Enzyme-based cleaning products use natural biological catalysts to break down stains and organic matter, offering a safer and eco-friendly alternative to harsh chemicals. Chemical-based cleaners often provide faster and more aggressive stain removal but may contain ingredients that can irritate skin or harm the environment. Choosing enzyme-based cleaners supports sustainability and reduces the risk of harmful residue while maintaining effective cleaning performance.
Table of Comparison
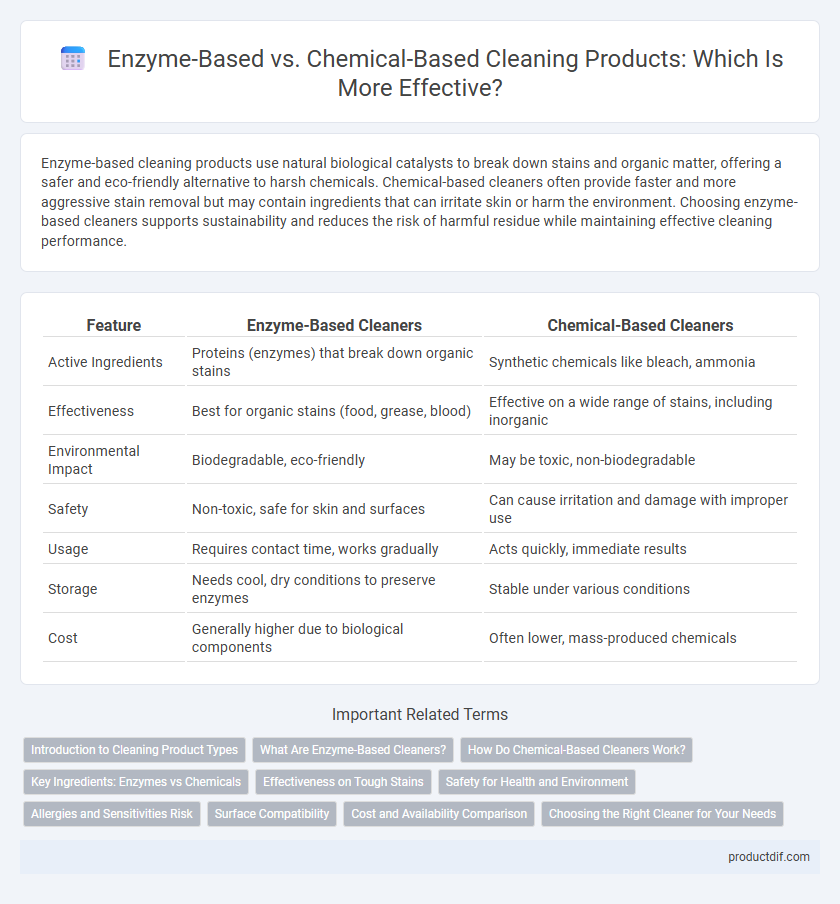
| Feature | Enzyme-Based Cleaners | Chemical-Based Cleaners |
|---|---|---|
| Active Ingredients | Proteins (enzymes) that break down organic stains | Synthetic chemicals like bleach, ammonia |
| Effectiveness | Best for organic stains (food, grease, blood) | Effective on a wide range of stains, including inorganic |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, eco-friendly | May be toxic, non-biodegradable |
| Safety | Non-toxic, safe for skin and surfaces | Can cause irritation and damage with improper use |
| Usage | Requires contact time, works gradually | Acts quickly, immediate results |
| Storage | Needs cool, dry conditions to preserve enzymes | Stable under various conditions |
| Cost | Generally higher due to biological components | Often lower, mass-produced chemicals |
Introduction to Cleaning Product Types
Enzyme-based cleaning products utilize natural biological catalysts to break down organic stains, making them highly effective for removing food, grease, and protein-based debris. Chemical-based cleaners rely on synthetic compounds like surfactants, bleach, and acids to dissolve dirt, disinfect surfaces, and eliminate tough stains. Understanding the differences in composition and mechanism helps consumers select the optimal cleaning solution for specific household or industrial applications.
