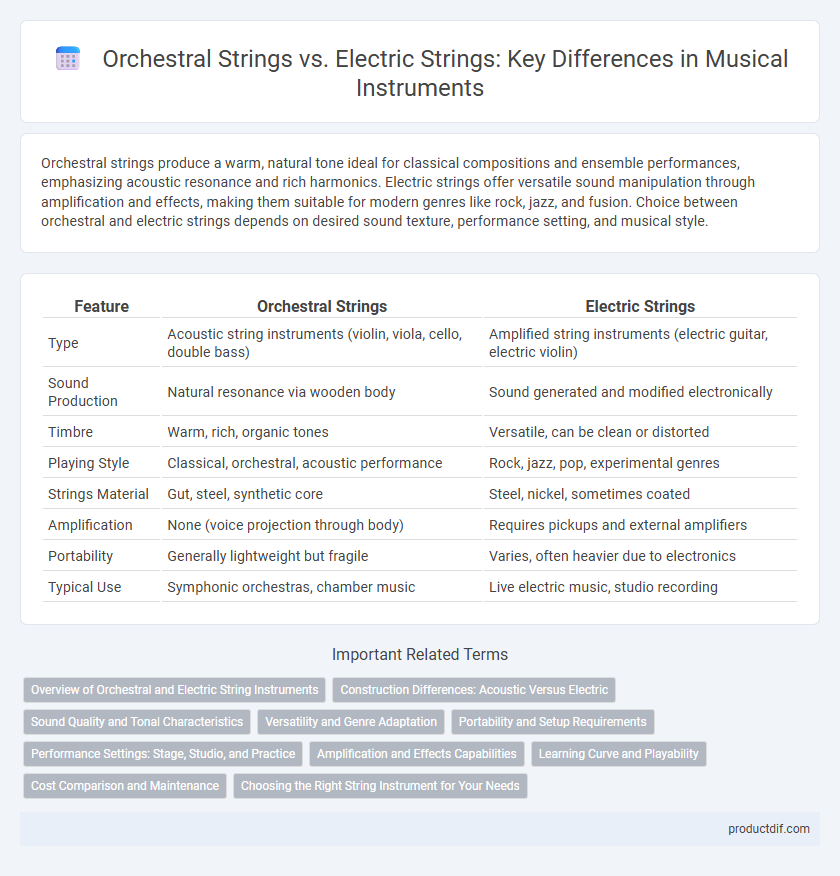
Orchestral strings produce a warm, natural tone ideal for classical compositions and ensemble performances, emphasizing acoustic resonance and rich harmonics. Electric strings offer versatile sound manipulation through amplification and effects, making them suitable for modern genres like rock, jazz, and fusion. Choice between orchestral and electric strings depends on desired sound texture, performance setting, and musical style.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Orchestral Strings | Electric Strings |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Acoustic string instruments (violin, viola, cello, double bass) | Amplified string instruments (electric guitar, electric violin) |
| Sound Production | Natural resonance via wooden body | Sound generated and modified electronically |
| Timbre | Warm, rich, organic tones | Versatile, can be clean or distorted |
| Playing Style | Classical, orchestral, acoustic performance | Rock, jazz, pop, experimental genres |
| Strings Material | Gut, steel, synthetic core | Steel, nickel, sometimes coated |
| Amplification | None (voice projection through body) | Requires pickups and external amplifiers |
| Portability | Generally lightweight but fragile | Varies, often heavier due to electronics |
| Typical Use | Symphonic orchestras, chamber music | Live electric music, studio recording |
Overview of Orchestral and Electric String Instruments
Orchestral string instruments, including the violin, viola, cello, and double bass, feature hollow wooden bodies designed for acoustic resonance and traditional bowing techniques. Electric string instruments such as electric violins and electric cellos utilize built-in pickups and amplification to produce sound, allowing for greater versatility in tone and effects. The key difference lies in their sound production methods, with orchestral strings relying on natural acoustics while electric strings depend on electronic amplification and sound modification.
