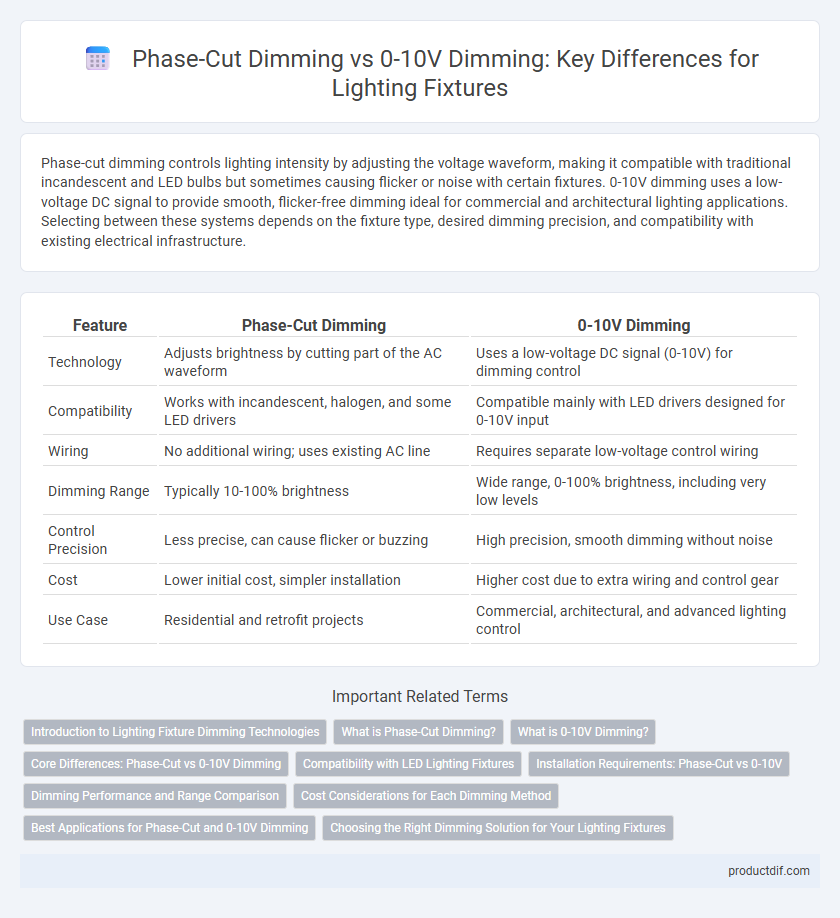
Phase-cut dimming controls lighting intensity by adjusting the voltage waveform, making it compatible with traditional incandescent and LED bulbs but sometimes causing flicker or noise with certain fixtures. 0-10V dimming uses a low-voltage DC signal to provide smooth, flicker-free dimming ideal for commercial and architectural lighting applications. Selecting between these systems depends on the fixture type, desired dimming precision, and compatibility with existing electrical infrastructure.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Phase-Cut Dimming | 0-10V Dimming |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | Adjusts brightness by cutting part of the AC waveform | Uses a low-voltage DC signal (0-10V) for dimming control |
| Compatibility | Works with incandescent, halogen, and some LED drivers | Compatible mainly with LED drivers designed for 0-10V input |
| Wiring | No additional wiring; uses existing AC line | Requires separate low-voltage control wiring |
| Dimming Range | Typically 10-100% brightness | Wide range, 0-100% brightness, including very low levels |
| Control Precision | Less precise, can cause flicker or buzzing | High precision, smooth dimming without noise |
| Cost | Lower initial cost, simpler installation | Higher cost due to extra wiring and control gear |
| Use Case | Residential and retrofit projects | Commercial, architectural, and advanced lighting control |
Introduction to Lighting Fixture Dimming Technologies
Phase-cut dimming, commonly used with incandescent and halogen fixtures, adjusts brightness by altering the voltage waveform through leading or trailing edge cutting, providing smooth dimming without additional wiring. In contrast, 0-10V dimming employs a low-voltage control signal ranging from 0 to 10 volts that adjusts LED and fluorescent fixtures' light levels, offering precise and flicker-free dimming suited for modern lighting systems. Understanding these technologies is crucial for selecting compatible dimmers and fixtures to achieve energy efficiency and desired ambiance in lighting design.
What is Phase-Cut Dimming?
