Active electronics in musical instruments use powered components such as preamps and equalizers, offering greater tone shaping and boosted signal output. Passive electronics rely solely on the instrument's natural pickups and passive components, delivering a more organic and vintage sound with less tonal coloration. Musicians often choose active electronics for versatility and clarity, while passive systems are favored for their simplicity and traditional warmth.
Table of Comparison
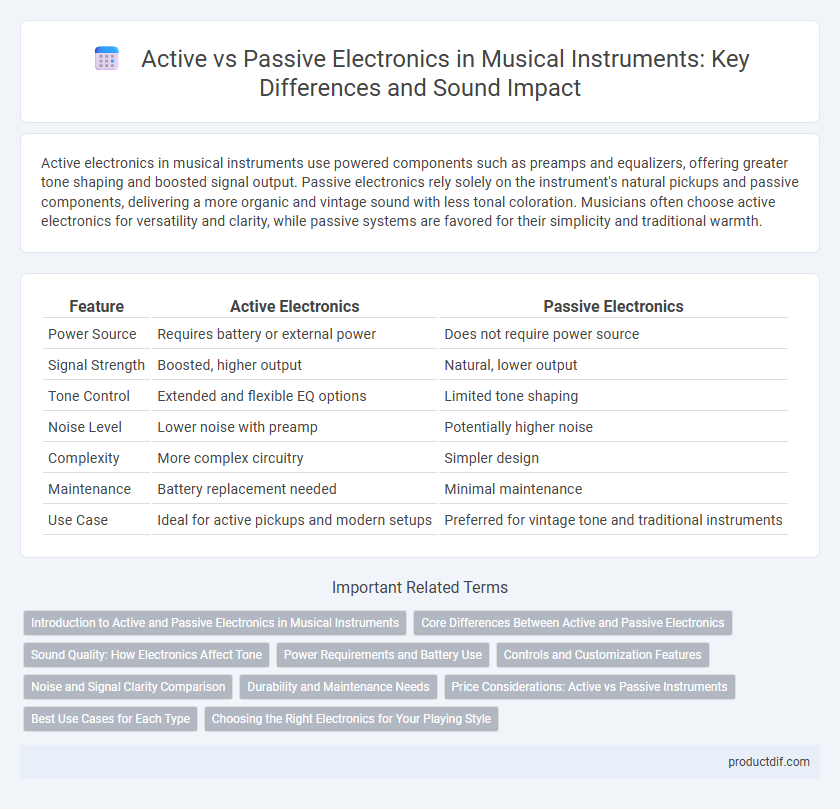
| Feature | Active Electronics | Passive Electronics |
|---|---|---|
| Power Source | Requires battery or external power | Does not require power source |
| Signal Strength | Boosted, higher output | Natural, lower output |
| Tone Control | Extended and flexible EQ options | Limited tone shaping |
| Noise Level | Lower noise with preamp | Potentially higher noise |
| Complexity | More complex circuitry | Simpler design |
| Maintenance | Battery replacement needed | Minimal maintenance |
| Use Case | Ideal for active pickups and modern setups | Preferred for vintage tone and traditional instruments |
Introduction to Active and Passive Electronics in Musical Instruments
Active electronics in musical instruments utilize powered components such as preamps and equalizers to boost and shape the audio signal, providing greater tonal versatility and higher output levels. Passive electronics rely solely on the instrument's pickups and passive components like tone and volume controls, preserving the natural sound without the need for an external power source. Understanding the differences between active and passive systems helps musicians choose the right electronics based on their desired sound characteristics and performance requirements.
Core Differences Between Active and Passive Electronics
Active electronics in musical instruments contain built-in preamps and require a power source, enabling signal boosting and tone shaping directly within the instrument. Passive electronics rely solely on magnets and coils, producing a natural, unaltered signal without the need for batteries or external power. The core difference lies in active systems offering enhanced output and tonal versatility, while passive systems provide simplicity and traditional sound characteristics.
Sound Quality: How Electronics Affect Tone
Active electronics in musical instruments use powered circuits to boost and shape the signal, resulting in a clearer, more defined tone with greater control over EQ settings. Passive electronics rely on the natural signal from the pickups and strings, producing a warmer, more organic sound but with less tonal flexibility. The choice between active and passive electronics significantly influences the overall sound quality and tonal characteristics of the instrument.
Power Requirements and Battery Use
Active electronics in musical instruments require external power sources, typically batteries, to operate preamps and provide consistent signal amplification, enhancing tonal control and output level. Passive electronics, conversely, function without batteries, relying solely on the natural electromagnetic induction of pickups, resulting in simpler wiring and maintenance-free performance but with less tonal versatility. Battery use in active systems necessitates regular replacement or recharging, impacting instrument reliability during extended playing sessions.
Controls and Customization Features
Active electronics in musical instruments feature built-in preamps and equalizers, offering enhanced signal control and broader tonal customization through onboard controls like bass, mid, and treble knobs. Passive electronics rely on traditional pickups and simple tone and volume controls, providing a more organic sound but limited adjustment options. Musicians seeking precise sound shaping prefer active systems, while those favoring vintage or raw tones often choose passive setups.
Noise and Signal Clarity Comparison
Active electronics in musical instruments typically offer greater signal clarity due to built-in preamps that boost the signal and reduce noise interference. Passive electronics rely on the natural properties of pickups and often generate more hum and signal degradation, especially with long cable runs. Musicians seeking a cleaner, noise-free output generally prefer active systems for improved tonal precision and dynamic range.
Durability and Maintenance Needs
Active electronics in musical instruments typically offer enhanced durability due to built-in preamps and batteries, but they require regular battery replacement and careful handling to avoid damage from power issues. Passive electronics are generally more robust with fewer maintenance demands, as they lack internal power sources and rely on simpler circuitry. Musicians seeking low-maintenance setups often prefer passive electronics for their longevity and reliability under various performance conditions.
Price Considerations: Active vs Passive Instruments
Active electronics in musical instruments generally increase the price due to integrated preamps and batteries, offering enhanced tonal control and signal strength. Passive electronics are more cost-effective, relying solely on magnets and wire without external power, resulting in simpler maintenance and lower initial costs. Choosing between active and passive setups depends on budget constraints and desired sound versatility for musicians.
Best Use Cases for Each Type
Active electronics, equipped with built-in preamps and powered components, excel in electric guitars and basses requiring higher output, consistent tone, and enhanced signal clarity, making them ideal for genres like rock, metal, and jazz fusion. Passive electronics, characterized by their simplicity and absence of onboard power, deliver a natural, warm sound preferred for blues, classic rock, and vintage-style instruments. Guitarists choosing active setups benefit from noise reduction and greater tonal control, while passive systems offer dynamic range and organic responsiveness favored in traditional playing styles.
Choosing the Right Electronics for Your Playing Style
Active electronics in musical instruments use powered circuits, offering greater tonal versatility, higher output, and noise reduction, ideal for genres requiring dynamic sound shaping like rock or jazz. Passive electronics rely solely on the instrument's natural pickups and tone controls, producing vintage warmth and organic tone preferred in blues or classic rock. Selecting the right electronics depends on your playing style: active systems suit modern, high-gain setups, while passive circuits favor traditional, expressive performances.
Active electronics vs Passive electronics Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com