Wall tiling offers durable and water-resistant surfaces ideal for high-moisture areas, making it a practical choice for pet owners concerned about spills and stains. Wall lamination provides a smooth, easy-to-clean finish that effectively protects walls from scratches and is available in various designs to complement home decor. Choosing between wall tiling and lamination depends on the balance between durability requirements and aesthetic preferences for pet-friendly spaces.
Table of Comparison
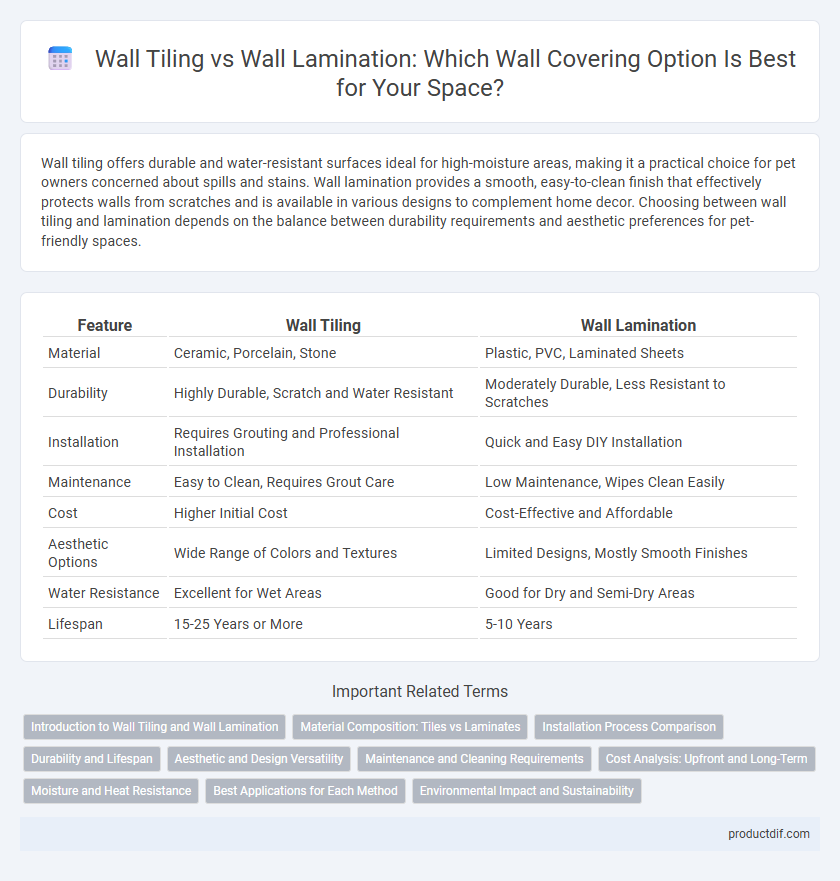
| Feature | Wall Tiling | Wall Lamination |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Ceramic, Porcelain, Stone | Plastic, PVC, Laminated Sheets |
| Durability | Highly Durable, Scratch and Water Resistant | Moderately Durable, Less Resistant to Scratches |
| Installation | Requires Grouting and Professional Installation | Quick and Easy DIY Installation |
| Maintenance | Easy to Clean, Requires Grout Care | Low Maintenance, Wipes Clean Easily |
| Cost | Higher Initial Cost | Cost-Effective and Affordable |
| Aesthetic Options | Wide Range of Colors and Textures | Limited Designs, Mostly Smooth Finishes |
| Water Resistance | Excellent for Wet Areas | Good for Dry and Semi-Dry Areas |
| Lifespan | 15-25 Years or More | 5-10 Years |
Introduction to Wall Tiling and Wall Lamination
Wall tiling involves applying ceramic, porcelain, or stone tiles to walls, offering durability and water resistance ideal for bathrooms and kitchens. Wall lamination uses laminated sheets made from plastic or composite materials to create a seamless, easy-to-clean surface with various designs and textures. Both methods enhance wall aesthetics but differ in application, maintenance, and material properties.
