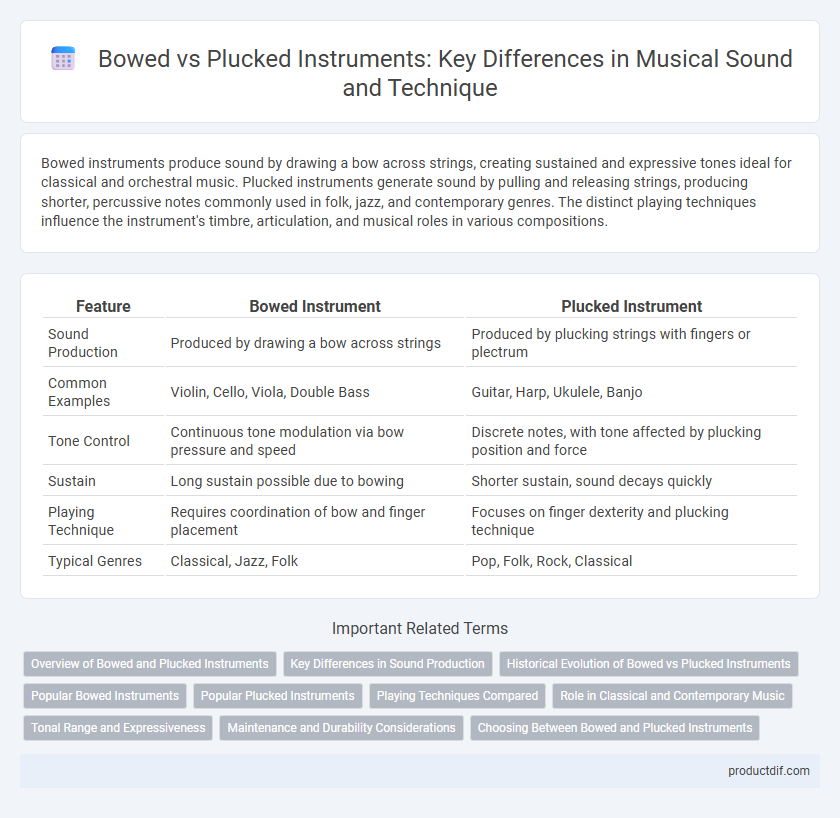
Bowed instruments produce sound by drawing a bow across strings, creating sustained and expressive tones ideal for classical and orchestral music. Plucked instruments generate sound by pulling and releasing strings, producing shorter, percussive notes commonly used in folk, jazz, and contemporary genres. The distinct playing techniques influence the instrument's timbre, articulation, and musical roles in various compositions.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Bowed Instrument | Plucked Instrument |
|---|---|---|
| Sound Production | Produced by drawing a bow across strings | Produced by plucking strings with fingers or plectrum |
| Common Examples | Violin, Cello, Viola, Double Bass | Guitar, Harp, Ukulele, Banjo |
| Tone Control | Continuous tone modulation via bow pressure and speed | Discrete notes, with tone affected by plucking position and force |
| Sustain | Long sustain possible due to bowing | Shorter sustain, sound decays quickly |
| Playing Technique | Requires coordination of bow and finger placement | Focuses on finger dexterity and plucking technique |
| Typical Genres | Classical, Jazz, Folk | Pop, Folk, Rock, Classical |
Overview of Bowed and Plucked Instruments
Bowed instruments produce sound by drawing a bow across strings, creating continuous vibrations that allow for sustained tones and expressive dynamics, common in violins, cellos, and violas. Plucked instruments generate sound by directly pulling or striking strings with fingers or a plectrum, resulting in distinct, percussive notes found in guitars, harps, and banjos. The primary difference lies in the method of sound production, with bowed instruments favoring sustained notes and plucked instruments providing rhythmic articulation.
