Calculators offer versatile functions including complex calculations, memory storage, and scientific operations, making them ideal for diverse office tasks. Adding machines specialize in rapid, accurate addition and are favored for repetitive financial tasks, enhancing efficiency in accounting environments. Choosing between the two depends on the specific needs for calculation complexity and speed in office supply management.
Table of Comparison
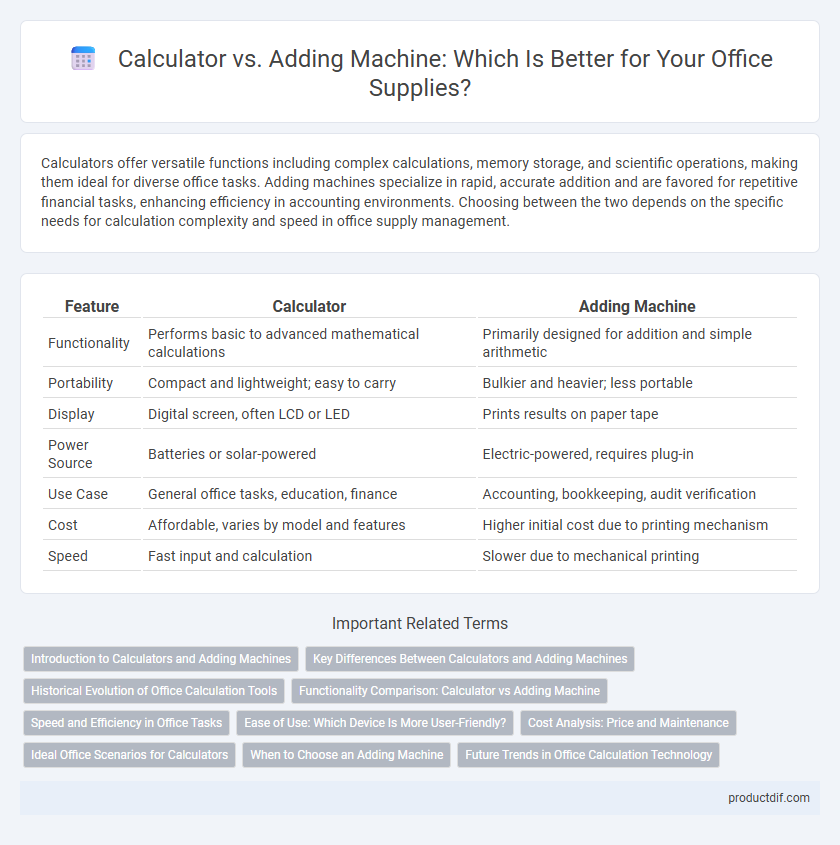
| Feature | Calculator | Adding Machine |
|---|---|---|
| Functionality | Performs basic to advanced mathematical calculations | Primarily designed for addition and simple arithmetic |
| Portability | Compact and lightweight; easy to carry | Bulkier and heavier; less portable |
| Display | Digital screen, often LCD or LED | Prints results on paper tape |
| Power Source | Batteries or solar-powered | Electric-powered, requires plug-in |
| Use Case | General office tasks, education, finance | Accounting, bookkeeping, audit verification |
| Cost | Affordable, varies by model and features | Higher initial cost due to printing mechanism |
| Speed | Fast input and calculation | Slower due to mechanical printing |
Introduction to Calculators and Adding Machines
Calculators and adding machines serve as essential tools for arithmetic operations in office environments, with calculators offering versatile functions including complex calculations beyond simple addition. Adding machines primarily focus on efficient, reliable addition and basic arithmetic, designed for rapid number entry and accounting tasks. Advances in technology have expanded calculators' capabilities to incorporate scientific, financial, and statistical functions, making them indispensable for diverse professional and educational applications.
