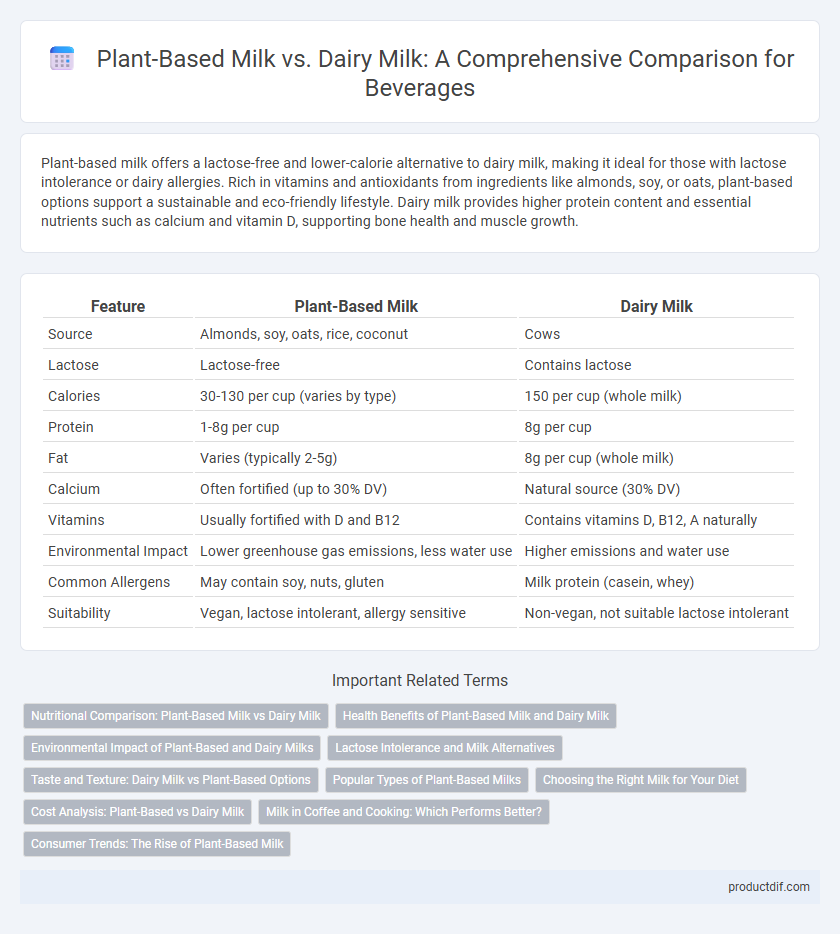
Plant-based milk offers a lactose-free and lower-calorie alternative to dairy milk, making it ideal for those with lactose intolerance or dairy allergies. Rich in vitamins and antioxidants from ingredients like almonds, soy, or oats, plant-based options support a sustainable and eco-friendly lifestyle. Dairy milk provides higher protein content and essential nutrients such as calcium and vitamin D, supporting bone health and muscle growth.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Plant-Based Milk | Dairy Milk |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Almonds, soy, oats, rice, coconut | Cows |
| Lactose | Lactose-free | Contains lactose |
| Calories | 30-130 per cup (varies by type) | 150 per cup (whole milk) |
| Protein | 1-8g per cup | 8g per cup |
| Fat | Varies (typically 2-5g) | 8g per cup (whole milk) |
| Calcium | Often fortified (up to 30% DV) | Natural source (30% DV) |
| Vitamins | Usually fortified with D and B12 | Contains vitamins D, B12, A naturally |
| Environmental Impact | Lower greenhouse gas emissions, less water use | Higher emissions and water use |
| Common Allergens | May contain soy, nuts, gluten | Milk protein (casein, whey) |
| Suitability | Vegan, lactose intolerant, allergy sensitive | Non-vegan, not suitable lactose intolerant |
Nutritional Comparison: Plant-Based Milk vs Dairy Milk
Plant-based milk options like almond, soy, and oat milk typically contain fewer calories and less saturated fat compared to dairy milk, which is richer in protein and calcium. Fortified plant-based milks often match or exceed dairy milk's calcium levels but may lack vitamin B12 unless supplemented. Dairy milk remains a superior source of natural nutrients such as vitamin D, riboflavin, and high-quality protein essential for muscle repair and bone health.
