Literary fiction emphasizes deep character development, stylistic innovation, and explores complex themes often reflecting the human condition. Genre fiction prioritizes plot-driven narratives, specific conventions, and caters to audience expectations within categories like mystery, romance, or science fiction. Both forms contribute uniquely to literature, blending creativity and entertainment to engage diverse readers.
Table of Comparison
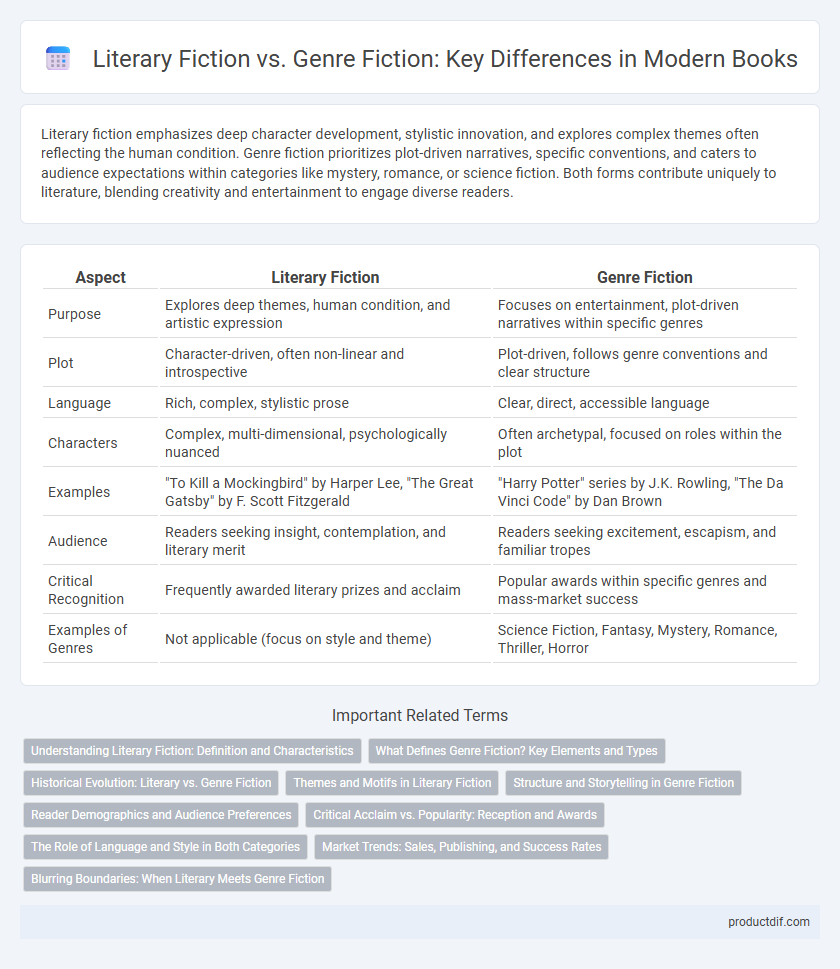
| Aspect | Literary Fiction | Genre Fiction |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Explores deep themes, human condition, and artistic expression | Focuses on entertainment, plot-driven narratives within specific genres |
| Plot | Character-driven, often non-linear and introspective | Plot-driven, follows genre conventions and clear structure |
| Language | Rich, complex, stylistic prose | Clear, direct, accessible language |
| Characters | Complex, multi-dimensional, psychologically nuanced | Often archetypal, focused on roles within the plot |
| Examples | "To Kill a Mockingbird" by Harper Lee, "The Great Gatsby" by F. Scott Fitzgerald | "Harry Potter" series by J.K. Rowling, "The Da Vinci Code" by Dan Brown |
| Audience | Readers seeking insight, contemplation, and literary merit | Readers seeking excitement, escapism, and familiar tropes |
| Critical Recognition | Frequently awarded literary prizes and acclaim | Popular awards within specific genres and mass-market success |
| Examples of Genres | Not applicable (focus on style and theme) | Science Fiction, Fantasy, Mystery, Romance, Thriller, Horror |
Understanding Literary Fiction: Definition and Characteristics
Literary fiction emphasizes complex characters, thematic depth, and stylistic innovation, often exploring the human condition through nuanced narratives. Its definition centers around artistic merit and introspective storytelling rather than plot-driven action or genre conventions. Characteristics include ambiguous endings, intricate prose, and a focus on character development over plot mechanics, distinguishing it from genre fiction's formulaic structures.
