Personal flotation devices (PFDs) are designed to keep a person afloat by providing buoyancy, making them essential for water safety in various recreational activities. Life vests, a type of PFD, offer more structured support and are typically equipped with additional features like straps and reflective material for enhanced visibility and security. Choosing the right personal flotation device depends on the activity, ensuring comfort, fit, and compliance with safety regulations.
Table of Comparison
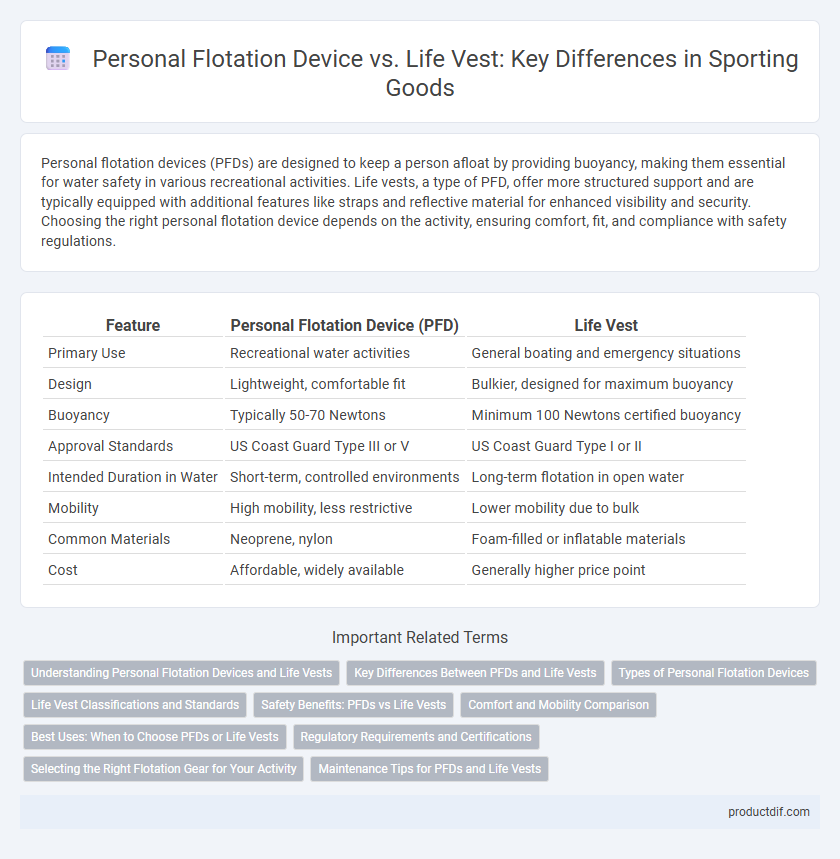
| Feature | Personal Flotation Device (PFD) | Life Vest |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Recreational water activities | General boating and emergency situations |
| Design | Lightweight, comfortable fit | Bulkier, designed for maximum buoyancy |
| Buoyancy | Typically 50-70 Newtons | Minimum 100 Newtons certified buoyancy |
| Approval Standards | US Coast Guard Type III or V | US Coast Guard Type I or II |
| Intended Duration in Water | Short-term, controlled environments | Long-term flotation in open water |
| Mobility | High mobility, less restrictive | Lower mobility due to bulk |
| Common Materials | Neoprene, nylon | Foam-filled or inflatable materials |
| Cost | Affordable, widely available | Generally higher price point |
Understanding Personal Flotation Devices and Life Vests
Personal flotation devices (PFDs) are designed to keep an individual afloat and vary in buoyancy levels depending on their type and intended use, such as Type I for offshore survival or Type III for recreational activities. Life vests, often used interchangeably with PFDs, specifically refer to wearable devices that provide buoyancy to prevent drowning by keeping the wearer's head above water. Understanding the distinctions between these devices is crucial for selecting the appropriate safety gear based on water conditions, activity type, and regulatory standards.
Key Differences Between PFDs and Life Vests
Personal flotation devices (PFDs) are designed for general buoyancy and come in various types based on activity and buoyancy levels, while life vests typically refer to PFDs with higher buoyancy intended specifically for survival situations. PFDs include Type I, II, III, IV, and V classifications, each with distinct features such as offshore use or recreational water sports, whereas life vests often meet stringent safety standards for prolonged flotation and impact resistance. The key differences lie in their intended use, buoyancy ratings, and design specifications, with life vests offering enhanced protection and visibility in emergencies compared to basic PFDs.
