Convection ovens use a fan to circulate hot air, ensuring even cooking and faster baking times compared to conventional ovens that rely on radiant heat from the top and bottom elements. This air circulation in convection ovens results in crispier exteriors and more consistent temperature distribution, making them ideal for roasting and baking delicate pastries. Conventional ovens, while slower, are typically better for recipes requiring gentle, steady heat without airflow, preserving moisture in dishes like casseroles and bread.
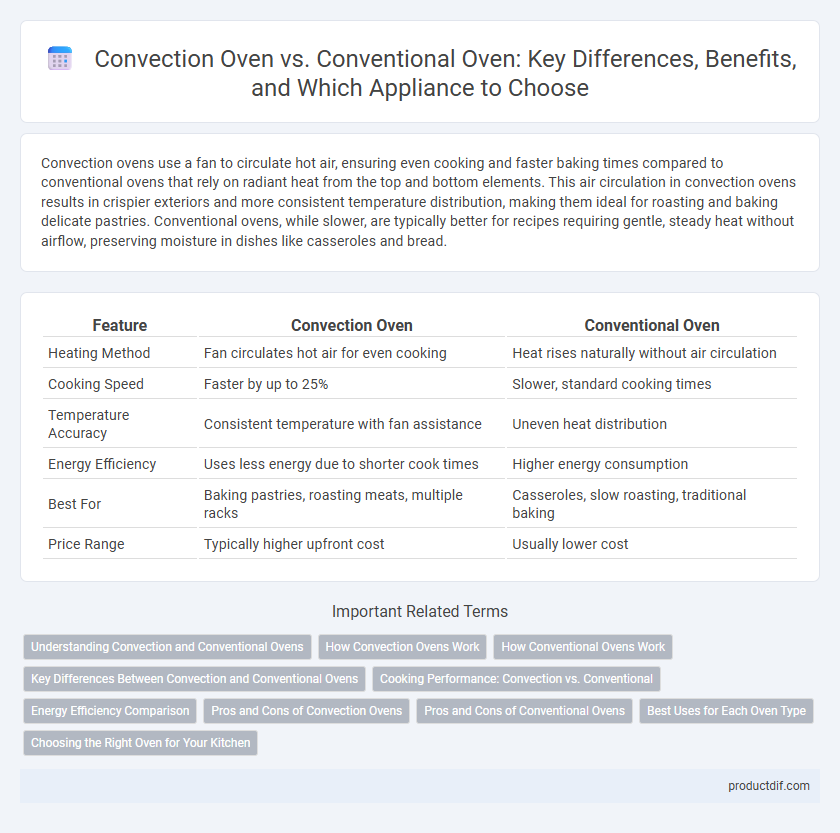
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Convection Oven | Conventional Oven |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Fan circulates hot air for even cooking | Heat rises naturally without air circulation |
| Cooking Speed | Faster by up to 25% | Slower, standard cooking times |
| Temperature Accuracy | Consistent temperature with fan assistance | Uneven heat distribution |
| Energy Efficiency | Uses less energy due to shorter cook times | Higher energy consumption |
| Best For | Baking pastries, roasting meats, multiple racks | Casseroles, slow roasting, traditional baking |
| Price Range | Typically higher upfront cost | Usually lower cost |
Understanding Convection and Conventional Ovens
Convection ovens use a fan to circulate hot air around the food, promoting even cooking and faster heat transfer compared to conventional ovens, which rely on radiant heat from fixed heating elements. The circulating air in convection ovens reduces hot spots and results in more consistent browning and crisping of dishes. Conventional ovens provide stable, indirect heat which is suitable for baking delicate items where slow, even cooking is preferred.
How Convection Ovens Work
Convection ovens use a built-in fan and exhaust system to circulate hot air evenly throughout the oven cavity, ensuring consistent cooking temperatures and reducing cooking time. This airflow eliminates hot and cold spots typical in conventional ovens, enabling more precise baking and roasting results. The efficient heat distribution makes convection ovens ideal for cooking multiple dishes simultaneously without flavor transfer.
How Conventional Ovens Work
Conventional ovens operate by heating the air inside the oven cavity through radiant heat from electric elements or gas burners, creating a steady and even temperature for cooking. The heat rises naturally and surrounds the food, which results in gradual and uniform cooking, ideal for baking and roasting. Thermal conduction from the hot air transfers heat to the food's surface, allowing for Maillard browning and caramelization.
Key Differences Between Convection and Conventional Ovens
Convection ovens use a built-in fan and exhaust system to circulate hot air evenly, resulting in faster and more uniform cooking compared to conventional ovens that rely solely on radiant heat. This airflow not only reduces cooking times by up to 25% but also promotes consistent browning and crisping of food surfaces. Conventional ovens often provide more gentle heat suitable for baking delicate dishes, whereas convection ovens excel in roasting and dehydrating due to their efficient heat distribution.
Cooking Performance: Convection vs. Conventional
Convection ovens use a fan to circulate hot air, ensuring even heat distribution and faster cooking times compared to conventional ovens, which rely on radiant heat from fixed heating elements. This results in more consistent browning, crispier textures, and improved energy efficiency in convection ovens. Conventional ovens, while offering reliable performance, may produce uneven cooking, especially in larger dishes or multiple racks.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
Convection ovens utilize a fan to circulate hot air, resulting in faster, more even cooking and typically consuming 20-30% less energy than conventional ovens. Conventional ovens rely on radiant heat without air circulation, often requiring longer cooking times and higher temperatures, which increases energy use. Energy-efficient convection ovens reduce utility costs and lower environmental impact by optimizing heat distribution and cooking time.
Pros and Cons of Convection Ovens
Convection ovens offer faster and more even cooking due to their built-in fan that circulates hot air, reducing cooking times by up to 25% and providing consistent temperature distribution. They are energy-efficient and ideal for roasting and baking multiple dishes simultaneously, but may cause uneven browning for delicate baked goods and require adjustments in cooking temperatures and times. Some users find the fan noise intrusive, and the initial cost typically exceeds that of conventional ovens.
Pros and Cons of Conventional Ovens
Conventional ovens offer even heat distribution, making them ideal for recipes requiring slow, consistent cooking such as roasts and casseroles. They tend to be more affordable and simpler to operate compared to convection ovens, with no fan to maintain or replace. However, they often cook food unevenly, leading to hot spots, and typically require longer cooking times, which can increase energy consumption.
Best Uses for Each Oven Type
Convection ovens excel in baking and roasting due to their even heat distribution and faster cooking times, making them ideal for pastries, cookies, and meats that benefit from crispy exteriors. Conventional ovens perform better for traditional recipes requiring steady, consistent heat, such as casseroles, bread, and delicate baked goods that may dry out under intense airflow. Choosing between convection and conventional ovens depends on the cooking style and desired dish texture, ensuring optimal results for specific culinary needs.
Choosing the Right Oven for Your Kitchen
Choosing the right oven for your kitchen depends on your cooking preferences and energy efficiency needs, with convection ovens offering faster, more even heat distribution through a fan, ideal for baking and roasting. Conventional ovens operate with radiant heat from the top and bottom elements, providing consistent temperatures for traditional recipes and slower cooking methods. Prioritize convection ovens for quicker cooking and energy savings, while conventional ovens suit recipes requiring gentle, uniform heat.
Convection Oven vs Conventional Oven Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com