What Defines Genre Fiction? Key Elements and Types
Genre fiction is defined by its adherence to specific conventions and tropes that cater to particular audience expectations, often emphasizing plot, character archetypes, and setting. Key elements include a clear narrative structure, recognizable themes such as mystery, romance, or science fiction, and consistent tone that aligns with the chosen genre. Popular types of genre fiction encompass fantasy, thriller, horror, romance, and crime, each offering distinct storytelling frameworks and emotional experiences.
Historical Evolution: Literary vs. Genre Fiction
Literary fiction emerged from classical and modernist traditions, emphasizing stylistic innovation, thematic depth, and character complexity, whereas genre fiction developed through popular markets, focusing on established narrative formulas and entertainment value. Over time, literary fiction gained prestige in academic and critical circles, while genre fiction evolved into diverse subgenres like mystery, science fiction, and romance, each cultivating dedicated readerships and cultural significance. The historical evolution reflects shifting cultural values, with genre fiction increasingly recognized for its artistic merit and literary fiction broadening to include genre elements.
Themes and Motifs in Literary Fiction
Literary fiction explores complex themes such as identity, morality, and existentialism, often delving into the human condition with nuanced character development and symbolic motifs. The narrative structure in literary fiction emphasizes introspection and ambiguity, allowing themes to unfold subtly through metaphor and allegory. This focus on layered meaning distinguishes literary fiction from genre fiction, which typically prioritizes plot-driven stories and clear thematic resolutions.
Structure and Storytelling in Genre Fiction
Genre fiction prioritizes structured narratives with clear conventions, often following formulaic plot arcs to guide reader expectations and maintain suspense. Its storytelling relies on well-defined tropes and archetypes to quickly establish settings and characters, facilitating immersive and fast-paced experiences. This approach contrasts with literary fiction's emphasis on experimental structures and nuanced thematic exploration, favoring plot-driven cohesion in genre fiction.
Reader Demographics and Audience Preferences
Literary fiction readers often prioritize complex characters and thematic depth, appealing mainly to adult audiences with higher education levels seeking intellectual engagement. Genre fiction attracts a broader demographic by providing familiar tropes and fast-paced plots, catering to readers looking for entertainment and escapism across various ages. Market data shows genre fiction consistently outperforms literary fiction in sales volume, reflecting its widespread appeal across diverse reader preferences.
Critical Acclaim vs. Popularity: Reception and Awards
Literary fiction often garners critical acclaim through prestigious awards such as the Pulitzer Prize and Man Booker Prize, emphasizing thematic depth and stylistic innovation. Genre fiction, including mystery, romance, and science fiction, typically achieves higher commercial popularity and widespread readership despite receiving fewer major literary accolades. The distinction in reception highlights a divide where literary fiction is celebrated for artistic merit, while genre fiction excels in market success and cultural impact.
The Role of Language and Style in Both Categories
Literary fiction prioritizes intricate language and stylistic innovation, emphasizing thematic depth and character complexity through nuanced prose. Genre fiction relies on clear, accessible language and established stylistic conventions to enhance plot-driven narratives and genre-specific expectations. The role of language in literary fiction often challenges readers to engage critically, while genre fiction focuses on immersive, fast-paced storytelling using familiar stylistic elements.
Market Trends: Sales, Publishing, and Success Rates
Literary fiction maintains steady sales in niche markets with critical acclaim driving long-term success, whereas genre fiction dominates mass-market sales due to broader audience appeal and higher turnover rates. Publishing trends show increased investment in genre fiction, particularly in subgenres like fantasy and thriller, reflecting strong consumer demand and lucrative franchising opportunities. Success rates favor genre fiction authors owing to more frequent publication cycles and greater marketing support from publishers targeting mainstream readers.
Blurring Boundaries: When Literary Meets Genre Fiction
Blurring boundaries between literary fiction and genre fiction has transformed contemporary storytelling by integrating complex character development and thematic depth into traditionally plot-driven genres. This fusion elevates genre fiction like science fiction, fantasy, or crime to critical literary status while enhancing literary fiction's accessibility and engagement through genre conventions. Readers increasingly seek narratives that combine the imaginative scope of genre fiction with the introspective nuance typical of literary works.
Literary Fiction vs Genre Fiction Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com