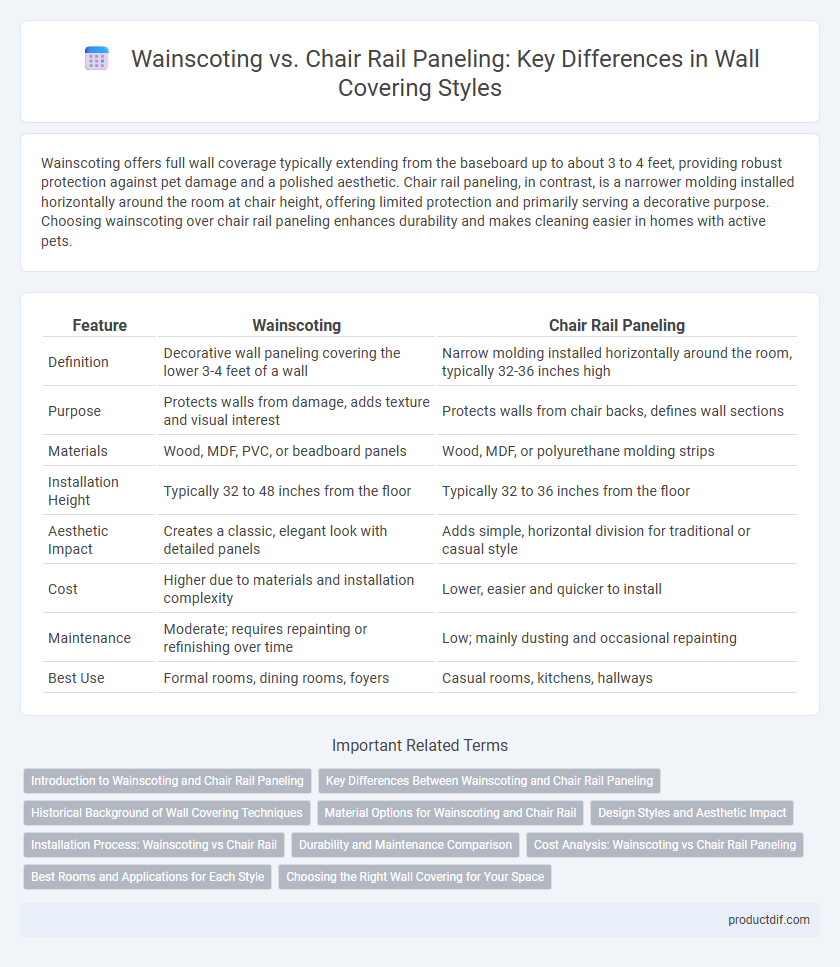
Wainscoting offers full wall coverage typically extending from the baseboard up to about 3 to 4 feet, providing robust protection against pet damage and a polished aesthetic. Chair rail paneling, in contrast, is a narrower molding installed horizontally around the room at chair height, offering limited protection and primarily serving a decorative purpose. Choosing wainscoting over chair rail paneling enhances durability and makes cleaning easier in homes with active pets.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Wainscoting | Chair Rail Paneling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Decorative wall paneling covering the lower 3-4 feet of a wall | Narrow molding installed horizontally around the room, typically 32-36 inches high |
| Purpose | Protects walls from damage, adds texture and visual interest | Protects walls from chair backs, defines wall sections |
| Materials | Wood, MDF, PVC, or beadboard panels | Wood, MDF, or polyurethane molding strips |
| Installation Height | Typically 32 to 48 inches from the floor | Typically 32 to 36 inches from the floor |
| Aesthetic Impact | Creates a classic, elegant look with detailed panels | Adds simple, horizontal division for traditional or casual style |
| Cost | Higher due to materials and installation complexity | Lower, easier and quicker to install |
| Maintenance | Moderate; requires repainting or refinishing over time | Low; mainly dusting and occasional repainting |
| Best Use | Formal rooms, dining rooms, foyers | Casual rooms, kitchens, hallways |
Introduction to Wainscoting and Chair Rail Paneling
Wainscoting consists of wooden panels installed on the lower portion of walls, offering both protection and decorative appeal, typically extending from the baseboard up to about three to four feet. Chair rail paneling features a horizontal molding positioned roughly 32 to 36 inches from the floor, designed originally to prevent chairs from damaging walls while adding architectural interest. Both techniques enhance interior aesthetics, but wainscoting provides more extensive coverage with panels, whereas chair rails serve as a charming dividing line between wall treatments.