Construction Differences: Acoustic Versus Electric
Orchestral strings, such as violins, violas, cellos, and double basses, are constructed with hollow wooden bodies designed to amplify sound acoustically through natural resonance chambers. Electric strings incorporate solid or semi-hollow bodies with magnetic or piezoelectric pickups that convert string vibrations into electrical signals for amplification. The materials and build of acoustic strings focus on enhancing organic sound projection, whereas electric strings emphasize electronic sound modification and amplification capabilities.
Sound Quality and Tonal Characteristics
Orchestral strings produce a rich, warm, and natural sound characterized by complex overtones and dynamic expressiveness, ideal for classical and acoustic genres. Electric strings offer a brighter, more focused tone with enhanced sustain and versatility, often manipulated through amplification and effects to suit various modern music styles. The choice between orchestral and electric strings depends on the desired tonal color and sound quality, with orchestral driving organic warmth and electric enabling sonic experimentation.
Versatility and Genre Adaptation
Orchestral strings, such as violins, violas, cellos, and double basses, offer rich tonal warmth and dynamic expressiveness suited for classical, film scores, and chamber music genres. Electric strings, including electric violins and electric cellos, provide versatile sound modification options through effects pedals and amplification, making them ideal for rock, jazz, pop, and experimental music. The adaptability of electric strings to various tones and styles surpasses traditional orchestral strings, enabling musicians to explore a broader genre spectrum with ease.
Portability and Setup Requirements
Orchestral strings, such as violins and cellos, often require careful handling, larger cases, and specific bows, making them less portable and demanding more setup time for tuning and rosin application. Electric strings, like electric violins and guitars, are typically compact, lighter, and designed for easier transport with onboard electronics that streamline setup through plug-and-play amplification. Musicians seeking convenience and quick readiness prefer electric strings, while traditionalists value the acoustic richness despite the complex setup of orchestral strings.
Performance Settings: Stage, Studio, and Practice
Orchestral strings deliver warm, natural tones ideal for stage performances and studio recordings where acoustic resonance is prized, while electric strings offer versatility and amplified sound suited for live concerts and versatile studio work. In practice settings, orchestral strings require controlled environments to maintain sound quality, whereas electric strings allow for headphone use and volume control, accommodating varied practice conditions. The choice between these strings often depends on the desired sound character and performance context, influencing musician preference and technical setup.
Amplification and Effects Capabilities
Orchestral strings rely on acoustic resonance for natural amplification, producing rich, warm tones without electronic enhancement. Electric strings incorporate built-in pickups that enable direct amplification and seamless integration with effects pedals and processors, allowing for versatile sound modulation. This electronic capability expands creative possibilities, making electric strings ideal for genres requiring dynamic sound alteration and volume control.
Learning Curve and Playability
Orchestral strings, such as violin and cello, have a steeper learning curve due to their reliance on precise finger placement, bowing techniques, and acoustic resonance control. Electric strings, including electric violin and electric bass, offer enhanced playability with features like adjustable volume and tone, solid-body construction reducing feedback, and easier integration with effects, making them more accessible for beginners and performers exploring diverse genres. Mastery of orchestral strings demands disciplined practice to develop nuanced dynamics, whereas electric strings provide more immediate sound manipulation with electronic amplification.
Cost Comparison and Maintenance
Orchestral strings, typically made from natural gut or steel, tend to be more expensive initially and require frequent tuning and occasional replacement due to sensitivity to humidity and wear. Electric strings, often composed of durable nickel or stainless steel alloys, offer a more cost-effective solution with longer lifespans and reduced maintenance needs, as they are less affected by environmental changes. Choosing between the two depends on budget considerations and the player's willingness to invest time and resources into upkeep.
Choosing the Right String Instrument for Your Needs
Orchestral strings, including violin, viola, cello, and double bass, offer rich acoustic tones ideal for classical, chamber, and orchestral music, emphasizing organic resonance and dynamic expression. Electric strings, such as electric violins and electric cellos, provide amplified sound versatility, equipped with pickups and effects that suit contemporary genres and stage performance. Selecting the right string instrument depends on musical style, performance environment, and desired sound output, balancing traditional acoustic warmth with modern amplification options.
Orchestral strings vs Electric strings Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com