Open-ended play encourages creativity and imagination by allowing children to explore toys without preset rules, fostering problem-solving skills and independent thinking. Structured play involves guided activities with specific goals or instructions, helping children develop discipline and understanding of rules. Balancing both types of play supports cognitive growth and social development in young learners.
Table of Comparison
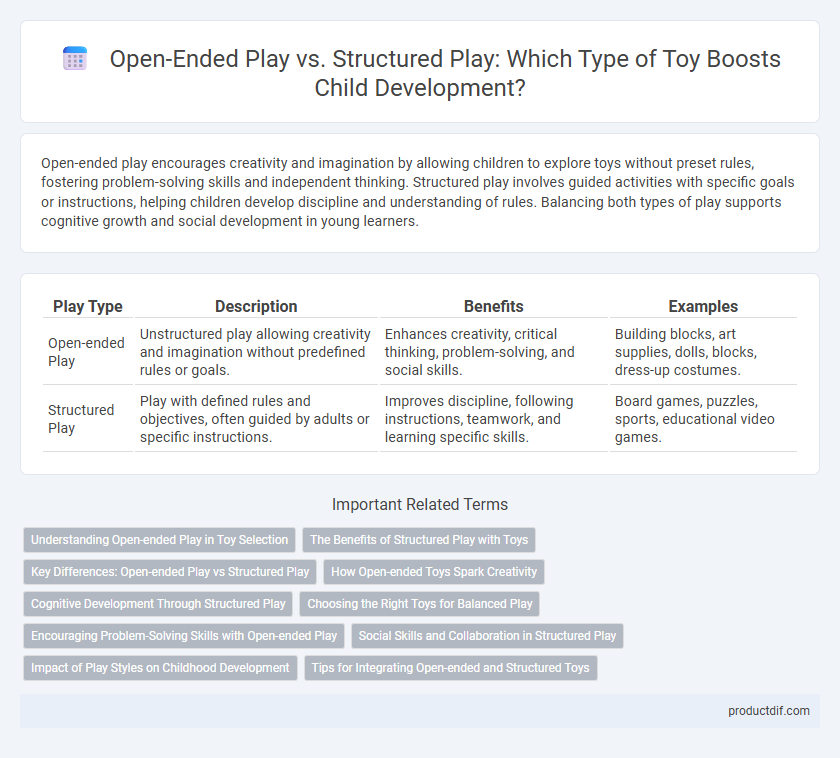
| Play Type | Description | Benefits | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Open-ended Play | Unstructured play allowing creativity and imagination without predefined rules or goals. | Enhances creativity, critical thinking, problem-solving, and social skills. | Building blocks, art supplies, dolls, blocks, dress-up costumes. |
| Structured Play | Play with defined rules and objectives, often guided by adults or specific instructions. | Improves discipline, following instructions, teamwork, and learning specific skills. | Board games, puzzles, sports, educational video games. |
Understanding Open-ended Play in Toy Selection
Open-ended play encourages creativity and problem-solving by allowing children to explore toys without fixed rules or outcomes, promoting cognitive and emotional development. Selecting toys that support open-ended play, such as building blocks, art supplies, or imaginative role-play sets, fosters independent thinking and adaptability. Emphasizing open-ended play in toy selection helps develop critical skills like innovation and decision-making, essential for lifelong learning.
The Benefits of Structured Play with Toys
Structured play with toys enhances cognitive development by providing clear goals and rules, which improve problem-solving skills and focus. It supports social learning through guided interactions, fostering cooperation and communication among children. Consistent use of structured play toys also promotes discipline and patience, crucial for academic success and emotional regulation.
Key Differences: Open-ended Play vs Structured Play
Open-ended play allows children to use imagination and creativity with toys like blocks or art supplies, offering limitless possibilities and promoting cognitive flexibility. Structured play involves specific rules and goals, usually guided by adults or instructions, such as board games or puzzles, enhancing problem-solving skills and discipline. Choosing the right balance between open-ended and structured play supports diverse developmental benefits in children.
How Open-ended Toys Spark Creativity
Open-ended toys such as building blocks, art supplies, and dolls stimulate creativity by encouraging children to invent their own narratives and solutions. These toys lack predefined rules or outcomes, allowing limitless exploration and imagination that fosters problem-solving and cognitive flexibility. Research indicates that children engaged in open-ended play develop stronger critical thinking skills and a deeper capacity for innovation compared to those primarily involved in structured play activities.
Cognitive Development Through Structured Play
Structured play, designed with specific goals and guided activities, enhances cognitive development by improving problem-solving skills, attention span, and memory retention in children. Through targeted tasks, structured play stimulates executive functions and promotes the acquisition of language and reasoning abilities. Toys such as puzzles, board games, and educational kits support this form of play by encouraging focused learning and cognitive growth.
Choosing the Right Toys for Balanced Play
Choosing the right toys for balanced play involves selecting both open-ended and structured options to support cognitive and motor development. Open-ended toys like building blocks and art supplies encourage creativity and problem-solving, while structured toys such as puzzles and board games promote rule-following and strategic thinking. A balanced mix fosters adaptability, critical thinking, and social skills in children.
Encouraging Problem-Solving Skills with Open-ended Play
Open-ended play stimulates problem-solving skills by allowing children to explore, experiment, and create without predefined rules or outcomes. Toys like building blocks, art supplies, and imaginative playsets promote critical thinking and adaptability by encouraging kids to devise their own solutions and narratives. This unrestricted creative environment fosters cognitive flexibility and resilience, essential for effective problem-solving.
Social Skills and Collaboration in Structured Play
Structured play promotes social skills and collaboration by encouraging children to follow rules, take turns, and work towards common goals with peers. Toys designed for structured play, such as board games and building sets with specific instructions, foster communication, teamwork, and problem-solving abilities. These interactive experiences enhance children's ability to cooperate and develop empathy in social settings.
Impact of Play Styles on Childhood Development
Open-ended play fosters creativity, problem-solving, and emotional resilience by allowing children to explore and direct their activities freely. Structured play, characterized by guided tasks and rules, enhances cognitive skills, social interaction, and discipline through clear objectives and feedback. Both play styles contribute uniquely to cognitive, social, and emotional development, promoting well-rounded growth and adaptability in childhood.
Tips for Integrating Open-ended and Structured Toys
Integrating open-ended and structured toys enhances children's development by balancing creativity with skill-building; provide a diverse toy selection that includes building blocks alongside puzzles to encourage both imaginative exploration and problem-solving. Rotate toys regularly to maintain interest and facilitate different types of play, allowing children to switch between freeform creation and guided tasks. Set specific play times for structured activities and leave ample room for open-ended play to support cognitive flexibility and social interaction.
Open-ended Play vs Structured Play Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com