Air-gap drains prevent backflow contamination by providing a physical break between the water supply and the drain line, making them ideal for plumbing fixture pets requiring stringent hygiene standards. Direct-connect drains offer a more streamlined installation by connecting the fixture drain directly to the waste pipe but risk potential siphoning and contamination without an air gap. Choosing between air-gap and direct-connect drains depends on balancing ease of installation with the necessity for water safety and local plumbing codes.
Table of Comparison
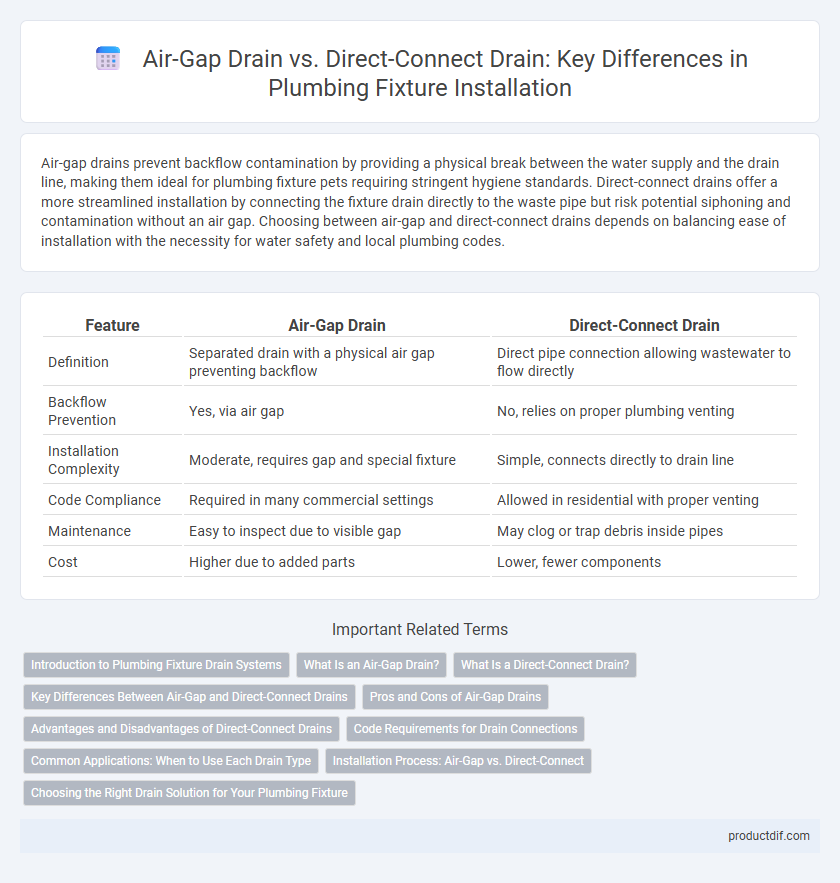
| Feature | Air-Gap Drain | Direct-Connect Drain |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Separated drain with a physical air gap preventing backflow | Direct pipe connection allowing wastewater to flow directly |
| Backflow Prevention | Yes, via air gap | No, relies on proper plumbing venting |
| Installation Complexity | Moderate, requires gap and special fixture | Simple, connects directly to drain line |
| Code Compliance | Required in many commercial settings | Allowed in residential with proper venting |
| Maintenance | Easy to inspect due to visible gap | May clog or trap debris inside pipes |
| Cost | Higher due to added parts | Lower, fewer components |
Introduction to Plumbing Fixture Drain Systems
Air-gap drains create a physical separation between the fixture outlet and the drainage system to prevent backflow contamination, ensuring sanitary conditions in plumbing fixtures. Direct-connect drains link the fixture directly to the drainpipe, providing a compact and efficient drainage path but requiring careful installation to avoid cross-contamination risks. Understanding the differences between these systems is crucial for compliance with plumbing codes and maintaining water safety standards.
What Is an Air-Gap Drain?