What Are Enzyme-Based Cleaners?
Enzyme-based cleaners utilize natural enzymes to break down organic stains and soils, targeting proteins, fats, and carbohydrates for efficient removal. These biodegradable products offer eco-friendly alternatives to chemical-based cleaners, minimizing harmful residues and reducing environmental impact. Their specificity in catalyzing biochemical reactions makes them ideal for applications in laundry, kitchen, and bathroom cleaning.
How Do Chemical-Based Cleaners Work?
Chemical-based cleaners work by utilizing reactive compounds such as acids, alkalis, solvents, and surfactants to break down dirt, grease, and stains at a molecular level. These cleaners alter the chemical structure of contaminants, allowing for easy removal through rinsing or wiping. Their effectiveness depends on the specific formulation designed to target various types of soils and surfaces.
Key Ingredients: Enzymes vs Chemicals
Enzyme-based cleaning products utilize natural enzymes such as protease, amylase, and lipase to break down organic stains like proteins, starches, and fats at a molecular level, enhancing stain removal efficiency and environmental safety. Chemical-based cleaners rely on synthetic agents like surfactants, bleach, and solvents that aggressively dissolve dirt and bacteria but may pose higher risks of toxicity and surface damage. The choice between enzymes and chemicals impacts cleaning effectiveness, biodegradability, and user safety, making enzyme formulations preferable for eco-friendly and sensitive-surface applications.
Effectiveness on Tough Stains
Enzyme-based cleaning products break down protein, starches, and fat molecules, making them highly effective against organic tough stains like blood, grease, and food residue. Chemical-based cleaners often rely on harsh solvents and surfactants that can dissolve a broad range of stains but may cause fabric damage or leave residues. Enzyme formulas provide targeted stain removal with biodegradability, while chemical cleaners deliver rapid action on synthetic or oil-based stains.
Safety for Health and Environment
Enzyme-based cleaning products use natural proteins that break down organic stains, offering a safer alternative with minimal toxicity and biodegradability that reduces environmental impact. Chemical-based cleaners often contain harsh substances like ammonia or chlorine, which can pose respiratory risks, skin irritation, and contribute to water pollution. Choosing enzyme-based formulations supports healthier indoor air quality and promotes sustainable cleaning practices by minimizing harmful chemical residues.
Allergies and Sensitivities Risk
Enzyme-based cleaning products typically pose a lower risk of allergies and sensitivities because they use natural biological catalysts that break down stains without harsh chemicals. Chemical-based cleaners often contain synthetic fragrances and detergents that can trigger skin irritation, respiratory issues, and allergic reactions in sensitive individuals. Choosing enzyme-based formulas can minimize exposure to allergens and is generally safer for those with chemical sensitivities.
Surface Compatibility
Enzyme-based cleaning products excel in surface compatibility by targeting organic stains without damaging delicate materials such as wood, fabric, and natural stone. Chemical-based cleaners often contain harsh agents that can degrade or discolor sensitive surfaces over time. Choosing enzyme-based solutions ensures effective cleaning while preserving the integrity of various surface types.
Cost and Availability Comparison
Enzyme-based cleaning products typically have a higher upfront cost compared to chemical-based alternatives due to their complex formulation and production process. Chemical-based cleaners are widely available in various retail outlets and offer lower prices, making them more accessible for everyday use. Despite the initial expense, enzyme-based products can provide long-term savings by effectively breaking down organic stains, reducing the amount of product needed per cleaning session.
Choosing the Right Cleaner for Your Needs
Enzyme-based cleaners effectively break down organic stains and odors by targeting proteins, fats, and carbohydrates, making them ideal for pet stains and food residue. Chemical-based cleaners offer powerful disinfection and stain removal for tough grime, grease, and bacteria on hard surfaces. Selecting the right cleaner depends on the specific cleaning task, surface type, and sensitivity to harsh chemicals or environmental impact.
Enzyme-based vs Chemical-based Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com