Low voltage lighting operates at 12 volts, providing enhanced safety and energy efficiency, making it ideal for outdoor pet areas and delicate spaces. Line voltage lighting uses the standard 120 volts, offering easier installation without transformers but can pose higher risks for pets due to its stronger electrical current. Choosing between low voltage and line voltage lighting depends on balancing safety, installation complexity, and energy consumption in pet-friendly environments.
Table of Comparison
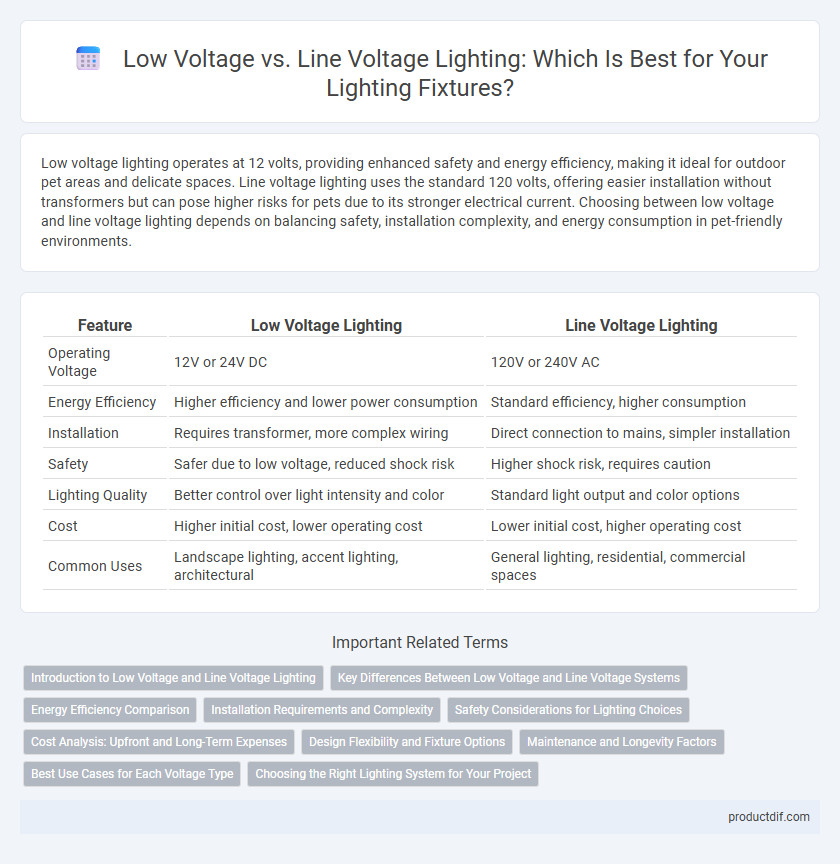
| Feature | Low Voltage Lighting | Line Voltage Lighting |
|---|---|---|
| Operating Voltage | 12V or 24V DC | 120V or 240V AC |
| Energy Efficiency | Higher efficiency and lower power consumption | Standard efficiency, higher consumption |
| Installation | Requires transformer, more complex wiring | Direct connection to mains, simpler installation |
| Safety | Safer due to low voltage, reduced shock risk | Higher shock risk, requires caution |
| Lighting Quality | Better control over light intensity and color | Standard light output and color options |
| Cost | Higher initial cost, lower operating cost | Lower initial cost, higher operating cost |
| Common Uses | Landscape lighting, accent lighting, architectural | General lighting, residential, commercial spaces |
Introduction to Low Voltage and Line Voltage Lighting
Low voltage lighting operates typically at 12 volts and requires a transformer to step down the standard 120-volt line voltage, making it ideal for landscape and accent lighting due to its energy efficiency and safety. Line voltage lighting runs directly on the household electrical system at 120 volts, providing brighter illumination and compatibility with existing fixtures without the need for a transformer. Understanding the voltage differences helps in selecting the right lighting solution based on installation complexity, energy consumption, and desired brightness.