Phase-cut dimming controls light intensity by altering the voltage waveform supplied to the fixture, typically by cutting part of the AC waveform using TRIAC or MOSFET dimmers. This method is commonly used with incandescent, halogen, and compatible LED lamps, providing smooth dimming without the need for additional wiring. Phase-cut dimmers are categorized into leading-edge and trailing-edge types, each optimized for specific lamp technologies to reduce flicker and extend lamp life.
What is 0-10V Dimming?
0-10V dimming is a widely used analog dimming method for lighting fixtures that adjusts brightness by varying a control voltage between 0 and 10 volts. When the voltage is at 10V, the light operates at full brightness, while at 0V, the fixture dims to its lowest level or turns off. This dimming technique offers smooth, flicker-free control suitable for commercial and architectural lighting systems.
Core Differences: Phase-Cut vs 0-10V Dimming
Phase-cut dimming modulates voltage by cutting portions of the AC waveform, making it compatible with traditional incandescent and some LED fixtures, while 0-10V dimming uses a low-voltage DC control signal to adjust brightness, offering precise, flicker-free control commonly used in commercial LED installations. Phase-cut dimmers typically handle line voltage and rely on leading-edge or trailing-edge technology, whereas 0-10V systems require separate control wiring and offer smoother dimming curves. Understanding these core differences is crucial for specifying compatible lighting fixtures and controls to achieve optimal performance and energy efficiency.
Compatibility with LED Lighting Fixtures
Phase-cut dimming is widely compatible with many LED lighting fixtures due to its ability to adjust voltage by cutting a portion of the AC waveform, making it suitable for retrofit applications where traditional dimmers exist. In contrast, 0-10V dimming offers precise and flicker-free control by varying a low-voltage DC signal, which is highly compatible with modern LED fixtures designed specifically for digital dimming. Selecting the appropriate dimming method depends on the LED driver's specifications and the desired dimming performance in terms of smoothness and range.
Installation Requirements: Phase-Cut vs 0-10V
Phase-cut dimming requires compatible LED drivers and typically integrates directly with existing AC wiring, simplifying installation but limiting compatibility with certain fixtures. In contrast, 0-10V dimming necessitates a separate low-voltage control wiring between the dimmer and driver, demanding more complex installation but offering precise dimming control across a wider range of lighting products. Proper understanding of wiring protocols and driver compatibility is essential to ensure optimal performance and compliance with electrical standards during installation.
Dimming Performance and Range Comparison
Phase-cut dimming offers smooth dimming performance with a typical range from 10% to 100%, ideal for incandescent and compatible LED fixtures, providing flicker-free operation at lower brightness levels. In contrast, 0-10V dimming delivers the widest dimming range from 1% to 100%, allowing precise control and compatibility with a broader array of LED drivers, but may require additional wiring and can exhibit minor flickering at very low levels. Both methods support energy savings and ambiance control, but 0-10V dimming generally outperforms phase-cut in terms of dimming granularity and lower minimum light output.
Cost Considerations for Each Dimming Method
Phase-cut dimming often has lower installation costs due to compatibility with existing wiring and simpler control components. In contrast, 0-10V dimming systems typically incur higher upfront expenses because of dedicated wiring requirements and separate dimmer modules. Long-term maintenance costs for 0-10V may be lower, as this method provides finer dimming control and reduced flicker, potentially extending fixture lifespan.
Best Applications for Phase-Cut and 0-10V Dimming
Phase-cut dimming is ideal for residential and retrofit applications where compatibility with existing incandescent or halogen fixtures is prioritized, delivering smooth, flicker-free dimming with standard wiring. 0-10V dimming excels in commercial and architectural lighting setups requiring precise, scalable control across multiple fixtures, supporting integration with advanced building management systems. Selecting between phase-cut and 0-10V dimming hinges on the specific lighting environment, fixture type, and control sophistication needed.
Choosing the Right Dimming Solution for Your Lighting Fixtures
Phase-cut dimming is ideal for incandescent and compatible LED fixtures, offering seamless integration with existing wall dimmers and simpler installation. 0-10V dimming provides precise brightness control for commercial LED systems, enabling smooth dimming from 100% to as low as 1%, making it suitable for advanced lighting setups requiring scalable control. Selecting the right dimming solution depends on fixture compatibility, control complexity, and desired dimming range to ensure optimal performance and energy efficiency.
Phase-cut dimming vs 0-10V dimming Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com