Underglaze decoration involves applying pigments to pottery before glazing, creating a durable, scratch-resistant finish ideal for everyday tableware. Overglaze, applied on top of the glaze and fired at lower temperatures, offers brighter colors and intricate designs but is more prone to wear. Choosing between underglaze and overglaze depends on the desired durability and aesthetic complexity of the pet tableware.
Table of Comparison
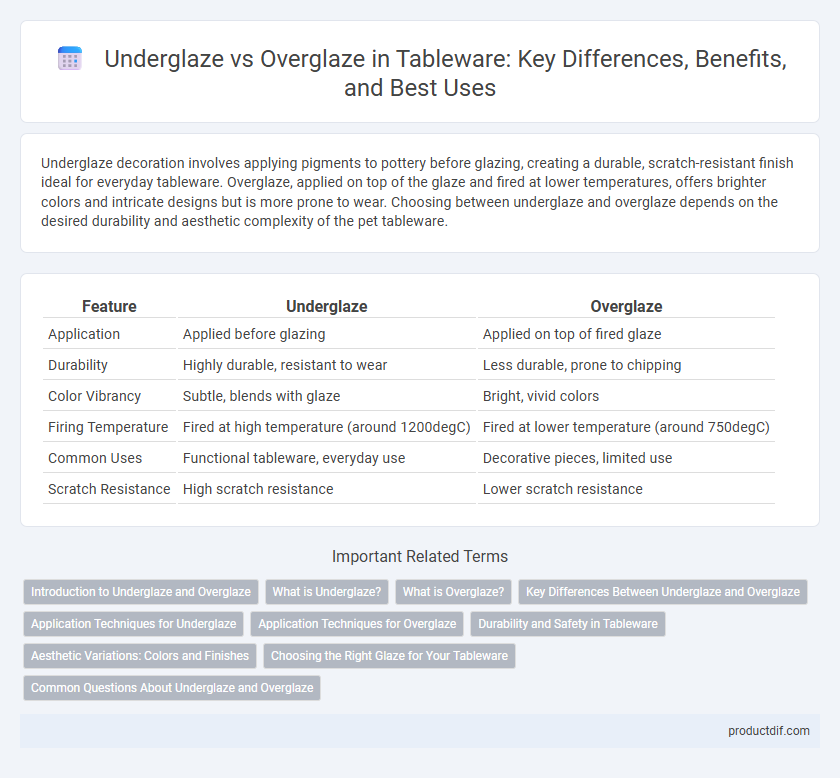
| Feature | Underglaze | Overglaze |
|---|---|---|
| Application | Applied before glazing | Applied on top of fired glaze |
| Durability | Highly durable, resistant to wear | Less durable, prone to chipping |
| Color Vibrancy | Subtle, blends with glaze | Bright, vivid colors |
| Firing Temperature | Fired at high temperature (around 1200degC) | Fired at lower temperature (around 750degC) |
| Common Uses | Functional tableware, everyday use | Decorative pieces, limited use |
| Scratch Resistance | High scratch resistance | Lower scratch resistance |
Introduction to Underglaze and Overglaze
Underglaze is a ceramic decoration technique applied to the pottery surface before glazing, ensuring the design is protected under a transparent glaze layer and offering durability and vibrant colors. Overglaze, also called on-glaze, involves painting designs onto the already glazed and fired pottery, which requires a subsequent low-temperature firing to fuse the decoration onto the surface, often used for intricate or metallic details. Both methods serve distinct aesthetic and functional purposes in tableware production, influencing the finish, texture, and longevity of decorative patterns.
What is Underglaze?
Underglaze is a ceramic decoration technique where colored pigments are applied to pottery before it is coated with a transparent glaze and fired at high temperatures. This method ensures the design is durable, resistant to scratching, and merges seamlessly with the ceramic body. Commonly used in fine tableware, underglaze decoration maintains vibrant colors and intricate patterns through heavy use and washing.
What is Overglaze?
Overglaze is a decorative technique applied on top of the already fired glaze of tableware, using enamel paints that are then fired at a lower temperature to fuse the design without melting the base glaze. This method allows for intricate, vibrant patterns and metallic finishes that enhance the visual appeal of ceramic plates, bowls, and cups. Overglaze decoration is commonly used for fine china and porcelain, offering durability while preserving the sharpness and color depth of the artwork.
Key Differences Between Underglaze and Overglaze
Underglaze involves applying pigments to pottery before the final clear glaze, resulting in durable, vibrant designs that resist wear and fading. Overglaze is painted on top of the fired glaze and requires a subsequent lower-temperature firing, allowing for intricate, raised decorations but with less durability. Key differences include application timing, firing process, and the longevity of the decoration, making underglaze ideal for functional tableware and overglaze suited for decorative pieces.
Application Techniques for Underglaze
Underglaze application involves painting or transferring designs onto pottery before the final glaze is applied, ensuring durability and vibrant colors that withstand firing temperatures. This technique allows precise detailing using brushes, sponges, or decals on raw or bisque-fired ceramics, creating intricate patterns that appear beneath a transparent glaze layer. The result is a smooth, glossy finish with designs protected from wear and fading, ideal for everyday tableware.
Application Techniques for Overglaze
Overglaze decoration involves applying color or design on the surface of already glazed and fired ceramic pieces, which then undergo a secondary firing at a lower temperature to fuse the overglaze without melting the original glaze. This technique allows for detailed and varied artistic effects, using enamel paints, gold, or other metallic finishes that require precise brushwork or transfer printing. Overglaze application demands expert control to avoid damaging the base glaze while achieving vibrant, durable embellishments that enhance tableware aesthetics.
Durability and Safety in Tableware
Underglaze decoration is highly durable in tableware, as it is applied beneath the glaze and fired at high temperatures, making it resistant to chipping and fading. Overglaze, being applied on top of the glaze and fired at lower temperatures, is more prone to wear and scratches over time. From a safety perspective, underglaze techniques generally use stable pigments that do not leach harmful substances, while overglaze may involve materials that are less resistant to heat and chemicals, potentially impacting food safety.
Aesthetic Variations: Colors and Finishes
Underglaze decoration offers muted, matte tones with designs sealed beneath a protective transparent glaze, resulting in durable, subtle aesthetics. Overglaze techniques provide vibrant, glossy colors and metallic accents applied on top of the glaze, enhancing brightness and intricate details. The choice between underglaze and overglaze significantly influences the tableware's visual appeal, ranging from understated elegance to vivid, ornamental finishes.
Choosing the Right Glaze for Your Tableware
Underglaze involves applying pigments beneath a clear glaze, offering durability and resistance to scratching, making it ideal for everyday tableware subjected to frequent use and washing. Overglaze decoration sits atop the glaze and allows for intricate designs but is more prone to wear, best suited for ornamental or less frequently used pieces. Selecting the right glaze depends on balancing longevity and aesthetic detail, ensuring tableware meets both functional and visual needs.
Common Questions About Underglaze and Overglaze
Underglaze and overglaze differ primarily in application and durability, with underglaze applied beneath the glaze resulting in a more permanent, scratch-resistant finish, while overglaze is painted on top of the glaze and often requires additional firing. Common questions include how each technique affects color vibrancy, with overglaze typically offering more vivid hues due to its surface position. Another frequent inquiry concerns the best use cases, where underglaze is preferred for everyday functional tableware and overglaze is chosen for decorative or collectible pieces.
Underglaze vs Overglaze Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com