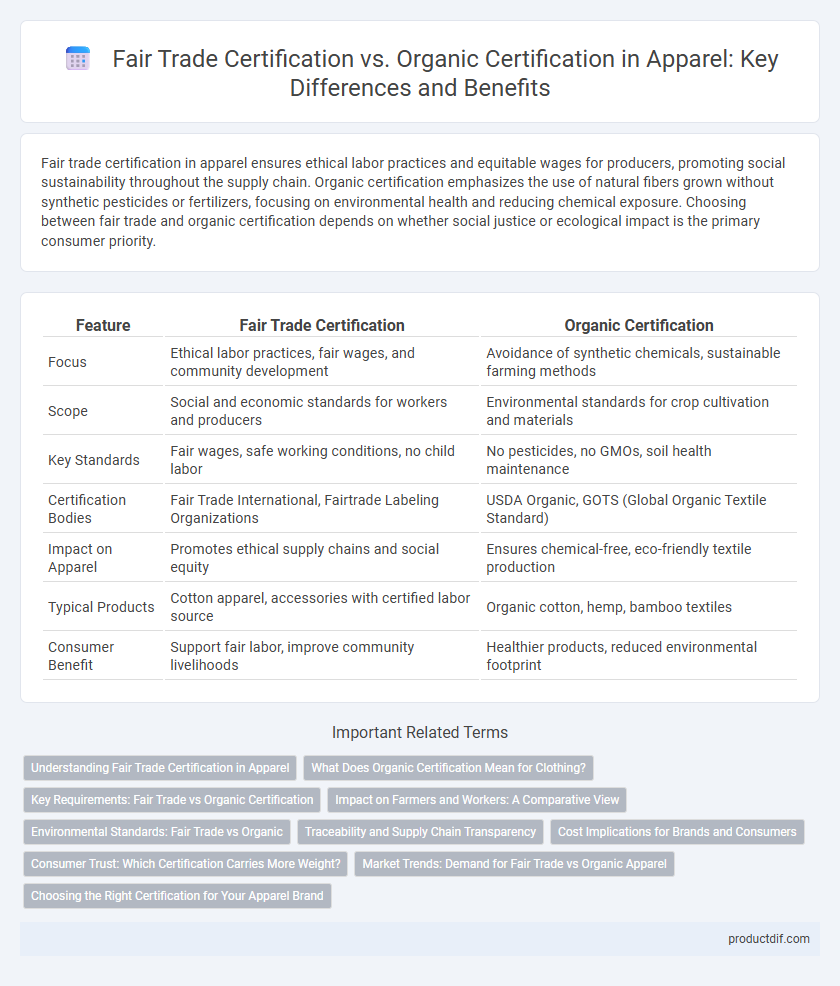
Fair trade certification in apparel ensures ethical labor practices and equitable wages for producers, promoting social sustainability throughout the supply chain. Organic certification emphasizes the use of natural fibers grown without synthetic pesticides or fertilizers, focusing on environmental health and reducing chemical exposure. Choosing between fair trade and organic certification depends on whether social justice or ecological impact is the primary consumer priority.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Fair Trade Certification | Organic Certification |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Ethical labor practices, fair wages, and community development | Avoidance of synthetic chemicals, sustainable farming methods |
| Scope | Social and economic standards for workers and producers | Environmental standards for crop cultivation and materials |
| Key Standards | Fair wages, safe working conditions, no child labor | No pesticides, no GMOs, soil health maintenance |
| Certification Bodies | Fair Trade International, Fairtrade Labeling Organizations | USDA Organic, GOTS (Global Organic Textile Standard) |
| Impact on Apparel | Promotes ethical supply chains and social equity | Ensures chemical-free, eco-friendly textile production |
| Typical Products | Cotton apparel, accessories with certified labor source | Organic cotton, hemp, bamboo textiles |
| Consumer Benefit | Support fair labor, improve community livelihoods | Healthier products, reduced environmental footprint |
Understanding Fair Trade Certification in Apparel
Fair Trade certification in apparel ensures that garments are produced under ethical labor conditions, fair wages, and community development standards. Unlike Organic certification, which focuses on sustainable farming practices and the absence of harmful chemicals in raw materials, Fair Trade emphasizes social equity within the supply chain. Brands with Fair Trade certification demonstrate commitment to transparency, workers' rights, and improved livelihoods, making it a critical factor for socially responsible apparel consumers.
