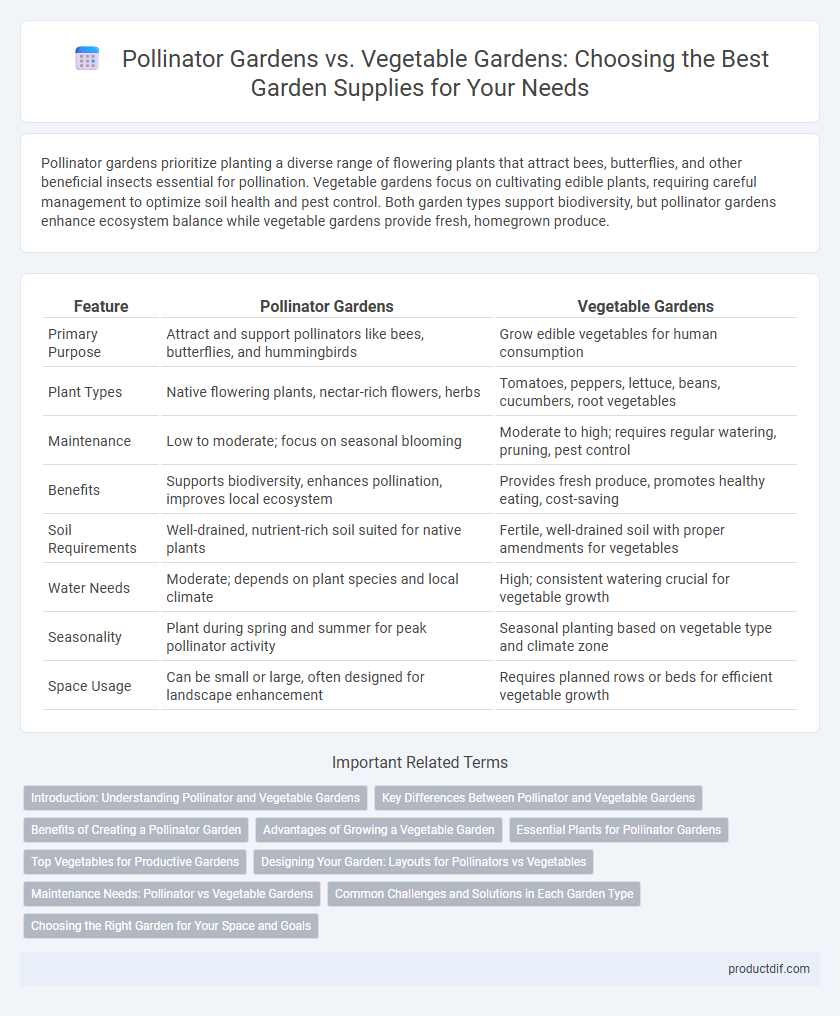
| Feature | Pollinator Gardens | Vegetable Gardens |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Attract and support pollinators like bees, butterflies, and hummingbirds | Grow edible vegetables for human consumption |
| Plant Types | Native flowering plants, nectar-rich flowers, herbs | Tomatoes, peppers, lettuce, beans, cucumbers, root vegetables |
| Maintenance | Low to moderate; focus on seasonal blooming | Moderate to high; requires regular watering, pruning, pest control |
| Benefits | Supports biodiversity, enhances pollination, improves local ecosystem | Provides fresh produce, promotes healthy eating, cost-saving |
| Soil Requirements | Well-drained, nutrient-rich soil suited for native plants | Fertile, well-drained soil with proper amendments for vegetables |
| Water Needs | Moderate; depends on plant species and local climate | High; consistent watering crucial for vegetable growth |
| Seasonality | Plant during spring and summer for peak pollinator activity | Seasonal planting based on vegetable type and climate zone |
| Space Usage | Can be small or large, often designed for landscape enhancement | Requires planned rows or beds for efficient vegetable growth |
Introduction: Understanding Pollinator and Vegetable Gardens
Pollinator gardens are designed to attract beneficial insects such as bees, butterflies, and hummingbirds, which help improve plant pollination and biodiversity. Vegetable gardens focus on cultivating edible plants like tomatoes, carrots, and lettuce for home consumption, emphasizing soil health and pest management. Understanding the unique roles and requirements of pollinator and vegetable gardens enhances garden productivity and ecological balance.
