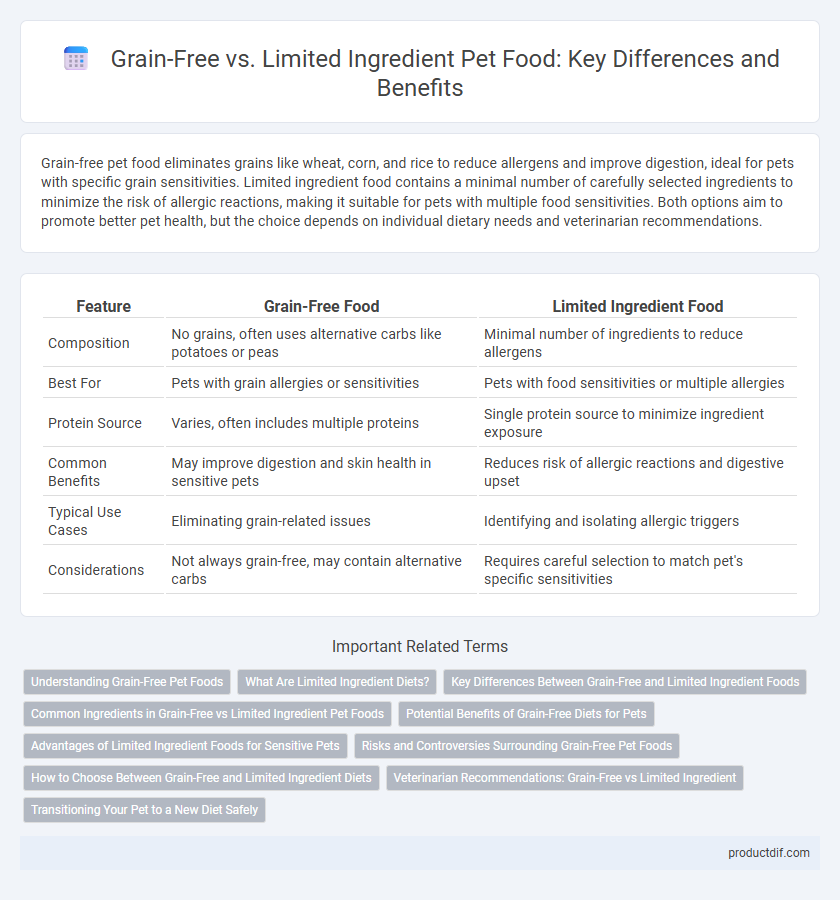
Grain-free pet food eliminates grains like wheat, corn, and rice to reduce allergens and improve digestion, ideal for pets with specific grain sensitivities. Limited ingredient food contains a minimal number of carefully selected ingredients to minimize the risk of allergic reactions, making it suitable for pets with multiple food sensitivities. Both options aim to promote better pet health, but the choice depends on individual dietary needs and veterinarian recommendations.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Grain-Free Food | Limited Ingredient Food |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | No grains, often uses alternative carbs like potatoes or peas | Minimal number of ingredients to reduce allergens |
| Best For | Pets with grain allergies or sensitivities | Pets with food sensitivities or multiple allergies |
| Protein Source | Varies, often includes multiple proteins | Single protein source to minimize ingredient exposure |
| Common Benefits | May improve digestion and skin health in sensitive pets | Reduces risk of allergic reactions and digestive upset |
| Typical Use Cases | Eliminating grain-related issues | Identifying and isolating allergic triggers |
| Considerations | Not always grain-free, may contain alternative carbs | Requires careful selection to match pet's specific sensitivities |
Understanding Grain-Free Pet Foods
Grain-free pet foods eliminate common grains like wheat, corn, and soy to reduce potential allergens and digestive issues in pets sensitive to these ingredients. These formulas often feature alternative carbohydrate sources such as sweet potatoes or peas, offering a balanced nutrient profile without traditional grains. Understanding grain-free pet foods helps pet owners make informed decisions based on their pet's specific dietary needs and potential food sensitivities.
What Are Limited Ingredient Diets?