What Does Organic Certification Mean for Clothing?
Organic certification for clothing guarantees that the fabric is produced from natural fibers grown without synthetic pesticides or fertilizers, reducing environmental impact and promoting healthier ecosystems. This certification ensures transparency in the supply chain, confirming that textiles meet strict standards for sustainable agriculture and processing methods. Choosing organic certified apparel supports soil health, conserves water, and minimizes chemical exposure for farmers and consumers alike.
Key Requirements: Fair Trade vs Organic Certification
Fair trade certification requires compliance with ethical labor practices, fair wages, safe working conditions, and community development investment, while organic certification mandates adherence to strict agricultural standards like avoiding synthetic pesticides, GMOs, and chemical fertilizers. Fair trade emphasizes social and economic criteria, ensuring producers' rights and sustainable livelihoods, whereas organic certification focuses on environmental sustainability and soil health in crop production. Brands seeking both certifications must navigate distinct regulatory frameworks, with fair trade addressing human rights and organic certification prioritizing ecological impact.
Impact on Farmers and Workers: A Comparative View
Fair Trade certification prioritizes fair wages, safe working conditions, and community development, directly benefiting farmers and workers by ensuring ethical labor practices and stable incomes. Organic certification emphasizes environmentally sustainable farming methods that reduce exposure to harmful chemicals, improving the health and safety of agricultural workers. Both certifications contribute to better livelihoods, but Fair Trade focuses more on social equity while Organic certification centers on ecological health and worker safety.
Environmental Standards: Fair Trade vs Organic
Fair Trade certification emphasizes environmentally sustainable farming practices that reduce chemical use and promote biodiversity, aiming to support both the ecosystem and farmers' livelihoods. Organic certification requires strict adherence to avoiding synthetic pesticides and fertilizers, ensuring soil health and water conservation through natural methods. Both certifications enhance environmental standards, but Organic certification typically enforces more rigorous restrictions on chemical inputs and land management.
Traceability and Supply Chain Transparency
Fair Trade certification emphasizes traceability through ethical sourcing and ensures supply chain transparency by mandating fair labor practices and community benefits throughout production stages. Organic certification prioritizes traceability of raw materials by verifying agricultural methods that exclude synthetic pesticides and fertilizers, focusing primarily on environmental sustainability. Both certifications enhance supply chain transparency but target different aspects: Fair Trade focuses on social impact, while Organic certification concentrates on ecological integrity.
Cost Implications for Brands and Consumers
Fair trade certification generally involves higher production costs due to stricter labor and environmental standards, leading to increased prices for brands and consumers compared to organic certification, which primarily focuses on sustainable farming practices. Brands investing in fair trade certification often face premiums associated with ethical sourcing and fair wages, whereas organic certification costs largely stem from compliance with pesticide-free growing methods and soil health management. Consumers purchasing fair trade apparel typically pay more as a direct contribution to social equity, while organic products emphasize environmental benefits at a slightly lower price premium.
Consumer Trust: Which Certification Carries More Weight?
Fair Trade certification emphasizes ethical labor practices and fair wages, fostering strong consumer trust in social responsibility, while Organic certification assures chemical-free, environmentally sustainable fiber production, appealing primarily to health-conscious and eco-friendly buyers. Studies show consumers increasingly value Fair Trade labels for social impact, but Organic certification maintains high trust for safety and environmental benefits. Combining both certifications often maximizes consumer confidence by addressing ethical and ecological concerns in apparel sourcing.
Market Trends: Demand for Fair Trade vs Organic Apparel
Demand for fair trade apparel has surged as consumers prioritize ethical labor practices and social equity, with market growth driven by increased awareness of workers' rights. Organic apparel maintains consistent popularity due to its environmental benefits, particularly soil health and reduced chemical usage, attracting eco-conscious buyers. Market trends show a growing convergence where brands increasingly obtain both fair trade and organic certifications to meet comprehensive consumer expectations for sustainability and ethics.
Choosing the Right Certification for Your Apparel Brand
Fair trade certification ensures ethical labor practices, fair wages, and community support, making it ideal for brands emphasizing social responsibility. Organic certification focuses on sustainable farming without harmful chemicals, appealing to environmentally conscious consumers prioritizing eco-friendly fabrics. Selecting the right certification depends on your brand's core values and target market preferences within the apparel industry.
Fair trade certification vs Organic certification Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com