Induction cooktops offer faster heating, precise temperature control, and improved energy efficiency compared to gas stoves. Gas appliances provide immediate visual feedback with open flames and are favored for their compatibility with all cookware types. Choosing between induction and gas depends on cooking style preferences, safety considerations, and long-term energy savings.
Table of Comparison
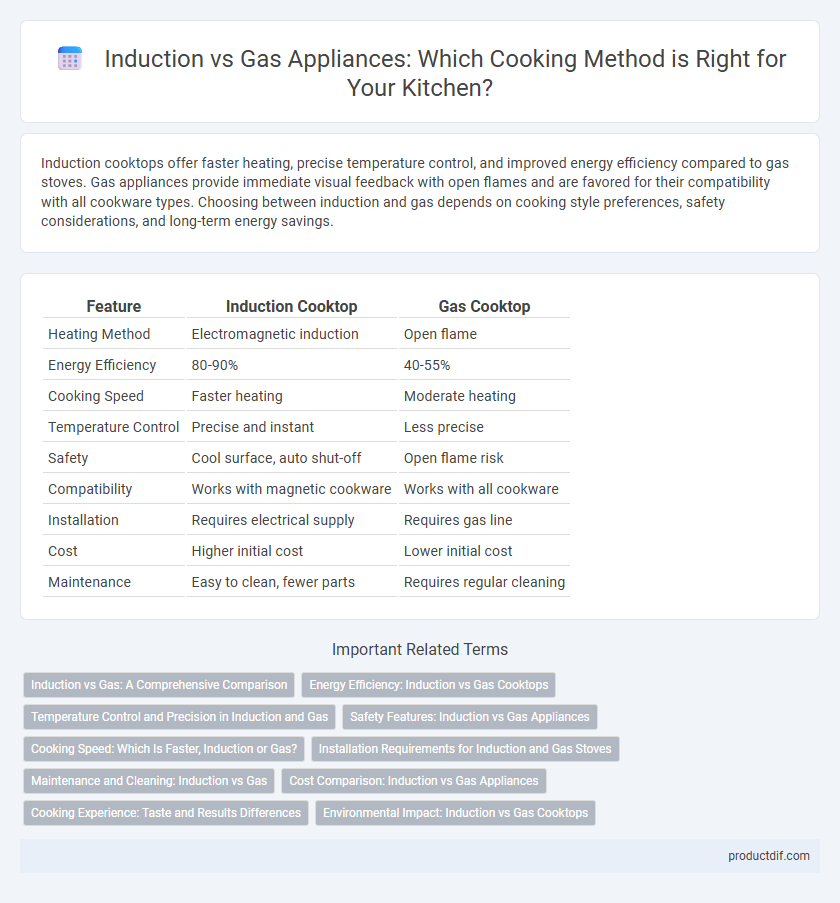
| Feature | Induction Cooktop | Gas Cooktop |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Electromagnetic induction | Open flame |
| Energy Efficiency | 80-90% | 40-55% |
| Cooking Speed | Faster heating | Moderate heating |
| Temperature Control | Precise and instant | Less precise |
| Safety | Cool surface, auto shut-off | Open flame risk |
| Compatibility | Works with magnetic cookware | Works with all cookware |
| Installation | Requires electrical supply | Requires gas line |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower initial cost |
| Maintenance | Easy to clean, fewer parts | Requires regular cleaning |
Induction vs Gas: A Comprehensive Comparison
Induction cooktops use electromagnetic fields to directly heat pots and pans, offering precise temperature control, faster cooking times, and enhanced energy efficiency compared to traditional gas stoves. Gas ranges provide visible flame control, immediate heat adjustment, and compatibility with all cookware types, appealing to chefs who prioritize tactile cooking experience. Choosing between induction and gas depends on factors like kitchen infrastructure, cooking style preferences, and energy costs, with induction favored for safety and efficiency and gas for its versatility and instant heat.