An air-gap drain is a plumbing fixture designed to prevent backflow contamination by creating a physical separation between the water outlet and the drainage system. It typically features a gap of at least two inches between the sink drain and the flood-level rim of the fixture, ensuring wastewater cannot siphon back into the clean water supply. This safety measure is commonly used in dishwashers and commercial kitchens to maintain sanitary conditions and comply with plumbing codes.
What Is a Direct-Connect Drain?
A direct-connect drain is a plumbing fixture that attaches directly to the dishwasher's drain hose, allowing wastewater to flow straight into the sink drain or garbage disposal without an air gap. Unlike air-gap drains, this system lacks a physical barrier preventing backflow, which can increase the risk of contamination in the dishwasher. Direct-connect drains are commonly used in residential kitchens for their compact installation and cost efficiency but require proper check valves or high loops to ensure compliance with plumbing codes.
Key Differences Between Air-Gap and Direct-Connect Drains
Air-gap drains incorporate a physical air space to prevent wastewater backflow, ensuring better protection against contamination by breaking the siphon effect, while direct-connect drains attach plumbing fixtures directly to the drainpipe without an air gap, making them simpler and often more cost-effective. Air-gap systems comply with many plumbing codes and are preferred for sanitary fixtures like dishwashers and sinks to maintain hygiene, whereas direct-connect drains are common in applications where backflow prevention is less critical. Choosing between them depends on local regulations, risk of contamination, and fixture type, with air-gap drains offering superior safety in preventing cross-contamination.
Pros and Cons of Air-Gap Drains
Air-gap drains provide a critical backflow prevention method by maintaining a physical separation between the fixture's water outlet and the drainage system, significantly reducing the risk of contaminated water reentering the potable supply. Their main advantage lies in compliance with plumbing codes and enhanced sanitation, which is especially vital in commercial kitchens and medical facilities. However, air-gap drains require more installation space and can cause water splashing or noise compared to direct-connect drains, which have a more compact design but higher risk of cross-contamination.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Direct-Connect Drains
Direct-connect drains offer a streamlined plumbing setup by connecting appliances directly to the drain system, reducing installation time and space requirements. However, they pose an increased risk of backflow contamination without an air gap, which compromises water safety and code compliance in certain jurisdictions. Maintenance challenges also arise due to potential clogs and lack of visible separation between the appliance and drain line.
Code Requirements for Drain Connections
Air-gap drains require a physical separation between the fixture outlet and the drainage piping to prevent backflow contamination, meeting strict plumbing codes that emphasize safety and water quality. Direct-connect drains, while space-efficient, must incorporate approved backflow prevention devices to comply with local building codes and avoid cross-contamination hazards. Adhering to these code requirements ensures sanitary waste disposal and protects potable water systems in residential and commercial plumbing installations.
Common Applications: When to Use Each Drain Type
Air-gap drains are commonly used in commercial kitchens, laboratories, and dishwashers where preventing backflow contamination is critical. Direct-connect drains are ideal for residential washing machines and appliances in homes where space is limited, and backflow risk is minimal. Choosing the correct drain type ensures compliance with local plumbing codes and optimizes system sanitation and safety.
Installation Process: Air-Gap vs. Direct-Connect
The installation process for an air-gap drain requires a physical separation between the dishwasher drain hose and the sink drain, typically mounting an air-gap outlet on the sink or countertop, which prevents backflow and contamination. Direct-connect drains involve connecting the dishwasher drain hose directly to the sink drain tailpiece or garbage disposal, offering a simpler, more compact installation but relying on a high loop to prevent backflow. Air-gap installations comply with certain local plumbing codes ensuring maximum sanitation, while direct-connect methods may require additional measures like high loops and check valves to meet health standards.
Choosing the Right Drain Solution for Your Plumbing Fixture
Choosing the right drain solution for your plumbing fixture hinges on understanding the differences between air-gap drains and direct-connect drains. Air-gap drains prevent backflow contamination by creating a physical gap between the fixture and the wastewater system, making them essential for dishwashers and sinks in compliance with local plumbing codes. Direct-connect drains offer a more streamlined installation but require precise venting and are best suited for fixtures with reliable backflow prevention mechanisms.
air-gap drain vs direct-connect drain Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com