Reclaimed wood offers a unique, rustic charm by repurposing aged materials, reducing waste, and preserving historical character in furniture design. Sustainable wood comes from responsibly managed forests, ensuring long-term ecological balance while providing durable and eco-friendly furniture options. Choosing between reclaimed and sustainable wood depends on the desired aesthetic impact and environmental priorities of your furniture project.
Table of Comparison
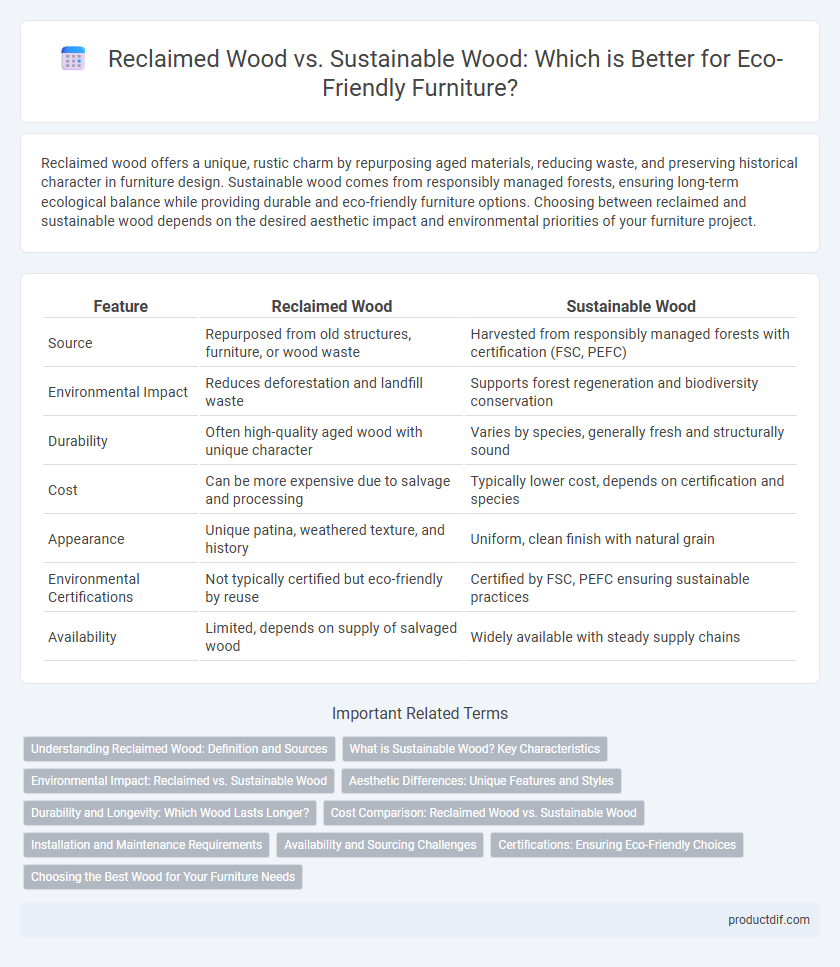
| Feature | Reclaimed Wood | Sustainable Wood |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Repurposed from old structures, furniture, or wood waste | Harvested from responsibly managed forests with certification (FSC, PEFC) |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces deforestation and landfill waste | Supports forest regeneration and biodiversity conservation |
| Durability | Often high-quality aged wood with unique character | Varies by species, generally fresh and structurally sound |
| Cost | Can be more expensive due to salvage and processing | Typically lower cost, depends on certification and species |
| Appearance | Unique patina, weathered texture, and history | Uniform, clean finish with natural grain |
| Environmental Certifications | Not typically certified but eco-friendly by reuse | Certified by FSC, PEFC ensuring sustainable practices |
| Availability | Limited, depends on supply of salvaged wood | Widely available with steady supply chains |
Understanding Reclaimed Wood: Definition and Sources
Reclaimed wood refers to timber that has been salvaged from old structures such as barns, factories, and warehouses, repurposed to reduce environmental impact and preserve natural resources. This wood often features unique textures and historic character, making it highly valued in sustainable furniture design. Sourcing reclaimed wood involves careful extraction and processing to ensure durability while minimizing waste and promoting eco-friendly practices in the furniture industry.
