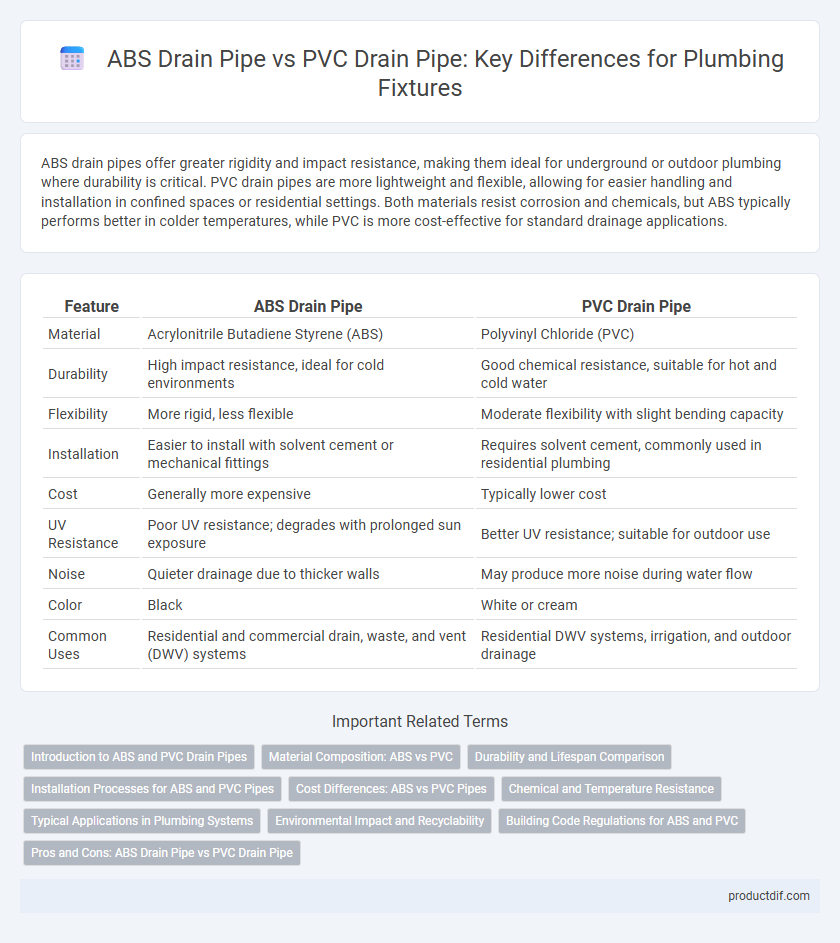
ABS drain pipes offer greater rigidity and impact resistance, making them ideal for underground or outdoor plumbing where durability is critical. PVC drain pipes are more lightweight and flexible, allowing for easier handling and installation in confined spaces or residential settings. Both materials resist corrosion and chemicals, but ABS typically performs better in colder temperatures, while PVC is more cost-effective for standard drainage applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | ABS Drain Pipe | PVC Drain Pipe |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) |
| Durability | High impact resistance, ideal for cold environments | Good chemical resistance, suitable for hot and cold water |
| Flexibility | More rigid, less flexible | Moderate flexibility with slight bending capacity |
| Installation | Easier to install with solvent cement or mechanical fittings | Requires solvent cement, commonly used in residential plumbing |
| Cost | Generally more expensive | Typically lower cost |
| UV Resistance | Poor UV resistance; degrades with prolonged sun exposure | Better UV resistance; suitable for outdoor use |
| Noise | Quieter drainage due to thicker walls | May produce more noise during water flow |
| Color | Black | White or cream |
| Common Uses | Residential and commercial drain, waste, and vent (DWV) systems | Residential DWV systems, irrigation, and outdoor drainage |
Introduction to ABS and PVC Drain Pipes
ABS drain pipes are made from acrylonitrile butadiene styrene, known for their rigidity, impact resistance, and ability to handle lower temperatures, making them suitable for residential drain, waste, and vent systems. PVC drain pipes consist of polyvinyl chloride, offering superior chemical resistance, lighter weight, and greater flexibility, which enhances their popularity in commercial and residential plumbing applications. Both ABS and PVC pipes meet plumbing codes but differ in color, with ABS typically black and PVC white or gray, facilitating easy identification and appropriate usage in drainage systems.