Limited ingredient diets for pets focus on reducing the number of components in their food to minimize potential allergens and digestive issues. These diets typically contain a single protein source and a limited number of carbohydrates, making them ideal for pets with food sensitivities or allergies. Grain-free food differs by excluding grains but may still contain multiple ingredients, while limited ingredient diets emphasize simplicity and minimalism to better identify and manage dietary intolerances.
Key Differences Between Grain-Free and Limited Ingredient Foods
Grain-free pet food eliminates all grains such as wheat, corn, and rice to reduce allergens and improve digestion, while limited ingredient food focuses on minimizing the number of protein and carbohydrate sources to pinpoint food sensitivities. Grain-free diets typically use alternative carbohydrates like sweet potatoes or peas, whereas limited ingredient diets emphasize a simplified recipe with fewer ingredients to avoid common allergens. Understanding these key differences helps pet owners choose the appropriate diet for pets with specific allergies or digestive issues.
Common Ingredients in Grain-Free vs Limited Ingredient Pet Foods
Grain-free pet foods typically replace grains with ingredients such as peas, lentils, potatoes, and other legumes to provide carbohydrates without gluten or common grain allergens. Limited ingredient diets focus on minimizing the number of components and often feature single protein sources like duck or salmon combined with one or two easily digestible carbohydrates, such as sweet potatoes or rice. Both formulations aim to reduce allergies and sensitivities, though grain-free uses diverse alternatives, while limited ingredient emphasizes simplicity and minimal exposure to potential irritants.
Potential Benefits of Grain-Free Diets for Pets
Grain-free diets for pets may reduce the risk of food allergies and sensitivities by eliminating common allergens like wheat, corn, and soy. These diets often emphasize higher protein content from meats and legumes, supporting muscle maintenance and overall energy levels. Grain-free foods can also aid in promoting better digestion and improved coat condition due to their tailored nutrient profiles.
Advantages of Limited Ingredient Foods for Sensitive Pets
Limited ingredient foods benefit sensitive pets by reducing the number of potential allergens and irritants, which helps minimize adverse reactions and digestive issues. These formulas typically contain a single protein source and fewer carbohydrates, enhancing digestibility and promoting better nutrient absorption. Feeding limited ingredient diets supports pets with food sensitivities or allergies, leading to improved skin health, reduced itching, and more stable energy levels.
Risks and Controversies Surrounding Grain-Free Pet Foods
Grain-free pet foods have become popular but carry risks such as a potential link to canine dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM), a serious heart condition. Limited ingredient diets offer a controlled formulation to reduce allergens but may not fully address nutritional imbalances that grain-free trends sometimes entail. Pet owners should consult veterinarians before choosing grain-free diets due to ongoing controversies about their long-term safety and efficacy.
How to Choose Between Grain-Free and Limited Ingredient Diets
Choosing between grain-free and limited ingredient diets for pets depends on their specific health needs and allergies. Grain-free diets eliminate grains such as wheat, corn, and rice, catering to pets with grain sensitivities or allergies. Limited ingredient diets reduce the number of components in food, focusing on novel proteins and minimal additives to support pets with multiple food sensitivities or digestive issues.
Veterinarian Recommendations: Grain-Free vs Limited Ingredient
Veterinarians often recommend limited ingredient diets for pets with food sensitivities or allergies, as these formulas reduce the risk of adverse reactions by minimizing protein and carbohydrate sources. Grain-free diets may be suggested for pets with specific grain allergies or intolerances, but caution is advised due to potential links to heart health issues in certain breeds. Ultimately, professional guidance ensures the chosen diet supports optimal pet health and addresses individual nutritional needs effectively.
Transitioning Your Pet to a New Diet Safely
Gradually transitioning your pet to grain-free or limited ingredient food over 7 to 10 days minimizes digestive upset and allows their system to adapt. Start by mixing a small portion of the new food with their current diet, slowly increasing the amount each day while monitoring for any adverse reactions such as vomiting or diarrhea. Consistent hydration and regular veterinary check-ups during this period ensure your pet's health remains stable throughout the diet change.
Grain-free food vs limited ingredient food Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com