Monophonic synthesizers produce one note at a time, ideal for basslines and lead melodies with clear, focused sound. Polyphonic synthesizers can play multiple notes simultaneously, enabling complex chords and richer harmonic textures essential for layered compositions. Choosing between monophonic and polyphonic synths depends on the desired musical expression and arrangement complexity.
Table of Comparison
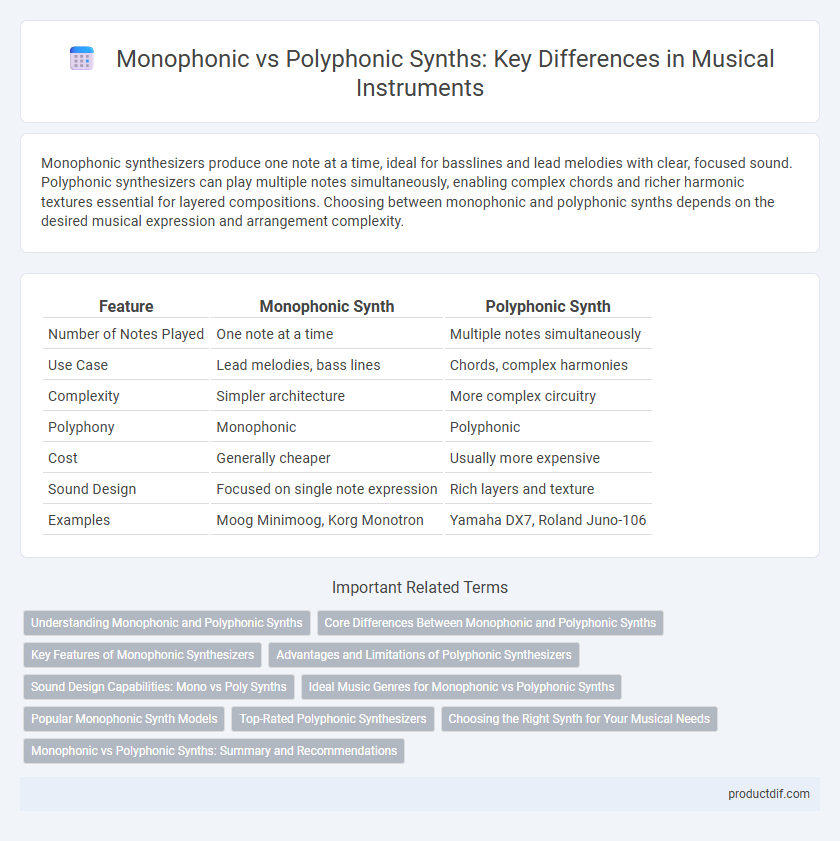
| Feature | Monophonic Synth | Polyphonic Synth |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Notes Played | One note at a time | Multiple notes simultaneously |
| Use Case | Lead melodies, bass lines | Chords, complex harmonies |
| Complexity | Simpler architecture | More complex circuitry |
| Polyphony | Monophonic | Polyphonic |
| Cost | Generally cheaper | Usually more expensive |
| Sound Design | Focused on single note expression | Rich layers and texture |
| Examples | Moog Minimoog, Korg Monotron | Yamaha DX7, Roland Juno-106 |
Understanding Monophonic and Polyphonic Synths
Monophonic synths produce a single note at a time, making them ideal for basslines and lead melodies with a clear, focused sound. Polyphonic synths can play multiple notes simultaneously, allowing for rich chords and complex harmonies essential in layered compositions. Understanding the difference between monophonic and polyphonic synths helps musicians choose the right tool for their desired musical texture and expression.
Core Differences Between Monophonic and Polyphonic Synths
Monophonic synths produce one note at a time, making them ideal for basslines and lead melodies with expressive pitch bends and slides. Polyphonic synths can play multiple notes simultaneously, allowing complex chords and rich harmonies essential for lush pads and intricate arrangements. The core difference lies in voice allocation, where monophonic synths use a single oscillator patch while polyphonic synths deploy multiple oscillator voices to enable layered sounds.
Key Features of Monophonic Synthesizers
Monophonic synthesizers generate sound one note at a time, which allows precise control over pitch, modulation, and articulation for lead and bass lines. They feature simpler signal paths with a single oscillator, filter, and envelope generator, making them ideal for creating expressive, dynamic tones with pitch bends and portamento effects. These synths often include features like glide, filter resonance, and analog warmth that appeal to electronic, rock, and experimental musicians.
Advantages and Limitations of Polyphonic Synthesizers
Polyphonic synthesizers enable musicians to play multiple notes simultaneously, allowing for richer chords and complex harmonies that enhance musical expression. Their advantage lies in versatility, especially in genres requiring layered textures, but they often have higher costs and increased complexity compared to monophonic synths. Limitations include restricted voice counts per model, which can lead to voice-stealing when exceeding polyphony limits, and potentially increased CPU or hardware resource consumption in digital units.
Sound Design Capabilities: Mono vs Poly Synths
Monophonic synths excel in sound design by allowing precise control over a single note, ideal for crafting intricate basslines and lead sounds with detailed modulation. Polyphonic synths enable multiple notes to be played simultaneously, offering rich harmonic textures and complex chord progressions essential for layered musical arrangements. The choice between mono and poly synths significantly impacts sound design flexibility, with monophonics favoring detailed articulation and polyphonics supporting harmonic density.
Ideal Music Genres for Monophonic vs Polyphonic Synths
Monophonic synths excel in genres like techno, bass music, and funk due to their ability to produce thick, expressive basslines and leads with precise control over each note. Polyphonic synths are ideal for genres such as jazz, pop, and ambient music where rich chord progressions and layered pads create complex harmonic textures. The choice between monophonic and polyphonic synthesizers significantly impacts sound design, influencing a track's melodic and harmonic depth.
Popular Monophonic Synth Models
Popular monophonic synth models like the Moog Minimoog Model D and the Korg MS-20 offer distinct advantages for basslines and lead sounds due to their single-note focus. These synths excel at producing thick, powerful tones with rich analog warmth, often preferred in electronic, funk, and rock music. Their simple architecture allows precise control over envelopes and filters, making them favorites among sound designers and performers seeking expressive, cutting-edge timbres.
Top-Rated Polyphonic Synthesizers
Top-rated polyphonic synthesizers such as the Sequential Prophet-6, Yamaha Montage, and Korg Kronos offer rich, multi-voice capabilities that enable complex chord progressions and layered textures unattainable with monophonic synths. Their advanced digital and analog hybrid architectures provide enhanced modulation options, high-quality sound engines, and extensive MIDI compatibility for live performance and studio production. These instruments are favored by professional musicians seeking versatile sound design and expansive sonic palettes.
Choosing the Right Synth for Your Musical Needs
Monophonic synthesizers produce one note at a time, ideal for bass lines and lead melodies, offering tight control over sound modulation and expressiveness. Polyphonic synthesizers can play multiple notes simultaneously, making them suitable for chords, complex harmonies, and rich textures in music production. Choosing the right synth depends on your musical style, whether you prioritize melodic simplicity with unique sound design or layered arrangements and harmonic complexity.
Monophonic vs Polyphonic Synths: Summary and Recommendations
Monophonic synthesizers produce one note at a time, ideal for basslines, leads, and solos due to their simplicity and pitch control. Polyphonic synthesizers allow multiple notes simultaneously, making them suitable for chords, pads, and complex arrangements in modern music production. For beginners, monophonic synths offer straightforward learning and sound design, while polyphonic synths provide greater versatility for advanced players seeking rich harmonic textures.
Monophonic synth vs Polyphonic synth Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com