A MIDI controller sends digital signals to external devices or software, allowing users to manipulate sounds without generating audio on its own. Synthesizers create sounds internally through analog or digital circuits, providing autonomous sound design capabilities. Choosing between a MIDI controller and a synthesizer depends on whether you need flexible control over virtual instruments or standalone sound synthesis.
Table of Comparison
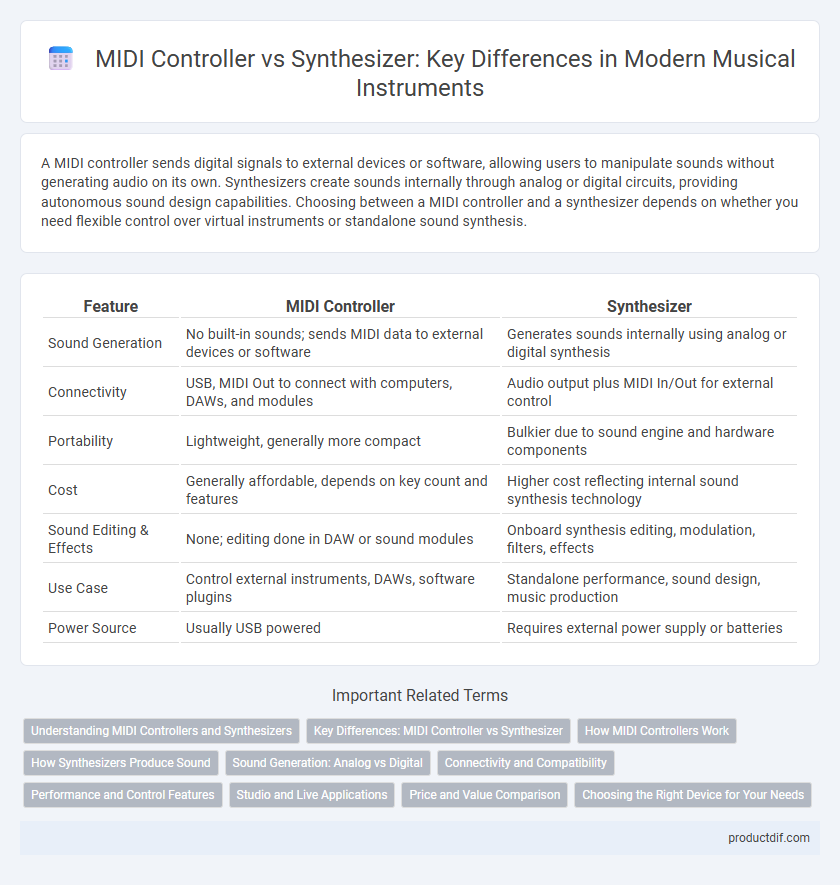
| Feature | MIDI Controller | Synthesizer |
|---|---|---|
| Sound Generation | No built-in sounds; sends MIDI data to external devices or software | Generates sounds internally using analog or digital synthesis |
| Connectivity | USB, MIDI Out to connect with computers, DAWs, and modules | Audio output plus MIDI In/Out for external control |
| Portability | Lightweight, generally more compact | Bulkier due to sound engine and hardware components |
| Cost | Generally affordable, depends on key count and features | Higher cost reflecting internal sound synthesis technology |
| Sound Editing & Effects | None; editing done in DAW or sound modules | Onboard synthesis editing, modulation, filters, effects |
| Use Case | Control external instruments, DAWs, software plugins | Standalone performance, sound design, music production |
| Power Source | Usually USB powered | Requires external power supply or batteries |
Understanding MIDI Controllers and Synthesizers
MIDI controllers transmit digital signals to external sound modules or software, allowing musicians to control virtual instruments without generating sound independently. Synthesizers produce audio directly by generating and shaping sound waves through oscillators, filters, and envelopes within the hardware or software. Understanding the fundamental difference helps users choose between MIDI controllers for versatility in digital setups and synthesizers for hands-on sound design and audio generation.
