Mortise and tenon joinery offers superior strength and durability compared to dowel joinery, making it ideal for heavy-duty furniture pieces such as tables and chairs. This traditional technique creates a tight, interlocking fit that resists twisting and pulling forces better than dowels, which rely more on adhesives and precision drilling. While dowel joinery is quicker and easier to assemble, mortise and tenon joints provide longer-lasting structural integrity and a cleaner aesthetic.
Table of Comparison
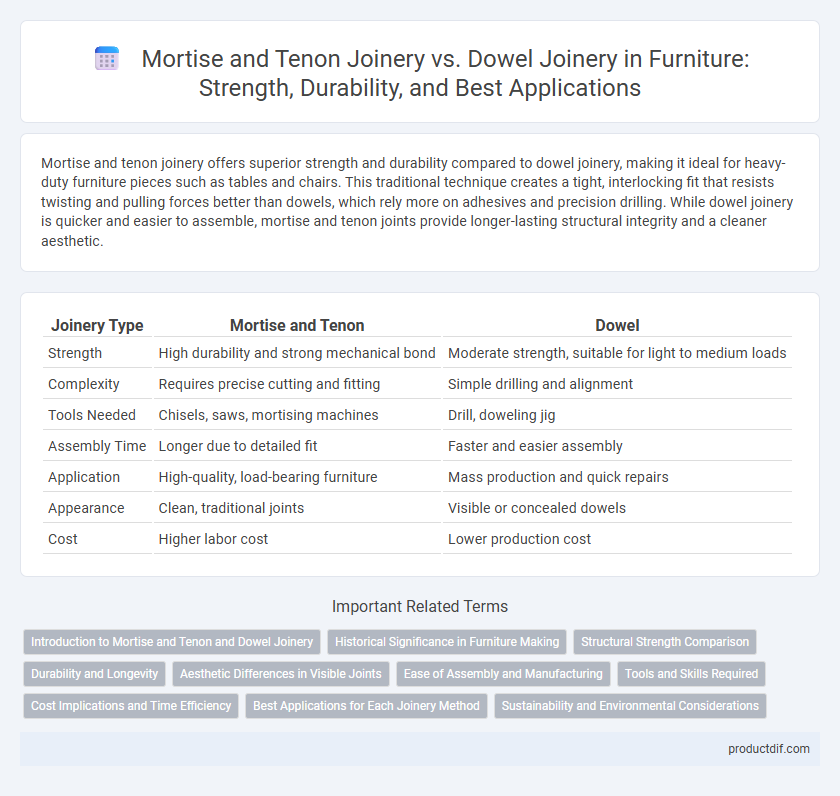
| Joinery Type | Mortise and Tenon | Dowel |
|---|---|---|
| Strength | High durability and strong mechanical bond | Moderate strength, suitable for light to medium loads |
| Complexity | Requires precise cutting and fitting | Simple drilling and alignment |
| Tools Needed | Chisels, saws, mortising machines | Drill, doweling jig |
| Assembly Time | Longer due to detailed fit | Faster and easier assembly |
| Application | High-quality, load-bearing furniture | Mass production and quick repairs |
| Appearance | Clean, traditional joints | Visible or concealed dowels |
| Cost | Higher labor cost | Lower production cost |
Introduction to Mortise and Tenon and Dowel Joinery
Mortise and tenon joinery involves fitting a protruding tenon into a corresponding mortise cavity, offering exceptional strength and durability in furniture construction. Dowel joinery uses cylindrical wooden pins inserted into aligned holes to connect pieces, providing a simpler and faster assembly method. Both techniques are fundamental in woodworking, with mortise and tenon favored for heavy-duty joints and dowels preferred for ease and precision in lightweight frames.