What is Sustainable Wood? Key Characteristics
Sustainable wood refers to timber sourced from responsibly managed forests that prioritize environmental health, biodiversity, and regeneration. Key characteristics include certification by organizations such as FSC or PEFC, ensuring the wood comes from forests that are harvested at a rate allowing natural regrowth and minimal ecological impact. This type of wood supports eco-friendly furniture production by reducing deforestation and promoting long-term forest conservation.
Environmental Impact: Reclaimed vs. Sustainable Wood
Reclaimed wood significantly reduces deforestation by repurposing existing materials, lowering carbon emissions associated with harvesting new timber. Sustainable wood, sourced from responsibly managed forests, ensures ongoing carbon sequestration and biodiversity preservation through certified forestry practices. Both options minimize environmental impact compared to conventional hardwood, but reclaimed wood offers a higher immediate reduction in waste and resource demand.
Aesthetic Differences: Unique Features and Styles
Reclaimed wood boasts distinctive character with weathered textures, knots, and natural imperfections that create a rustic, vintage aesthetic ideal for one-of-a-kind furniture pieces. Sustainable wood, often sourced from responsibly managed forests, features a cleaner, uniform grain and finish that complements modern, minimalist designs. Both materials offer environmentally conscious options, but reclaimed wood emphasizes charm and history while sustainable wood prioritizes consistency and sleek style.
Durability and Longevity: Which Wood Lasts Longer?
Reclaimed wood offers exceptional durability due to its aged and well-seasoned nature, often outperforming new sustainable wood in longevity. Sustainable wood, sourced from responsibly managed forests, combines environmental benefits with reliable strength but may require treatment to match reclaimed wood's resistance to wear. When prioritizing long-term use, reclaimed wood's dense fibers and historical aging generally ensure a longer lifespan in furniture construction.
Cost Comparison: Reclaimed Wood vs. Sustainable Wood
Reclaimed wood often presents higher upfront costs due to the intensive labor required for harvesting, cleaning, and processing, whereas sustainable wood typically has more predictable and lower pricing driven by regulated forestry practices. Long-term expenses for reclaimed wood can potentially be lower because of its durability and reduced need for frequent replacement. Sustainable wood benefits from certifications like FSC or PEFC, which can justify its cost by ensuring responsible sourcing and environmental impact reduction.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Reclaimed wood often demands more careful installation due to its irregularities and prior wear, requiring specialized tools and skilled labor to ensure structural integrity. Maintenance for reclaimed wood involves regular sealing and vigilant protection against moisture to prevent deterioration, while sustainable wood, typically milled for uniformity, allows easier installation with standard tools and faster fitting. Sustainable wood generally requires less frequent maintenance, benefiting from treatments that enhance resistance to pests and decay, making it a more straightforward choice for long-term upkeep.
Availability and Sourcing Challenges
Reclaimed wood offers limited availability due to its dependence on salvaged materials from old structures, requiring careful inspection and processing to meet quality standards. Sustainable wood is more readily accessible, sourced from responsibly managed forests certified by organizations like FSC, but may face regional restrictions and harvesting regulations that impact supply. Both types present sourcing challenges, with reclaimed wood constrained by quantity and condition, while sustainable wood demands adherence to environmental certifications and supply chain transparency.
Certifications: Ensuring Eco-Friendly Choices
Reclaimed wood often carries certifications like FSC Reclaimed, verifying it comes from salvaged sources and reducing demand for new timber. Sustainable wood is typically certified by organizations such as FSC (Forest Stewardship Council) or PEFC (Programme for the Endorsement of Forest Certification), ensuring it is harvested responsibly to maintain forest health. Choosing furniture with these certifications guarantees eco-friendly practices and supports conservation efforts.
Choosing the Best Wood for Your Furniture Needs
Reclaimed wood offers unique character and environmental benefits by repurposing aged timber, reducing deforestation and waste. Sustainable wood comes from responsibly managed forests, ensuring a continuous supply while protecting ecosystems and biodiversity. Choosing between reclaimed and sustainable wood depends on your furniture style preferences, durability requirements, and commitment to environmental impact.
Reclaimed wood vs Sustainable wood Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com