Key Differences Between Wainscoting and Chair Rail Paneling
Wainscoting typically covers the lower portion of a wall with full panels or beadboard, providing both protection and decorative appeal, whereas chair rail paneling involves a horizontal molding installed about 32 inches above the floor to prevent chair damage and add visual interest. Wainscoting extends vertically and can cover up to one-third of the wall height, creating a more substantial and textured effect, while chair rails serve as a boundary line between different wall treatments or colors. The material depth and installation complexity also differ, with wainscoting often requiring more materials and effort compared to the simpler, narrower chair rail molding.
Historical Background of Wall Covering Techniques
Wainscoting originated in 16th-century England as a practical solution to insulate rooms and protect lower walls from dampness, evolving into an ornate architectural detail in classical interiors. Chair rail paneling emerged in the 18th century, primarily serving to safeguard walls from chair damage while incorporating decorative molding that enhanced room proportions. Both techniques reflect historical shifts in interior design priorities, blending functionality with aesthetic appeal in period architecture.
Material Options for Wainscoting and Chair Rail
Wainscoting typically offers a variety of material options including wood, MDF, and PVC, providing durability and aesthetic flexibility for wall covering projects. Chair rail paneling is often crafted from solid wood, medium-density fiberboard, or polyurethane, designed to protect walls while adding decorative detail. Both materials can be painted or stained to match interior designs, with choices influenced by budget, moisture resistance, and desired texture.
Design Styles and Aesthetic Impact
Wainscoting offers a more substantial and traditional design style, covering the lower portion of walls with raised or recessed panels that create depth and architectural interest. Chair rail paneling is a narrower, horizontal molding installed at chair height, providing a subtle decorative boundary that complements various interior styles without overwhelming the space. Both options enhance a room's aesthetic impact by adding texture and elegance, but wainscoting delivers a more pronounced and classic visual effect compared to the understated charm of chair rail paneling.
Installation Process: Wainscoting vs Chair Rail
Wainscoting installation involves attaching large panel sections or planks to the lower portion of walls, usually requiring precise measurement, cutting, and secure fastening to ensure durability and alignment. Chair rail paneling installation focuses on mounting a horizontal molding strip approximately 32 inches from the floor, serving both decorative and protective purposes, which typically requires less material and time compared to full wainscoting. Both techniques demand surface preparation and finishing details to achieve a polished look, but wainscoting offers a more extensive wall coverage, increasing installation complexity.
Durability and Maintenance Comparison
Wainscoting offers superior durability due to its full wall coverage, providing enhanced protection against dents, scratches, and moisture compared to chair rail paneling, which only covers the lower portion of the wall. Maintenance for wainscoting is typically easier since it can be cleaned with mild soap and water, and damaged sections are easier to repair or replace without affecting the entire wall. Chair rail paneling requires more frequent upkeep to prevent damage above the rail and often needs repainting to maintain its aesthetic appeal.
Cost Analysis: Wainscoting vs Chair Rail Paneling
Wainscoting typically costs more than chair rail paneling due to the additional materials and labor required for installation, averaging $15 to $50 per square foot compared to chair rail's $5 to $15 per linear foot. The higher expense of wainscoting reflects its greater durability and decorative impact, often involving detailed molding and full wall coverage. Chair rail paneling serves as a more budget-friendly option, providing basic wall protection and aesthetic appeal with simpler installation and lower material costs.
Best Rooms and Applications for Each Style
Wainscoting suits formal dining rooms, entryways, and traditional living spaces by providing full lower wall coverage that enhances elegance and durability. Chair rail paneling is ideal for casual dining areas or hallways, where a protective horizontal molding prevents wall damage while allowing wallpaper or paint above for design flexibility. Choosing wainscoting or chair rail depends on the desired aesthetic impact and the functional needs of high-traffic or decorative spaces.
Choosing the Right Wall Covering for Your Space
Wainscoting offers full lower wall coverage with decorative panels that protect walls and add classic texture, ideal for high-traffic areas. Chair rail paneling features a narrow horizontal molding typically installed 32 to 36 inches from the floor, providing subtle protection and visual interest without covering the entire wall. Selecting between wainscoting and chair rail paneling depends on desired aesthetic, room function, and maintenance preferences, with wainscoting delivering more extensive coverage and chair rails offering minimalist elegance.
Wainscoting vs Chair Rail Paneling Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com