Historical Significance in Furniture Making
Mortise and tenon joinery has been a cornerstone of traditional furniture making for thousands of years, favored for its strength and durability in crafting timber frames and antique cabinetry. Dowel joinery, emerging prominently in the 19th century with industrial advancements, offers quicker assembly and consistent alignment, revolutionizing mass-produced furniture. The historical significance of mortise and tenon lies in its role in handcrafted masterpieces, while dowel joinery marks the shift toward mechanization and efficiency in furniture construction.
Structural Strength Comparison
Mortise and tenon joinery provides superior structural strength due to the large surface area for glue adhesion and interlocking wood fibers, making it ideal for load-bearing furniture joints. Dowel joinery, while easier to assemble, offers less mechanical strength and may loosen over time under stress or heavy use. For applications requiring durability and long-lasting stability, mortise and tenon joints outperform dowel joints in resisting shear and tensile forces.
Durability and Longevity
Mortise and tenon joinery offers superior durability and longevity due to its deep, interlocking connection, which evenly distributes stress and resists shear forces over time. Dowel joinery, while easier to assemble, relies heavily on glue and is more prone to joint failure under heavy loads or prolonged use. For high-quality furniture requiring structural strength and extended lifespan, mortise and tenon remains the preferred technique among craftsmen.
Aesthetic Differences in Visible Joints
Mortise and tenon joinery offers clean, seamless joints that blend effortlessly with wood grain, enhancing the furniture's natural beauty and providing a traditional handcrafted appearance. Dowel joinery, often visible through small circular plugs or patches, can interrupt the wood's continuity and may require additional finishing to achieve a smooth aesthetic. The choice between these methods significantly impacts the visual appeal, with mortise and tenon favored for subtlety and dowel joinery noted for its ease but more noticeable joint marks.
Ease of Assembly and Manufacturing
Mortise and tenon joinery offers exceptional structural strength but requires precise workmanship and more time during assembly and manufacturing, making it less efficient for mass production. Dowel joinery simplifies the assembly process with standardized, pre-drilled holes and fast installation, significantly reducing manufacturing time and labor costs. Factories favor dowel joints for their repeatability and speed, while custom furniture makers often prefer mortise and tenon for superior durability despite its complexity.
Tools and Skills Required
Mortise and tenon joinery demands precise chisels, mallets, and saws, along with advanced woodworking skills to create tight, interlocking joints. Dowel joinery requires simpler tools, such as drills and dowel jigs, making it more accessible for beginners but less durable under heavy loads. Skilled craftsmen prefer mortise and tenon for its strength and traditional craftsmanship, while dowel joinery suits rapid assembly and basic furniture projects.
Cost Implications and Time Efficiency
Mortise and tenon joinery generally incurs higher labor costs due to its precise cutting and fitting requirements, making it less cost-efficient for mass production. Dowel joinery is faster to execute with standardized drilling, reducing assembly time and labor expenses, which enhances overall time efficiency. Factoring material costs, dowels are typically cheaper than the hardwood components needed for mortise and tenon joints, impacting budget considerations in furniture manufacturing.
Best Applications for Each Joinery Method
Mortise and tenon joinery excels in structural applications requiring high strength, such as chair frames and table legs, due to its deep interlocking design that distributes stress evenly. Dowel joinery is ideal for light to medium loads like cabinet assembly and drawer construction, offering quick alignment and ease of assembly without extensive woodworking tools. Both methods enhance durability, but mortise and tenon is preferred for traditional fine furniture, while dowels suit mass production and furniture with consistent repeatability.
Sustainability and Environmental Considerations
Mortise and tenon joinery offers superior durability and long-term repairability, reducing the need for replacement and minimizing waste in sustainable furniture design. Dowel joinery, often relying on synthetic adhesives and engineered dowels, can complicate recycling and lower the overall environmental performance of wooden products. Choosing mortise and tenon techniques promotes eco-friendly craftsmanship by enabling disassembly and reuse, aligning with circular economy principles in furniture manufacturing.
Mortise and tenon joinery vs Dowel joinery Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com