Material Composition: Tiles vs Laminates
Wall tiling is composed primarily of ceramic, porcelain, or stone materials known for their durability, moisture resistance, and heat tolerance, making them ideal for bathrooms and kitchens. Wall laminates consist of layers of kraft paper saturated with resin and topped with a decorative printed layer covered by a protective melamine coating, offering versatility and ease of installation. The rigid and hard surface of tiles contrasts with the flexible, thinner profile of laminates, influencing both aesthetic appeal and maintenance requirements.
Installation Process Comparison
Wall tiling installation involves carefully applying adhesive to the surface and placing tiles with precise spacing, followed by grouting and sealing to ensure durability and water resistance. Wall lamination requires bonding pre-finished laminate sheets directly onto the wall using strong adhesives, allowing for faster application and minimal drying time. While tiling demands skilled labor and longer installation time due to multiple steps, lamination offers a more straightforward and quicker solution with less mess and lower labor costs.
Durability and Lifespan
Wall tiling offers exceptional durability due to its resistance to moisture, scratches, and heat, often lasting several decades with minimal maintenance. Wall lamination provides a stylish finish but generally has a shorter lifespan, typically around 10 to 15 years, as it is more susceptible to peeling, fading, and damage from humidity. Choosing wall tiling over lamination ensures a longer-lasting surface ideal for high-traffic or moisture-prone areas.
Aesthetic and Design Versatility
Wall tiling offers rich aesthetic appeal with diverse materials like ceramic, porcelain, and natural stone, enabling intricate patterns and textures for a timeless, high-end look. Wall lamination provides superior design versatility through customizable prints and finishes, allowing seamless integration of colors, images, and textures for modern or thematic interiors. Both methods enhance wall decor but wall lamination excels in flexibility, while tiling delivers durability with classic elegance.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Wall tiling offers high durability with water-resistant surfaces that simplify cleaning using mild detergents and regular wiping, making it ideal for moisture-prone areas like kitchens and bathrooms. Wall lamination, while aesthetically versatile, requires gentle cleaning methods to avoid scratches and may degrade faster in humid conditions, demanding more frequent maintenance. The choice hinges on desired longevity and ease of upkeep, with wall tiles generally providing lower maintenance than laminated wall coverings.
Cost Analysis: Upfront and Long-Term
Wall tiling generally requires a higher upfront investment due to material and labor costs, especially for ceramic or porcelain options, but offers durability and low maintenance that can reduce expenses over time. Wall lamination presents a more budget-friendly initial cost with easier installation, yet may incur higher replacement or repair costs in the long run due to susceptibility to damage and wear. Evaluating the total cost of ownership should include material longevity, maintenance requirements, and potential need for future refurbishment.
Moisture and Heat Resistance
Wall tiling offers superior moisture and heat resistance compared to wall lamination, making it ideal for bathrooms and kitchens where exposure to water and high temperatures is frequent. Ceramic or porcelain tiles resist water penetration and withstand heat without warping or discoloration, ensuring durability and low maintenance. In contrast, wall lamination, typically made from synthetic materials, may be prone to swelling or peeling when exposed to excessive moisture or heat over time.
Best Applications for Each Method
Wall tiling is ideal for high-moisture areas such as bathrooms and kitchens, offering durability and easy cleaning through materials like ceramic, porcelain, or natural stone tiles. Wall lamination suits low-traffic spaces like living rooms and bedrooms, providing aesthetic versatility with materials such as PVC, vinyl, or acrylic laminates that resist scratches and stains. Selecting the appropriate method depends on factors like moisture exposure, maintenance needs, and design preferences to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Wall tiling typically uses natural materials like ceramic or porcelain, which have a longer lifespan and can be recyclable, reducing landfill waste. Wall lamination often involves synthetic materials and adhesives that may emit VOCs and are less biodegradable, negatively affecting indoor air quality and long-term sustainability. Choosing wall tiling supports eco-friendly practices through durability, lower emissions, and easier recycling compared to the environmental drawbacks of laminates.
Wall Tiling vs Wall Lamination Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com