Key Differences in Sound Production
Bowed instruments produce sound by drawing a bow across strings, causing continuous vibration that creates sustained, smooth tones, while plucked instruments generate sound by pulling and releasing strings, resulting in shorter, more percussive sounds. The bow's friction creates variable dynamics and expressive control in bowed instruments like the violin and cello, whereas plucked instruments such as the guitar and harp emphasize attack and decay characteristics from the initial pluck. These fundamental differences in sound production techniques lead to distinct timbral qualities and performance styles within orchestras and ensembles.
Historical Evolution of Bowed vs Plucked Instruments
Bowed instruments originated around 500 AD with early forms such as the rebab, evolving through the medieval period into modern violins and cellos, while plucked instruments like the lute and harp trace back to ancient Mesopotamia and Egypt. The medieval and Renaissance eras saw significant advancements in bowed instrument construction, enhancing sustain and expressiveness, whereas plucked instruments developed diverse forms adapted for accompaniment and solo performance. The contrasting playing techniques influenced musical styles and compositions, cementing bowed instruments in orchestral settings and plucked instruments in folk and chamber music traditions.
Popular Bowed Instruments
Popular bowed instruments such as the violin, viola, cello, and double bass dominate orchestral and classical music due to their rich tonal qualities and expressive capabilities. These string instruments produce sound by drawing a horsehair bow across their strings, enabling sustained tones and dynamic articulation that plucked instruments cannot achieve. While plucked instruments like the guitar and harp offer distinct timbres and percussive effects, bowed instruments remain essential for achieving emotive depth and continuous sound in musical compositions.
Popular Plucked Instruments
Popular plucked instruments include the guitar, harp, and banjo, which produce sound by pulling and releasing strings. These instruments offer diverse tonal qualities and are prevalent in various music genres such as folk, rock, and classical. Their portability and ease of play contribute to widespread use across cultures worldwide.
Playing Techniques Compared
Bowed instruments produce sound by drawing a bow strung with horsehair across the strings, generating continuous vibrations that allow for sustained notes and dynamic expressiveness. Plucked instruments create sound by plucking the strings with fingers or a plectrum, resulting in a more percussive and detached tone with quicker decay. Techniques for bowed instruments include vibrato and legato bowing, while plucked instruments emphasize techniques such as fingerpicking, strumming, and harmonics.
Role in Classical and Contemporary Music
Bowed instruments, such as the violin and cello, play a critical role in classical music by providing sustained, expressive melodies and rich harmonic textures essential to orchestral and chamber compositions. Plucked instruments like the guitar and harp are pivotal in both classical and contemporary music, offering rhythmic complexity and distinctive tonal colors that enhance solo and ensemble performances. The contrasting sound production techniques of bowed versus plucked instruments contribute uniquely to the emotional and dynamic range across diverse musical genres.
Tonal Range and Expressiveness
Bowed instruments like violins and cellos produce a wide tonal range through continuous vibration of strings, allowing for smooth dynamic shifts and sustained, expressive sound. Plucked instruments such as guitars and harps generate distinct, percussive tones with quicker decay, limiting sustained expressiveness but offering precise articulation. The tonal versatility and emotive control of bowed instruments often surpass those of plucked instruments, making them ideal for nuanced musical expression.
Maintenance and Durability Considerations
Bowed instruments require regular maintenance such as rehairing the bow, cleaning the fingerboard, and frequent string replacement due to constant friction, which affects their durability. Plucked instruments typically demand less frequent maintenance but need occasional tuning, string replacement, and care for the instrument's body to prevent cracks caused by environmental changes. Durability of bowed instruments tends to be lower because of their delicate components like horsehair bows, while plucked instruments often withstand harsher conditions with proper care.
Choosing Between Bowed and Plucked Instruments
Choosing between bowed and plucked instruments depends on the desired sound texture and musical style. Bowed instruments, such as violins and cellos, produce continuous, sustained tones ideal for expressive melodies and dynamic variations. Plucked instruments like guitars and harps create crisp, rhythmic articulation suited for harmonic accompaniment and percussive effects.
Bowed instrument vs Plucked instrument Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com