Health Benefits of Plant-Based Milk and Dairy Milk
Plant-based milk, such as almond, soy, and oat milk, offers health benefits including lower saturated fat content, cholesterol-free composition, and rich sources of vitamins like vitamin E and antioxidants. Dairy milk provides essential nutrients like calcium, vitamin D, and high-quality protein crucial for bone health and muscle maintenance. Choosing between plant-based and dairy milk depends on dietary restrictions, lactose intolerance, and personal health goals.
Environmental Impact of Plant-Based and Dairy Milks
Plant-based milks such as almond, oat, and soy typically have a lower environmental impact compared to dairy milk, requiring less water and emitting fewer greenhouse gases during production. Dairy milk production is associated with higher methane emissions and extensive land use, contributing significantly to climate change. Choosing plant-based milk reduces carbon footprint and promotes sustainable agriculture practices.
Lactose Intolerance and Milk Alternatives
Plant-based milk offers a lactose-free alternative for individuals with lactose intolerance, providing options such as almond, soy, oat, and coconut milk that are easier to digest compared to dairy milk. These milk alternatives often contain added vitamins and minerals like calcium and vitamin D to match the nutritional profile of cow's milk. Consumers seeking dairy-free beverages benefit from the diverse flavors and lower allergen potential of plant-based milk options, supporting digestive health without compromising taste or nutrition.
Taste and Texture: Dairy Milk vs Plant-Based Options
Dairy milk offers a creamy texture and rich taste due to its natural fat content and lactose, which contributes to its sweetness and mouthfeel. Plant-based milks like almond, oat, and soy vary in texture and flavor, often lighter and less creamy, with nutty or grainy notes depending on the source. Consumers seeking a similar creaminess to dairy might prefer oat milk, while those sensitive to lactose may opt for soy or almond alternatives with distinct flavor profiles.
Popular Types of Plant-Based Milks
Almond milk, oat milk, and soy milk are the most popular plant-based milk alternatives due to their nutritional profiles and versatility in beverages. Almond milk offers a low-calorie option rich in vitamin E, while oat milk is praised for its creamy texture and high fiber content. Soy milk provides a protein level comparable to dairy milk, making it a favored choice among plant-based consumers.
Choosing the Right Milk for Your Diet
Plant-based milk offers a lactose-free alternative packed with vitamins like B12 and D, essential for vegan and lactose-intolerant individuals, while dairy milk provides natural calcium, protein, and vitamin B2 beneficial for bone health. Evaluating nutritional needs, such as protein content and dietary restrictions, helps in selecting between almond, soy, or oat milk versus cow, goat, or organic dairy milk. Considering environmental impact and potential allergens are crucial factors in choosing the right milk to support a balanced, health-conscious diet.
Cost Analysis: Plant-Based vs Dairy Milk
Plant-based milk generally has a higher retail price compared to dairy milk due to expensive raw materials like almonds, oats, or soybeans and specialized processing techniques. Dairy milk benefits from economies of scale and established supply chains, making it more cost-effective per liter for consumers. Despite higher upfront costs, plant-based milk may offer long-term savings through health benefits and reduced environmental impact, which influence consumer value beyond price alone.
Milk in Coffee and Cooking: Which Performs Better?
Plant-based milk varieties such as almond, oat, and soy offer unique flavor profiles and frothing capabilities in coffee, with oat milk often praised for its creamy texture and barista-friendly foam. Dairy milk provides consistent richness and a natural sweetness that enhances coffee's flavor and delivers reliable results in cooking, especially in baking and creamy sauces. When choosing milk for coffee and cooking, consider factors like protein content, fat levels, and desired texture to achieve optimal taste and performance.
Consumer Trends: The Rise of Plant-Based Milk
The rising consumer preference for plant-based milk is driven by increasing awareness of health benefits, environmental sustainability, and lactose intolerance issues, making almond, oat, and soy alternatives more popular. Market data reveals a double-digit growth rate in plant-based milk sales worldwide, outpacing traditional dairy milk consumption. This shift reflects evolving dietary choices and growing demand for ethical and allergen-friendly beverage options.
Plant-Based Milk vs Dairy Milk Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com