Types of Personal Flotation Devices
Personal flotation devices (PFDs) are classified into five main types based on buoyancy and intended use: Type I offers the most buoyancy for open water and is designed for unconscious wearers, Type II is a near-shore buoyant vest suitable for calm waters, Type III provides comfort and mobility for activities like kayaking and is ideal for conscious users, Type IV refers to throwable devices such as ring buoys, and Type V includes specialized PFDs tailored for specific activities or conditions, like offshore racing or windsurfing. Life vests typically correspond to Type III PFDs, emphasizing comfort and fit for extended wear during water sports. Understanding these types ensures users select appropriate safety gear aligned with their water activity and risk level.
Life Vest Classifications and Standards
Life vests are classified into five types by the U.S. Coast Guard based on buoyancy and usage: Type I (Offshore Life Jackets), Type II (Near-Shore Buoyancy Vests), Type III (Flotation Aids), Type IV (Throwable Devices), and Type V (Special Use Devices). Each type meets specific standards for flotation and safety, ensuring proper performance in various water activities and conditions. Compliance with ISO 12402 or ANSI/UL 1191 standards guarantees reliable buoyancy, materials, and design for personal safety on the water.
Safety Benefits: PFDs vs Life Vests
Personal flotation devices (PFDs) provide essential buoyancy to keep users afloat in water, featuring various types such as Type I, II, and III designed for different water conditions and activities. Life vests, a subset of PFDs, typically offer greater buoyancy and automatic inflation mechanisms, enhancing safety in emergencies by ensuring the wearer remains face-up for optimal breathing. Understanding the specific safety benefits of each, including their buoyancy ratings and intended use, is crucial for selecting the appropriate gear to prevent drowning and improve survival chances in aquatic environments.
Comfort and Mobility Comparison
Personal flotation devices (PFDs) typically offer greater comfort due to lightweight materials and ergonomic designs that reduce bulk and enhance breathability. Life vests may provide more buoyancy but often sacrifice mobility because of their heavier padding and restrictive fit. Choosing between a PFD and a life vest depends on balancing comfort for prolonged wear against the level of mobility required for specific water activities.
Best Uses: When to Choose PFDs or Life Vests
Personal flotation devices (PFDs) are ideal for active water sports such as kayaking, paddleboarding, or fishing due to their flexibility and lighter design. Life vests provide superior buoyancy and are best suited for boating, water rescue, and emergency situations where maximum flotation is critical. Selecting the proper gear depends on activity type, water conditions, and required safety standards like those from the U.S. Coast Guard.
Regulatory Requirements and Certifications
Personal flotation devices (PFDs) and life vests must comply with strict regulatory requirements established by agencies such as the U.S. Coast Guard (USCG) and European CE standards to ensure safety and performance. PFDs are categorized into different types (Type I-IV) based on buoyancy and intended use, each requiring certification that verifies compliance with rigorous testing for flotation, stability, and durability. Life vests, often designed for specific activities, must meet specific certification standards reflecting usage scenarios, with proper labeling and approval marks indicating adherence to legal safety mandates.
Selecting the Right Flotation Gear for Your Activity
Choosing the right flotation gear depends on the specific water activity you plan to engage in, as personal flotation devices (PFDs) and life vests offer different levels of buoyancy and mobility. PFDs are designed for active water sports like kayaking or paddleboarding, providing freedom of movement while ensuring safety, whereas life vests are bulkier and intended for emergencies or less active scenarios such as boating or fishing. Properly fitting flotation gear that meets U.S. Coast Guard certification standards enhances safety, comfort, and performance on the water.
Maintenance Tips for PFDs and Life Vests
Regular inspection of personal flotation devices (PFDs) and life vests for tears, punctures, and worn straps ensures optimal buoyancy and safety performance. Cleaning with mild soap and warm water, followed by air drying away from direct sunlight, prevents material degradation and extends the lifespan of flotation gear. Storing PFDs and life vests in a cool, dry place away from chemicals and extreme temperatures maintains their structural integrity and reliability during water activities.
Personal flotation device vs life vest Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com