Compost bins and worm bins both recycle organic waste but differ in process and ideal use. Compost bins rely on aerobic decomposition, breaking down materials through heat and microbial activity, making them suitable for larger yard waste. Worm bins use vermicomposting, where worms consume food scraps, producing nutrient-rich castings ideal for indoor or small-scale composting.
Table of Comparison
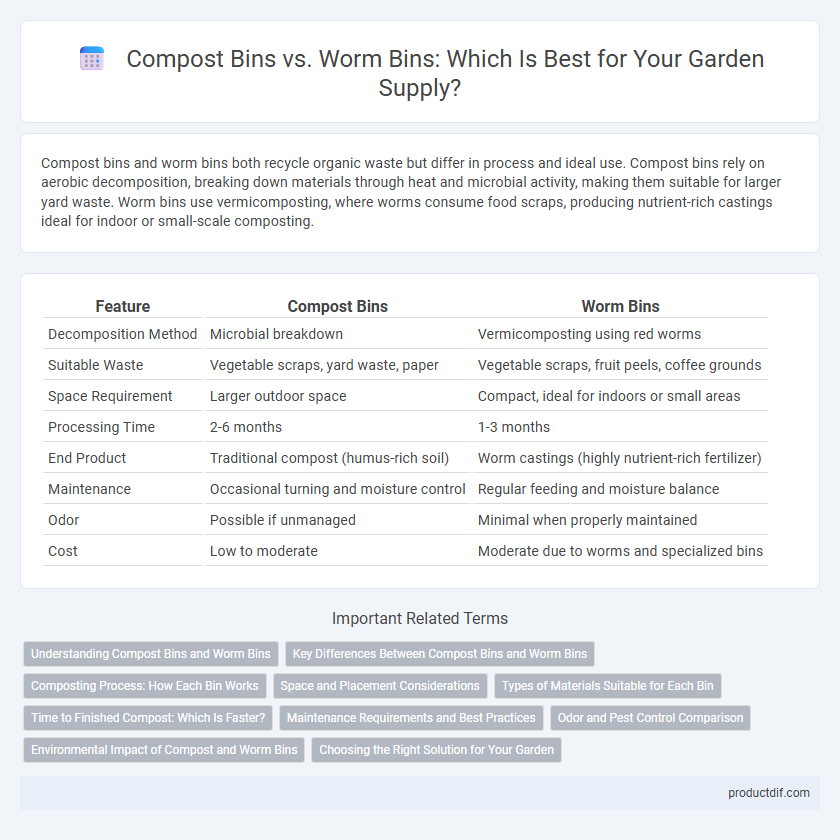
| Feature | Compost Bins | Worm Bins |
|---|---|---|
| Decomposition Method | Microbial breakdown | Vermicomposting using red worms |
| Suitable Waste | Vegetable scraps, yard waste, paper | Vegetable scraps, fruit peels, coffee grounds |
| Space Requirement | Larger outdoor space | Compact, ideal for indoors or small areas |
| Processing Time | 2-6 months | 1-3 months |
| End Product | Traditional compost (humus-rich soil) | Worm castings (highly nutrient-rich fertilizer) |
| Maintenance | Occasional turning and moisture control | Regular feeding and moisture balance |
| Odor | Possible if unmanaged | Minimal when properly maintained |
| Cost | Low to moderate | Moderate due to worms and specialized bins |
Understanding Compost Bins and Worm Bins
Compost bins and worm bins serve distinct roles in organic waste decomposition, with compost bins utilizing aerobic microbes to break down yard and kitchen scraps into nutrient-rich soil amendments. Worm bins, or vermicomposting systems, employ specific earthworm species like Eisenia fetida to accelerate organic matter decomposition while producing high-quality worm castings beneficial for plant growth. Understanding these differences helps gardeners select the most efficient composting method for their available space and waste type.
Key Differences Between Compost Bins and Worm Bins
Compost bins use aerobic decomposition by microorganisms to break down kitchen scraps and garden waste into nutrient-rich humus, typically requiring regular turning and adequate airflow. Worm bins, also known as vermicomposters, employ earthworms to consume organic waste, producing highly concentrated worm castings that enhance soil fertility and water retention. Key differences include decomposition speed, odor control, space requirements, and the type of organic waste processed, with worm bins favoring softer scraps and compost bins handling a broader variety of materials.
Composting Process: How Each Bin Works
Compost bins aerate organic waste and promote decomposition through microbial activity, breaking down materials into nutrient-rich humus over several months. Worm bins utilize red wigglers to consume food scraps, producing worm castings that accelerate nutrient cycling and create a highly fertile compost in a shorter time. Both systems enhance soil health but differ in processing speed and the role of decomposers involved.
Space and Placement Considerations
Compost bins require more outdoor space due to their larger size and need for proper ventilation, making them ideal for gardens with ample room. Worm bins are compact and can be placed indoors or on small patios, suitable for limited-space environments like apartments. Choosing between the two depends on available space and whether the bin will be kept inside or outside.
Types of Materials Suitable for Each Bin
Compost bins effectively decompose a wide range of garden waste, including fruit and vegetable scraps, coffee grounds, grass clippings, and leaves, supporting aerobic microbial activity. Worm bins are optimized for kitchen scraps such as fruit peels, vegetable trimmings, and crushed eggshells, providing a suitable environment for red wiggler worms to break down organic matter into nutrient-rich vermicompost. Avoid meat, dairy, and oily foods in both bins to prevent odors and pests, ensuring efficient decomposition and healthy soil amendment production.
Time to Finished Compost: Which Is Faster?
Worm bins produce finished compost faster than traditional compost bins, typically taking 4 to 6 weeks due to the accelerated breakdown by red wigglers. Traditional compost bins can require 2 to 6 months depending on conditions like aeration, moisture, and material composition. Choosing worm bins optimizes time efficiency for gardeners seeking rapid nutrient-rich soil amendments.
Maintenance Requirements and Best Practices
Compost bins require regular turning and aeration to maintain optimal decomposition and prevent odors, while worm bins need consistent moisture levels and proper feeding with kitchen scraps to support worm health. Maintaining a balanced carbon-to-nitrogen ratio is crucial in both systems to ensure efficient breakdown of organic matter and avoid pest issues. Best practices include placing compost bins in a well-drained, shaded area and using bedding materials like shredded newspaper in worm bins to promote a healthy environment.
Odor and Pest Control Comparison
Compost bins and worm bins differ significantly in odor and pest control, with worm bins producing minimal odor due to efficient organic waste breakdown by worms, while traditional compost bins may emit stronger smells if not aerated properly. Worm bins naturally deter pests by maintaining a controlled environment and reducing food residues that attract insects, whereas compost bins require regular turning and careful management to prevent pest infestations. Choosing between the two depends on desired maintenance levels and the importance of odor and pest mitigation in garden waste management.
Environmental Impact of Compost and Worm Bins
Compost bins promote aerobic decomposition, reducing methane emissions and enhancing soil health through nutrient-rich humus production. Worm bins accelerate organic waste breakdown via vermicomposting, producing highly bioavailable nutrients and lowering landfill contributions. Both methods decrease greenhouse gas emissions compared to traditional disposal, with worm bins offering a compact solution ideal for urban environments.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Garden
Compost bins and worm bins both offer effective organic waste recycling but cater to different gardening needs and spaces. Compost bins excel at breaking down larger quantities of yard waste and produce nutrient-rich soil amendments, while worm bins are ideal for small-scale kitchens and provide worm castings that enhance soil fertility. Choosing the right solution depends on your garden size, type of organic waste, and how quickly you want to enrich your soil.
Compost bins vs Worm bins Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com