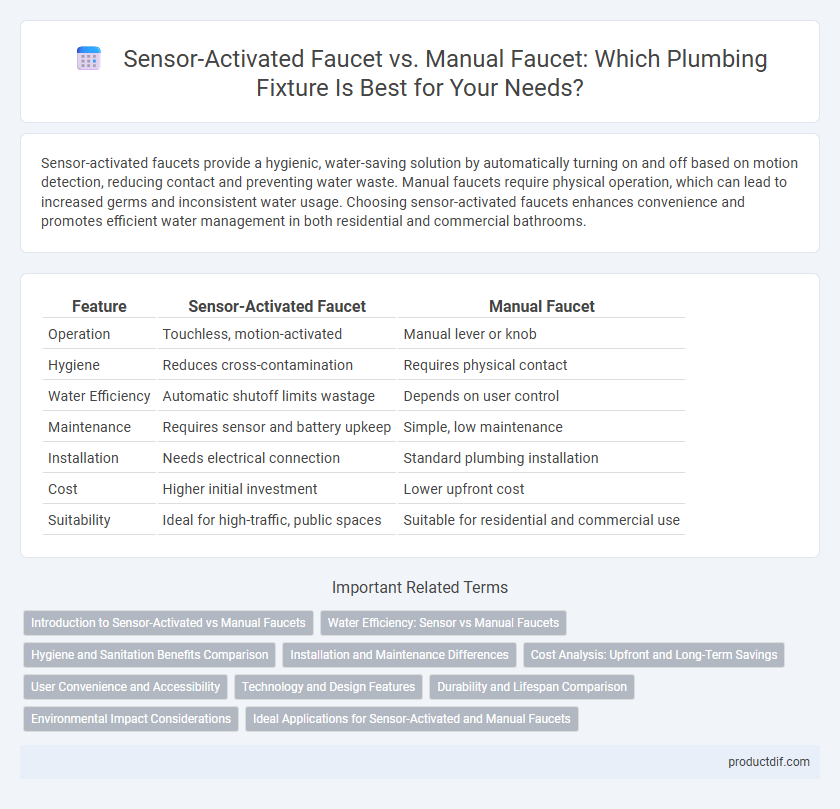
Sensor-activated faucets provide a hygienic, water-saving solution by automatically turning on and off based on motion detection, reducing contact and preventing water waste. Manual faucets require physical operation, which can lead to increased germs and inconsistent water usage. Choosing sensor-activated faucets enhances convenience and promotes efficient water management in both residential and commercial bathrooms.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Sensor-Activated Faucet | Manual Faucet |
|---|---|---|
| Operation | Touchless, motion-activated | Manual lever or knob |
| Hygiene | Reduces cross-contamination | Requires physical contact |
| Water Efficiency | Automatic shutoff limits wastage | Depends on user control |
| Maintenance | Requires sensor and battery upkeep | Simple, low maintenance |
| Installation | Needs electrical connection | Standard plumbing installation |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | Lower upfront cost |
| Suitability | Ideal for high-traffic, public spaces | Suitable for residential and commercial use |
Introduction to Sensor-Activated vs Manual Faucets
Sensor-activated faucets use infrared sensors to detect hand presence, enabling water flow without physical contact, which promotes hygiene and conserves water. Manual faucets operate through traditional handles or knobs, requiring users to turn them on and off, offering straightforward control but increased touchpoints. Choosing between sensor-activated and manual faucets involves evaluating factors such as water efficiency, user convenience, maintenance requirements, and installation cost.
Water Efficiency: Sensor vs Manual Faucets
Sensor-activated faucets significantly reduce water wastage by automatically shutting off when not in use, ensuring water flows only during handwashing or rinsing. Manual faucets often suffer from longer, unmonitored flow periods leading to higher water consumption. Studies show sensor faucets can decrease water usage by up to 30-50% compared to traditional manual models.
Hygiene and Sanitation Benefits Comparison
Sensor-activated faucets significantly reduce the risk of cross-contamination by eliminating the need to touch handles, thereby minimizing germ transfer in public and residential restrooms. Manual faucets require physical contact, increasing the likelihood of spreading bacteria and viruses, especially in high-traffic areas. Touchless technology promotes enhanced hygiene and sanitation by ensuring faucets operate only when hands are detected, maintaining a cleaner environment.
Installation and Maintenance Differences
Sensor-activated faucets require electrical connections or batteries for installation, whereas manual faucets need only basic plumbing hookups. Maintenance for sensor faucets involves regular sensor calibration and battery replacement, while manual faucets primarily demand routine checks for leaks and cartridge replacements. These differences impact both the initial setup complexity and ongoing upkeep requirements for residential or commercial plumbing fixtures.
Cost Analysis: Upfront and Long-Term Savings
Sensor-activated faucets typically have a higher upfront cost due to advanced technology components, but they offer significant long-term savings by reducing water waste and lowering utility bills. Manual faucets generally cost less initially but can lead to increased water consumption and higher maintenance expenses over time. Evaluating total cost of ownership reveals that sensor faucets provide better economic value in commercial and high-traffic environments.
User Convenience and Accessibility
Sensor-activated faucets provide enhanced user convenience by allowing hands-free operation, reducing the need for physical contact and minimizing the spread of germs. These faucets improve accessibility for individuals with limited mobility or dexterity, as users can activate water flow with simple gestures. Manual faucets require physical effort to operate, which can be challenging for people with disabilities or elderly users, making sensor-activated models a more inclusive choice in plumbing fixtures.
Technology and Design Features
Sensor-activated faucets utilize infrared or capacitive sensors to detect hand presence, enabling touchless operation that enhances hygiene and conserves water by reducing unnecessary flow. Manual faucets rely on traditional handles or knobs, offering straightforward mechanical control but lacking automated functionality and potential water savings. Advanced designs of sensor faucets often incorporate adjustable flow rates, temperature presets, and sleek, modern aesthetics, whereas manual faucets prioritize simplicity and durability in their construction.
Durability and Lifespan Comparison
Sensor-activated faucets typically feature advanced electronic components and durable solenoid valves designed for longevity, often surpassing manual faucets in lifespan due to reduced mechanical wear and tear. Manual faucets, while simpler in design, may experience faster deterioration of internal parts like washers and cartridges from frequent physical operation. The enhanced durability of sensor faucets leads to extended maintenance intervals, minimizing replacement costs over time despite higher initial investment.
Environmental Impact Considerations
Sensor-activated faucets significantly reduce water wastage by automatically shutting off the flow when not in use, leading to an average water savings of 30% compared to manual faucets. These fixtures also help lower energy consumption by minimizing hot water use, thereby reducing household carbon footprints. In contrast, manual faucets often result in prolonged water flow due to human error, contributing to resource inefficiency and increased environmental impact.
Ideal Applications for Sensor-Activated and Manual Faucets
Sensor-activated faucets are ideal for high-traffic public restrooms, healthcare facilities, and food service areas where hygiene and water conservation are priorities. Manual faucets are better suited for residential settings and standalone sinks where precise temperature and flow control are needed. Both types enhance user experience, but sensor faucets excel in environments requiring hands-free operation to reduce contamination.
sensor-activated faucet vs manual faucet Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com