Material Composition: ABS vs PVC
ABS drain pipes are made from acrylonitrile butadiene styrene, a tough thermoplastic known for impact resistance and durability, making it suitable for underground and exposed installations. PVC drain pipes consist of polyvinyl chloride, offering chemical resistance, lightweight properties, and cost-effectiveness, commonly used in residential and commercial plumbing systems. The material composition affects temperature tolerance, flexibility, and compatibility with certain solvents, influencing the choice between ABS and PVC for specific drainage applications.
Durability and Lifespan Comparison
ABS drain pipes are known for their higher resistance to impact and temperature fluctuations, contributing to enhanced durability in colder climates. PVC drain pipes offer excellent chemical resistance and UV stability, which helps prolong their lifespan in exposed outdoor applications. Both materials typically provide a lifespan of 50 years or more, but ABS tends to perform better in low-temperature environments, while PVC excels under direct sunlight exposure.
Installation Processes for ABS and PVC Pipes
Installation of ABS drain pipes typically involves solvent welding with an ABS cement designed to chemically bond the fittings and pipes, ensuring a strong, durable joint resistant to leaks. PVC drain pipe installation requires a similar solvent welding process using a purple primer followed by PVC cement to prepare and securely join the pipe sections. Both materials demand clean, dry surfaces for effective adhesion, but ABS pipes are often preferred for colder climates due to their greater resistance to impact and flexibility during installation.
Cost Differences: ABS vs PVC Pipes
ABS drain pipes generally cost more upfront compared to PVC pipes due to their higher impact resistance and suitability for colder climates. PVC pipes offer a more budget-friendly option with lower material costs and wide availability, making them popular for many residential plumbing applications. Installation expenses may vary, as ABS requires special cement and primers, which can slightly increase labor costs compared to the easier-to-install PVC.
Chemical and Temperature Resistance
ABS drain pipes exhibit superior chemical resistance to acidic and alkaline substances, making them well-suited for industrial or harsh chemical drainage systems. PVC drain pipes offer higher temperature resistance, typically withstanding temperatures up to 140degF (60degC), which makes them ideal for residential plumbing applications involving hot water. Both materials resist corrosion but selecting between ABS and PVC depends on specific environmental exposure and chemical compatibility requirements.
Typical Applications in Plumbing Systems
ABS drain pipes are commonly used in residential drainage, waste, and vent systems due to their durability and resistance to impact in cold temperatures. PVC drain pipes are preferred in both residential and commercial plumbing for their chemical resistance, lightweight nature, and ease of installation, especially in water supply, irrigation, and venting applications. Both materials meet plumbing code requirements but are selected based on specific environmental conditions and pressure ratings within the system.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
ABS drain pipes are made from acrylonitrile butadiene styrene, which is less recyclable and can release toxic fumes when burned, contributing to environmental pollution. PVC drain pipes, constructed from polyvinyl chloride, offer better recycling options through specialized facilities and have a lower carbon footprint during production. Choosing PVC over ABS can reduce long-term environmental impact due to improved recyclability and safer disposal methods.
Building Code Regulations for ABS and PVC
Building code regulations generally approve both ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) and PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) drain pipes for residential and commercial plumbing systems, with specific guidelines based on local jurisdictions. ABS pipes are often favored for below-ground drainage due to their impact resistance and may require certification meeting ASTM standards such as ASTM D2661, while PVC pipes are commonly used in above-ground applications and must comply with ASTM D2665 or ASTM F891 standards. Compliance with plumbing codes like the International Residential Code (IRC) or Uniform Plumbing Code (UPC) ensures proper installation, venting, and waste disposal efficiency for both ABS and PVC drainage systems.
Pros and Cons: ABS Drain Pipe vs PVC Drain Pipe
ABS drain pipes offer superior impact resistance and perform better in colder temperatures, making them ideal for underground or exposed areas prone to freezing. PVC drain pipes are lighter, easier to install, and resistant to chemical corrosion but can become brittle over time when exposed to UV light. Both materials are widely used in plumbing, with ABS favored for durability and PVC preferred for cost-effectiveness and versatility in residential applications.
ABS drain pipe vs PVC drain pipe Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com