Key Differences Between Low Voltage and Line Voltage Systems
Low voltage lighting systems operate typically at 12 volts and require a transformer to step down from the line voltage, offering enhanced energy efficiency and increased safety for residential and landscape applications. Line voltage lighting runs directly at 120 volts or higher, providing a simpler installation process and compatibility with a wide range of standard fixtures, but with higher energy consumption and potential safety risks. Key differences include voltage level, installation complexity, energy efficiency, and typical use cases, making low voltage lighting preferable for detailed, energy-conscious designs while line voltage suits more robust, general-purpose lighting needs.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
Low voltage lighting systems operate at 12 volts, using transformers to reduce energy consumption and minimize heat production, enhancing overall energy efficiency. Line voltage lighting runs directly at 120 volts, often drawing more power and generating higher heat, leading to greater energy loss. Selecting low voltage lighting fixtures typically results in lower electricity bills and improved energy savings for residential and commercial applications.
Installation Requirements and Complexity
Low voltage lighting typically requires a transformer to reduce the standard 120V line voltage to 12V, necessitating careful transformer placement and additional wiring considerations that can increase installation complexity. Line voltage lighting connects directly to the standard electrical system without transformers, allowing for simpler wiring but often requiring adherence to stricter electrical codes and safety standards. Installing low voltage systems demands more planning for voltage drops and compatibility with dimmers, whereas line voltage fixtures generally offer straightforward installation but less flexibility in customization.
Safety Considerations for Lighting Choices
Low voltage lighting operates at 12 volts or less, significantly reducing the risk of electrical shock and making it safer for residential and outdoor installations. Line voltage lighting runs at the standard household voltage of 120 volts, requiring proper insulation and grounding to prevent electrical hazards during installation and use. Choosing low voltage lighting enhances safety by minimizing fire risks and ensuring compliance with electrical codes in sensitive environments.
Cost Analysis: Upfront and Long-Term Expenses
Low voltage lighting fixtures typically have higher upfront costs due to the need for transformers but offer lower energy consumption, reducing long-term electricity expenses. Line voltage lighting systems generally require less initial investment but incur higher operational costs due to greater energy usage. Evaluating the total cost of ownership involves balancing initial installation expenses against ongoing power consumption and maintenance requirements.
Design Flexibility and Fixture Options
Low voltage lighting systems offer greater design flexibility with smaller fixtures and adjustable beam angles, ideal for accent and task lighting in intricate spaces. Line voltage lighting fixtures provide a broader selection of bulbs and fittings, supporting high-intensity output suitable for ambient and general lighting applications. Choosing between low and line voltage depends on desired aesthetic, control options, and compatibility with architectural elements.
Maintenance and Longevity Factors
Low voltage lighting fixtures typically require less maintenance due to their lower heat output, which reduces wear on components and extends bulb life, often lasting up to 25,000 hours. Line voltage lighting systems operate at standard 120V or 240V, generating more heat that can degrade parts faster, necessitating more frequent replacement and maintenance. Choosing low voltage lighting improves longevity and reduces upkeep costs, making it ideal for energy-efficient and durable lighting installations.
Best Use Cases for Each Voltage Type
Low voltage lighting, typically operating at 12 volts, is best suited for accent lighting, landscape illumination, and under-cabinet applications where precise control and energy efficiency are essential. Line voltage lighting, running at standard 120 volts, excels in general room illumination, outdoor security lighting, and locations requiring direct wiring without transformers. Choosing the appropriate voltage type depends on factors such as installation complexity, energy consumption, and desired lighting intensity.
Choosing the Right Lighting System for Your Project
Low voltage lighting operates at 12 volts, offering greater energy efficiency and enhanced safety, making it ideal for residential and landscape projects requiring precise control and softer illumination. Line voltage lighting runs at the standard 120 volts, providing brighter and more powerful lighting suitable for commercial spaces and areas needing high-intensity illumination. Selecting the right lighting system depends on factors such as project scale, required brightness, installation complexity, and budget constraints to ensure optimal performance and energy use.
Low voltage lighting vs Line voltage lighting Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com