Energy Efficiency: Induction vs Gas Cooktops
Induction cooktops deliver superior energy efficiency by using electromagnetic energy to directly heat cookware, minimizing heat loss and reaching up to 90% energy transfer efficiency. Gas cooktops typically convert only about 40-55% of energy into usable heat, with significant heat escaping around the burner. This higher efficiency of induction reduces overall energy consumption, leading to lower utility bills and a smaller carbon footprint.
Temperature Control and Precision in Induction and Gas
Induction cooktops deliver superior temperature control with rapid, precise adjustments through electromagnetic fields, allowing temperatures to change instantly and maintain consistent heat. Gas stoves provide visual flame control but often experience slower temperature transitions and less exact heat distribution. Precision in induction cooking supports delicate tasks like melting chocolate or simmering sauces, while gas excels in high-heat searing with slightly less accuracy.
Safety Features: Induction vs Gas Appliances
Induction appliances offer enhanced safety features by using electromagnetic fields to heat cookware directly, minimizing the risk of burns and fire hazards, as the cooktop surface remains cool to the touch. Gas appliances rely on an open flame, posing risks such as gas leaks, accidental ignition, and carbon monoxide exposure if not properly maintained. Modern induction cooktops often include automatic shut-off and child lock functions, increasing overall safety compared to conventional gas stoves.
Cooking Speed: Which Is Faster, Induction or Gas?
Induction cooktops use electromagnetic energy to heat pots directly, resulting in faster cooking times compared to gas stoves that rely on flame to transfer heat. Studies show induction can boil water up to 50% quicker than gas, making it the preferred option for speedy meal preparation. The precise temperature control of induction also reduces heat-up and cool-down periods, further enhancing overall cooking speed.
Installation Requirements for Induction and Gas Stoves
Induction stoves require a compatible electrical outlet, often 240 volts, and must be installed on a flat, heat-resistant surface to ensure safety and optimal performance. Gas stoves need a properly connected gas line with secure fittings and ventilation to prevent gas leaks and ensure safe combustion. Both appliances may require professional installation to meet local building codes and safety standards.
Maintenance and Cleaning: Induction vs Gas
Induction cooktops feature smooth, flat surfaces made of glass or ceramic that are easy to clean with a simple wipe, resisting spills and stains more effectively than gas stovetops. Gas cooktops require frequent deep cleaning of burners, grates, and drip pans to prevent grease buildup and maintain flame efficiency, which can be time-consuming. Induction cooktops have fewer mechanical parts exposed to food debris, reducing overall maintenance and extending appliance longevity.
Cost Comparison: Induction vs Gas Appliances
Induction cooktops typically incur higher upfront costs, averaging $1,000 to $3,000, compared to gas ranges that range from $400 to $1,500. Despite the initial investment, induction appliances offer greater energy efficiency, potentially lowering operating expenses by 10-20% over time. Gas stoves, while cheaper to purchase, often have higher energy costs due to less efficient fuel combustion and increased ventilation needs.
Cooking Experience: Taste and Results Differences
Induction cooking offers precise temperature control and even heat distribution, resulting in consistently cooked meals with enhanced flavor retention. Gas cooking provides immediate heat adjustment and visible flame control, which many chefs prefer for achieving traditional caramelization and charring effects. Differences in cooking experience affect taste nuances, with induction favoring uniform cooking and gas enabling more tactile and variable results.
Environmental Impact: Induction vs Gas Cooktops
Induction cooktops significantly reduce carbon emissions by using electricity efficiently, especially when powered by renewable energy sources, unlike gas cooktops that release methane and carbon dioxide directly into the atmosphere. Gas cooktops contribute to indoor air pollution through combustion byproducts such as nitrogen dioxide and carbon monoxide, posing health risks and environmental concerns. The overall environmental impact favors induction technology due to its higher energy efficiency and potential for lower greenhouse gas emissions.
Induction vs Gas Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com