Ammonia-based cleaning products excel at cutting through grease and grime on glass and hard surfaces, offering streak-free shines and fast evaporation. Alcohol-based cleaners provide powerful disinfectant properties, evaporate quickly without leaving residue, and are ideal for sanitizing electronics and non-porous surfaces. Choosing between ammonia-based and alcohol-based cleaners depends on the cleaning task, surface type, and desired disinfecting effect.
Table of Comparison
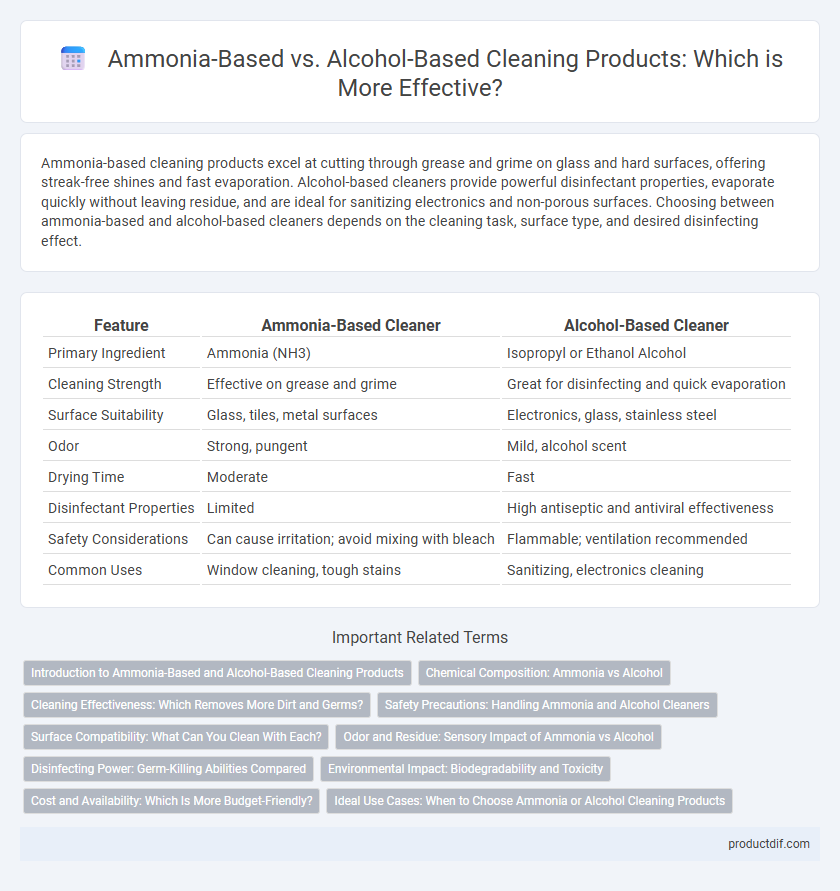
| Feature | Ammonia-Based Cleaner | Alcohol-Based Cleaner |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Ingredient | Ammonia (NH3) | Isopropyl or Ethanol Alcohol |
| Cleaning Strength | Effective on grease and grime | Great for disinfecting and quick evaporation |
| Surface Suitability | Glass, tiles, metal surfaces | Electronics, glass, stainless steel |
| Odor | Strong, pungent | Mild, alcohol scent |
| Drying Time | Moderate | Fast |
| Disinfectant Properties | Limited | High antiseptic and antiviral effectiveness |
| Safety Considerations | Can cause irritation; avoid mixing with bleach | Flammable; ventilation recommended |
| Common Uses | Window cleaning, tough stains | Sanitizing, electronics cleaning |
Introduction to Ammonia-Based and Alcohol-Based Cleaning Products
Ammonia-based cleaning products contain ammonium hydroxide, which effectively cuts through grease, grime, and tough stains on surfaces like glass and kitchen countertops. Alcohol-based cleaners primarily use isopropyl or ethyl alcohol, providing fast evaporation and strong disinfectant properties ideal for sanitizing electronics and high-touch areas. Understanding the chemical composition and typical uses of these products helps in selecting the right cleaner for specific cleaning tasks.