Key Differences: MIDI Controller vs Synthesizer
MIDI controllers send digital signals to software or external hardware, providing no sound on their own, while synthesizers generate audio signals internally using oscillators and filters. Synthesizers often include built-in sound engines for standalone performance, whereas MIDI controllers require connection to a computer or sound module. The tactile control of MIDI keyboards focuses on input versatility, whereas synthesizers offer direct sound design capabilities.
How MIDI Controllers Work
MIDI controllers generate digital signals through button presses, knobs, and keys that send MIDI data to external sound modules or software instruments, enabling precise and versatile control over musical parameters. Unlike synthesizers, which produce sound internally, MIDI controllers rely on connected hardware or software synthesizers to generate audio, offering flexibility in sound design. These devices communicate via MIDI protocols to manipulate pitch, velocity, modulation, and other expressive elements during music production and live performance.
How Synthesizers Produce Sound
Synthesizers generate sound by electronically creating and manipulating waveforms through oscillators, filters, and amplifiers. Unlike MIDI controllers that send performance data, synthesizers directly produce audio signals using voltage-controlled or digital components. The unique timbres of synthesizers arise from shaping raw waveforms with modulation sources such as envelopes and low-frequency oscillators (LFOs).
Sound Generation: Analog vs Digital
MIDI controllers do not generate sound themselves; they send digital signals to external devices or software that produce audio, allowing flexible control over a wide range of synthesizers and sound modules. Synthesizers, on the other hand, directly generate sound either through analog circuitry, which produces warm and rich tones via voltage-controlled oscillators and filters, or digital methods that use complex algorithms and sampling for diverse, precise sound design. Understanding the difference between analog synthesis's organic sound character and digital synthesis's versatility helps musicians choose the right instrument for their production needs.
Connectivity and Compatibility
MIDI controllers offer extensive connectivity options, including USB, traditional 5-pin MIDI ports, and wireless Bluetooth compatibility, enabling seamless integration with a wide range of digital audio workstations and software instruments. Synthesizers typically feature built-in sound engines with multiple output formats, such as audio jacks, CV/Gate, and sometimes MIDI, providing versatility for both studio and live performance environments. Compatibility is broader for MIDI controllers as they serve as input devices controlling external sound modules, while synthesizers function as standalone instruments with embedded sound generation.
Performance and Control Features
MIDI controllers provide extensive performance and control features by allowing users to manipulate multiple software instruments with customizable knobs, pads, and faders, enhancing expressive playability. Synthesizers combine sound generation with tactile controls like oscillators, filters, and envelopes, offering immediate hands-on sound design and performance capabilities. While MIDI controllers rely on external sound modules, synthesizers deliver integrated sound creation and real-time modulation for dynamic musical expression.
Studio and Live Applications
MIDI controllers excel in studio and live applications by offering versatile control over virtual instruments and software synthesizers without generating sound independently. Synthesizers provide rich, built-in sound engines essential for live performance and studio production, delivering hands-on sound design and immediate auditory feedback. Combining a MIDI controller with a synthesizer enhances flexibility and creative potential across diverse musical setups.
Price and Value Comparison
MIDI controllers typically offer a more budget-friendly option, with prices ranging from $50 to $500, providing versatile control over various software instruments without built-in sound engines. Synthesizers generally cost between $300 and $3,000, delivering comprehensive sound design capabilities and onboard synthesis that add intrinsic value for musicians focused on hardware-generated tones. Choosing between the two depends on balancing initial investment against desired functionality and production workflow.
Choosing the Right Device for Your Needs
Choosing between a MIDI controller and a synthesizer depends on your production setup and sound design preferences. MIDI controllers offer versatile control over software instruments and digital audio workstations without generating sound independently, making them ideal for studio workflows that rely on virtual instruments. Synthesizers produce sound internally with built-in oscillators and filters, perfect for musicians seeking hands-on analog or digital tone creation and live performance capabilities.
MIDI controller vs Synthesizer Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com