Vented dryers expel moist air outside through a duct, making them highly efficient but requiring proper ventilation installation. Ventless dryers use a heat exchange system to condense moisture internally, offering flexible placement without ductwork but typically longer drying times. Choosing between vented and ventless dryers depends on home layout, installation options, and drying speed preferences.
Table of Comparison
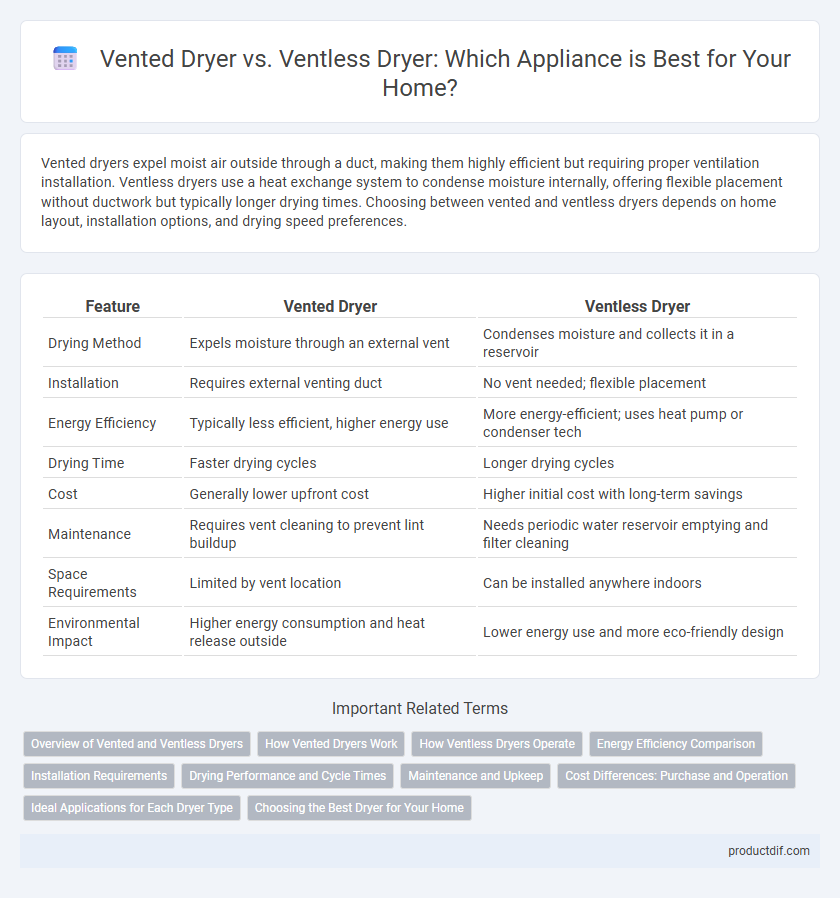
| Feature | Vented Dryer | Ventless Dryer |
|---|---|---|
| Drying Method | Expels moisture through an external vent | Condenses moisture and collects it in a reservoir |
| Installation | Requires external venting duct | No vent needed; flexible placement |
| Energy Efficiency | Typically less efficient, higher energy use | More energy-efficient; uses heat pump or condenser tech |
| Drying Time | Faster drying cycles | Longer drying cycles |
| Cost | Generally lower upfront cost | Higher initial cost with long-term savings |
| Maintenance | Requires vent cleaning to prevent lint buildup | Needs periodic water reservoir emptying and filter cleaning |
| Space Requirements | Limited by vent location | Can be installed anywhere indoors |
| Environmental Impact | Higher energy consumption and heat release outside | Lower energy use and more eco-friendly design |
Overview of Vented and Ventless Dryers
Vented dryers expel moist air through an external duct, requiring proper ventilation installation and making them suitable for homes with accessible outdoor vents. Ventless dryers, such as condenser and heat pump models, recycle air within the drum, eliminating the need for external vents and offering flexible placement options. Energy efficiency varies, with ventless dryers typically consuming less energy due to advanced condensation technology, while vented models often provide faster drying times.
How Vented Dryers Work
Vented dryers expel hot, moist air through a vent or exhaust duct, removing humidity from the drying chamber to prevent moisture buildup. They use a heating element and a blower fan to circulate air through the drum, evaporating water from clothes and pushing it outside. Proper installation of venting systems is essential to ensure efficient drying performance and prevent lint accumulation or indoor air quality issues.
How Ventless Dryers Operate
Ventless dryers use a heat exchanger system to remove moisture from clothes by condensing steam into water, which is then collected or drained away, eliminating the need for external venting. They recycle hot air within the drum, improving energy efficiency and allowing installation in spaces without vent access. This operation makes ventless dryers ideal for apartments or homes with limited ventilation options while reducing heat and humidity release into the surroundings.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
Vented dryers typically consume more energy due to their reliance on external air ventilation, which requires longer drying cycles and increased heat output. Ventless dryers utilize advanced heat pump technology to recycle heat within the drum, significantly reducing energy consumption by up to 50% compared to vented models. Energy Star ratings consistently favor ventless dryers for their superior energy efficiency and lower utility costs over time.
Installation Requirements
Vented dryers require a direct exhaust vent to the outside, which involves ductwork installation and a proper external outlet to expel hot, moist air. Ventless dryers, including heat pump and condenser models, do not need external ventilation, making them ideal for apartments or spaces without outside walls. Installation for ventless dryers is simpler, requiring only an electrical outlet and space for the unit, with no need for ducting or exterior modifications.
Drying Performance and Cycle Times
Vented dryers typically offer faster drying performance due to efficient moisture expulsion through an external vent, reducing cycle times compared to ventless models. Ventless dryers rely on heat exchange or condensation systems to remove moisture, which can extend drying cycles but provide greater installation flexibility. Energy efficiency varies, with ventless dryers often consuming less energy despite longer cycles, making performance dependent on specific user needs.
Maintenance and Upkeep
Vented dryers require regular cleaning of the lint trap and vent duct to prevent clogs, which can reduce efficiency and pose fire hazards. Ventless dryers need routine maintenance of the condenser or heat exchanger to avoid moisture buildup and odors, often involving filter cleaning or replacement. Both types benefit from periodic inspection to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Cost Differences: Purchase and Operation
Vented dryers generally have a lower initial purchase price but higher operational costs due to increased energy consumption and the need for external vent installation. Ventless dryers, including condenser and heat pump models, typically cost more upfront but offer greater energy efficiency, resulting in lower monthly utility bills. Evaluating long-term expenses should consider both the initial investment and ongoing energy savings to determine the most cost-effective option.
Ideal Applications for Each Dryer Type
Vented dryers are ideal for homes with existing venting systems and ample outdoor space to expel moist air, making them suitable for large laundry loads and high-efficiency drying. Ventless dryers, including condenser and heat pump models, fit perfectly in apartments, condos, or spaces without external vents due to their ability to recycle air and operate in confined areas. Choosing between vented and ventless dryers depends largely on installation feasibility, space constraints, and energy consumption preferences.
Choosing the Best Dryer for Your Home
Vented dryers expel moist air through an external vent, requiring proper installation near an exterior wall and providing faster drying times ideal for large households. Ventless dryers, including condenser and heat pump models, recycle moisture internally without the need for venting, making them perfect for apartments or homes with limited outdoor access. Choosing the best dryer depends on your home's ventilation options, energy efficiency preferences, and space constraints.
Vented Dryer vs Ventless Dryer Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com