Chemical Composition: Ammonia vs Alcohol
Ammonia-based cleaning products contain ammonium hydroxide, a compound with strong alkaline properties effective at breaking down grease and grime on hard surfaces. Alcohol-based cleaners primarily use isopropyl or ethyl alcohol, known for their rapid evaporation and ability to disinfect by denaturing proteins and dissolving oils. The chemical composition differences influence their cleaning applications, with ammonia excelling in heavy-duty degreasing and alcohol favored for sanitizing and quick-drying uses.
Cleaning Effectiveness: Which Removes More Dirt and Germs?
Ammonia-based cleaners excel at cutting through tough grease, grime, and baked-on stains on surfaces like glass and tile, making them highly effective for deep cleaning tasks. Alcohol-based cleaners, particularly those with at least 70% isopropyl alcohol, are superior at killing a wide range of bacteria and viruses, providing strong disinfectant properties on high-touch surfaces. For optimal cleaning effectiveness, ammonia-based products are best for heavy-duty dirt removal, while alcohol-based solutions are preferred for rapid germ elimination.
Safety Precautions: Handling Ammonia and Alcohol Cleaners
Ammonia-based cleaners require proper ventilation due to their strong fumes and should never be mixed with bleach, as this produces toxic chloramine vapors. Alcohol-based cleaners, such as isopropyl alcohol, are flammable and must be stored away from heat sources and open flames while also used in well-ventilated areas to minimize inhalation risks. Both types of cleaners necessitate wearing gloves and eye protection to prevent skin irritation and eye damage during handling.
Surface Compatibility: What Can You Clean With Each?
Ammonia-based cleaners are highly effective on glass, tiles, and kitchen countertops, providing streak-free shine but can damage surfaces such as wood, aluminum, and painted finishes. Alcohol-based cleaners excel at disinfecting electronics, mirrors, and stainless steel without causing corrosion or discoloration, making them ideal for sensitive surfaces. Understanding surface compatibility ensures optimal cleaning results while preventing damage and preserving material integrity.
Odor and Residue: Sensory Impact of Ammonia vs Alcohol
Ammonia-based cleaners emit a sharp, pungent odor that can be overpowering but dissipates quickly, whereas alcohol-based cleaners release a milder, more neutral scent that lingers less on surfaces. Ammonia tends to leave behind a thin residue that might attract dust if not wiped thoroughly, while alcohol evaporates rapidly, minimizing residue and resulting in a streak-free finish. The sensory impact of ammonia is often perceived as harsher, making alcohol-based products preferable for environments sensitive to strong smells.
Disinfecting Power: Germ-Killing Abilities Compared
Ammonia-based cleaners exhibit strong disinfecting power against bacteria and viruses, effectively breaking down grease and organic matter to eliminate germs. Alcohol-based products typically contain isopropyl or ethyl alcohol, which rapidly denature proteins, providing superior virucidal action against flu viruses and coronaviruses. Both types offer potent germ-killing abilities, but alcohol-based disinfectants generally achieve faster microbial kill times on non-porous surfaces.
Environmental Impact: Biodegradability and Toxicity
Ammonia-based cleaning products typically exhibit moderate biodegradability but release nitrogen compounds that can contribute to environmental toxicity and water pollution. Alcohol-based cleaners tend to biodegrade more rapidly and break down into less harmful byproducts, reducing their ecological footprint. Both types require careful formulation and usage to minimize potential harm to aquatic life and soil health.
Cost and Availability: Which Is More Budget-Friendly?
Ammonia-based cleaners are generally more budget-friendly due to their lower production costs and widespread availability in most retail stores, making them accessible for regular household use. Alcohol-based cleaners tend to be pricier because of higher ingredient costs and demand spikes during health crises, but they offer faster evaporation and residue-free cleaning. Evaluating long-term expenses, ammonia solutions provide cost-efficiency for extensive cleaning tasks, while alcohol-based products may justify their price with superior sanitizing power.
Ideal Use Cases: When to Choose Ammonia or Alcohol Cleaning Products
Ammonia-based cleaning products excel in cutting through tough grease and grime on glass, mirrors, and kitchen surfaces, making them ideal for heavy-duty cleaning tasks. Alcohol-based cleaners are best suited for disinfecting surfaces, evaporating quickly on electronics or stainless steel where streak-free drying is essential. Choose ammonia formulations for deep cleaning and alcohol solutions for sanitizing and fast-drying applications.
Ammonia-based vs Alcohol-based Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com