Key Differences Between Pollinator and Vegetable Gardens
Pollinator gardens primarily attract bees, butterflies, and other beneficial insects by featuring diverse native flowering plants and providing essential habitats for pollination. Vegetable gardens focus on cultivating edible crops such as tomatoes, lettuce, and peppers, requiring nutrient-rich soil and regular maintenance to optimize yield. While pollinator gardens enhance biodiversity and ecosystem health, vegetable gardens prioritize food production and often need additional pest management strategies.
Benefits of Creating a Pollinator Garden
Creating a pollinator garden supports biodiversity by attracting essential insects like bees, butterflies, and hummingbirds that enhance plant pollination and boost local ecosystems. Pollinator gardens improve the yield and health of nearby vegetable gardens through increased pollen transfer, resulting in better fruit and seed production. These gardens also provide a sustainable habitat that helps combat the decline of pollinator populations critical for agricultural success and environmental balance.
Advantages of Growing a Vegetable Garden
Growing a vegetable garden provides fresh, nutrient-rich produce that supports a healthy diet and reduces grocery costs. It encourages sustainable living by minimizing food miles and promoting organic cultivation methods. Vegetable gardens also foster hands-on learning opportunities about plant biology and seasonal cycles, enhancing environmental awareness and self-sufficiency.
Essential Plants for Pollinator Gardens
Essential plants for pollinator gardens include native wildflowers such as milkweed (Asclepias spp.), coneflowers (Echinacea spp.), and black-eyed Susans (Rudbeckia hirta) which provide nectar and pollen for bees, butterflies, and hummingbirds. Incorporating flowering herbs like lavender, thyme, and bee balm enhances habitat suitability and extends blooming periods. These plants improve biodiversity and support pollination, distinguishing pollinator gardens from vegetable gardens that primarily focus on edible crop cultivation.
Top Vegetables for Productive Gardens
Tomatoes, peppers, cucumbers, and lettuce rank among the top vegetables for productive gardens due to their high yield and nutrient density. These crops thrive in well-drained soil and full sun, maximizing growth and harvest size. Incorporating companion planting with herbs like basil or marigolds can enhance pest control and improve vegetable garden productivity.
Designing Your Garden: Layouts for Pollinators vs Vegetables
Pollinator gardens prioritize diverse plant species with staggered bloom times to attract bees, butterflies, and other beneficial insects, optimizing habitat and foraging opportunities. Vegetable gardens require organized row or bed layouts to maximize space, sunlight exposure, and ease of maintenance for crops like tomatoes, carrots, and leafy greens. Effective garden design integrates pollinator-friendly plants near vegetable beds to enhance crop pollination and yield.
Maintenance Needs: Pollinator vs Vegetable Gardens
Pollinator gardens require minimal maintenance, emphasizing native plants that thrive with occasional watering and pruning to support bees, butterflies, and other beneficial insects. Vegetable gardens demand consistent care, including regular watering, fertilizing, pest control, and harvesting to ensure healthy crop yields. The maintenance intensity of vegetable gardens is significantly higher compared to pollinator gardens, making pollinator gardens a low-effort, eco-friendly option.
Common Challenges and Solutions in Each Garden Type
Pollinator gardens often face challenges such as attracting a diverse range of pollinators while managing pests without harmful pesticides, which can be addressed by planting native flowering species and incorporating organic pest control methods. Vegetable gardens commonly struggle with soil fertility and pest infestations, solved through crop rotation, compost enrichment, and using row covers to protect plants. Both garden types benefit from proper site selection, regular maintenance, and integrating companion planting to enhance growth and resilience.
Choosing the Right Garden for Your Space and Goals
Pollinator gardens attract bees, butterflies, and hummingbirds by featuring native flowering plants that enhance biodiversity and support ecosystem health, making them ideal for small spaces prioritizing wildlife conservation. Vegetable gardens focus on growing edible crops like tomatoes, lettuce, and peppers, optimizing space for food production and homegrown nutrition, which suits gardeners with goals for sustainable eating and self-sufficiency. Selecting the right garden depends on available sunlight, soil quality, maintenance capacity, and whether the priority is ecological impact or food yield.
Pollinator gardens vs Vegetable gardens Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com