Key Differences Between Calculators and Adding Machines
Calculators offer versatile functions including complex mathematical operations such as multiplication, division, and scientific calculations, while adding machines primarily focus on basic arithmetic such as addition and subtraction. Calculators feature digital displays and can handle a wider range of inputs and programmable functions, whereas adding machines often use mechanical or basic electronic keys geared towards rapid number entry for financial tasks. The portability and multifunctional capabilities of calculators make them suitable for diverse office environments, contrasting with the adding machine's specialization in accounting accuracy.
Historical Evolution of Office Calculation Tools
The historical evolution of office calculation tools reveals that adding machines, invented in the late 19th century, were the primary mechanical devices used for arithmetic before the advent of electronic calculators in the mid-20th century. Adding machines relied on levers and gears to perform basic addition and subtraction, making them indispensable in accounting and bookkeeping for decades. Electronic calculators introduced faster processing, portability, and multifunctional capabilities, eventually replacing bulky adding machines in modern office environments.
Functionality Comparison: Calculator vs Adding Machine
Calculators offer advanced functionality with capabilities for complex arithmetic, scientific calculations, and programming, while adding machines primarily focus on basic addition and subtraction tasks, often used in accounting. Calculators feature digital displays and memory storage, enabling versatile operations beyond simple summations, whereas adding machines tend to have mechanical or basic printing functions. The multifunctional design of calculators makes them essential tools for various professional and educational settings, contrasting with the specialized, limited use of adding machines.
Speed and Efficiency in Office Tasks
Calculators offer faster computation speeds and enhanced efficiency in office tasks compared to traditional adding machines, thanks to their digital processing capabilities and multifunctional features. Adding machines, while reliable for basic arithmetic, lack the advanced functions and quick data entry interfaces that calculators provide, slowing down workflow. Modern offices benefit from calculators' compact design and precision, streamlining repetitive calculations and improving overall productivity.
Ease of Use: Which Device Is More User-Friendly?
Calculators offer a more user-friendly experience with intuitive digital interfaces, customizable functions, and clear LCD displays that simplify complex calculations. Adding machines, while reliable for basic arithmetic and printing physical receipts, often lack modern features and require more manual input, making them less convenient for everyday office tasks. The portability and multi-functionality of calculators make them the preferred choice for ease of use in most office environments.
Cost Analysis: Price and Maintenance
Calculators typically offer a lower initial purchase price compared to adding machines, making them more cost-effective for everyday office use. Maintenance costs for calculators are minimal, mainly limited to battery replacements or occasional repairs, whereas adding machines often require more frequent servicing and parts replacement due to mechanical components. Evaluating long-term expenses, calculators provide better value through reduced upkeep and affordable pricing options tailored to varying business needs.
Ideal Office Scenarios for Calculators
Calculators excel in office environments requiring quick, versatile calculations such as budgeting, financial analysis, and real-time data entry, offering portability and advanced functions like percentage, square root, and memory storage. Unlike adding machines, which are suited for repetitive addition tasks and bulk tallying, calculators support diverse mathematical operations essential for accounting, sales forecasting, and complex problem-solving. Their compact design and multifunctionality make calculators ideal for dynamic office settings where efficient, on-the-go computation enhances productivity.
When to Choose an Adding Machine
Choosing an adding machine over a calculator is ideal for businesses that require high-speed, repetitive calculations and printed records for accounting or bookkeeping purposes. Adding machines offer durability and ease of use for long sessions of numerical input, especially in financial environments where paper trails are essential. They excel in tasks like invoice totaling and cash register operations, providing reliable physical documentation that calculators typically do not.
Future Trends in Office Calculation Technology
Future trends in office calculation technology emphasize the integration of AI-powered calculators capable of predictive analytics and voice recognition, surpassing traditional adding machines. Cloud-based calculation tools offer enhanced collaboration and real-time data processing, enabling seamless workflow in hybrid work environments. Advancements in portable, multifunctional devices are set to replace standalone adding machines, driving efficiency and accuracy in office supply solutions.
Calculator vs Adding Machine Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com