Integrated drivers in lighting fixtures offer a compact design by housing the power supply within the fixture, enhancing ease of installation and reducing clutter. External drivers, positioned separately, provide easier access for maintenance and replacement, allowing flexibility in managing heat dissipation and extending fixture lifespan. Choosing between integrated and external drivers depends on installation requirements, maintenance preferences, and overall fixture design considerations.
Table of Comparison
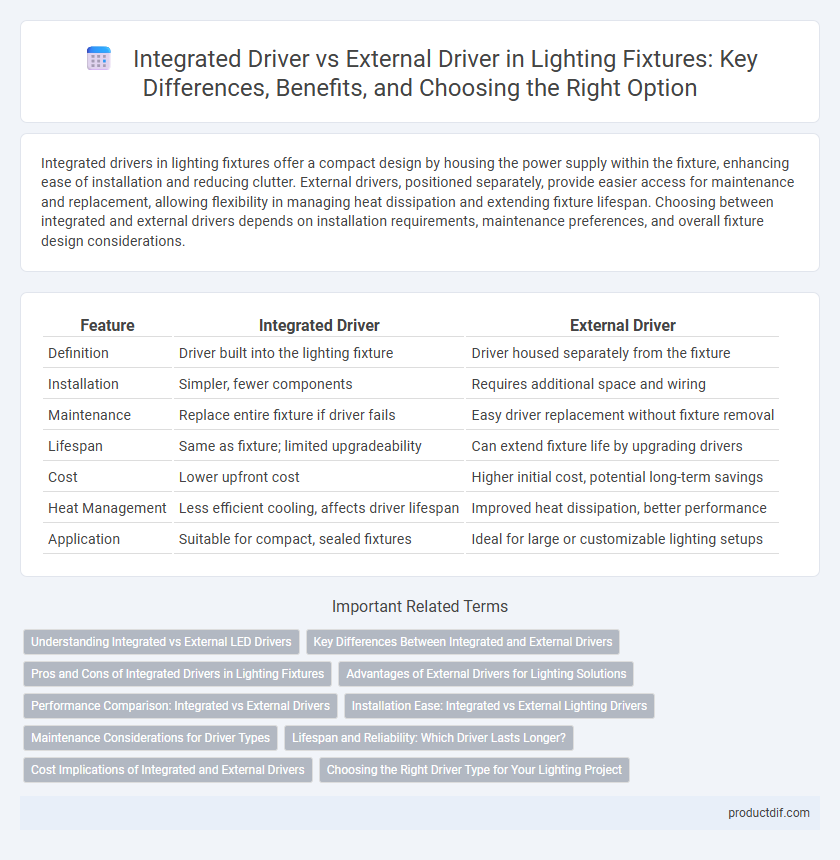
| Feature | Integrated Driver | External Driver |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Driver built into the lighting fixture | Driver housed separately from the fixture |
| Installation | Simpler, fewer components | Requires additional space and wiring |
| Maintenance | Replace entire fixture if driver fails | Easy driver replacement without fixture removal |
| Lifespan | Same as fixture; limited upgradeability | Can extend fixture life by upgrading drivers |
| Cost | Lower upfront cost | Higher initial cost, potential long-term savings |
| Heat Management | Less efficient cooling, affects driver lifespan | Improved heat dissipation, better performance |
| Application | Suitable for compact, sealed fixtures | Ideal for large or customizable lighting setups |
Understanding Integrated vs External LED Drivers
Integrated LED drivers are built directly into the lighting fixture, streamlining installation and reducing space requirements, ideal for compact designs and simpler wiring. External LED drivers operate separately from the fixture, offering easier replacement, enhanced heat dissipation, and greater flexibility for customizing light output and voltage levels. Choosing between integrated and external drivers depends on factors like maintenance accessibility, design constraints, and the specific electrical requirements of the lighting application.
Key Differences Between Integrated and External Drivers
Integrated drivers are built directly into the lighting fixture, offering a compact design and simplified installation, while external drivers are housed separately, allowing for easier maintenance and replacement. Integrated drivers typically result in a sleeker appearance and reduced fixture size, whereas external drivers provide greater heat dissipation and can accommodate higher power loads. The choice between integrated and external drivers impacts overall system reliability, energy efficiency, and installation flexibility for lighting applications.
Pros and Cons of Integrated Drivers in Lighting Fixtures
Integrated drivers in lighting fixtures offer compact design and simplified installation by combining the power supply within the fixture, reducing wiring complexity and saving space. However, integrated drivers can pose challenges in maintenance and replacement since any failure typically requires replacing the entire fixture, leading to higher long-term costs. Their thermal management is also critical, as heat buildup within a single enclosure can affect the lifespan and performance of both the driver and the light source.
Advantages of External Drivers for Lighting Solutions
External drivers for lighting fixtures offer superior heat dissipation, enhancing overall system reliability and longevity by preventing overheating issues common in integrated drivers. They provide greater flexibility in design and maintenance, allowing easy replacement or upgrading without disturbing the entire fixture. Additionally, external drivers often support higher power outputs and better electrical isolation, improving performance in complex lighting installations.
Performance Comparison: Integrated vs External Drivers
Integrated drivers in lighting fixtures offer compact design and reduced installation time, enhancing overall system efficiency. External drivers provide superior heat dissipation and easier maintenance, which can extend the lifespan and reliability of high-performance lighting setups. Performance comparison reveals integrated drivers suit smaller or residential applications, while external drivers are ideal for commercial or industrial environments demanding higher power and thermal management.
Installation Ease: Integrated vs External Lighting Drivers
Integrated lighting drivers streamline installation by reducing wiring complexity and minimizing space requirements within fixtures, offering a more compact and efficient setup. External drivers, while often bulkier and requiring separate mounting space, provide greater flexibility for maintenance and heat management, which can be advantageous in complex or large-scale lighting systems. Choosing between integrated and external drivers depends on the specific project needs, balancing ease of installation with adaptability and serviceability.
Maintenance Considerations for Driver Types
Integrated drivers in lighting fixtures simplify installation and reduce wiring complexity but can complicate maintenance since the entire fixture often requires replacement if the driver fails. External drivers offer easier servicing and replacement without disturbing the fixture, enhancing long-term maintenance efficiency and reducing downtime. Choosing between integrated and external drivers impacts overall maintenance costs, repair speed, and fixture lifespan.
Lifespan and Reliability: Which Driver Lasts Longer?
Integrated drivers in lighting fixtures often have a shorter lifespan compared to external drivers due to increased heat buildup and limited space for proper thermal management. External drivers typically allow for better heat dissipation, resulting in enhanced reliability and longer operational life, often exceeding 50,000 hours. Choosing an external driver can significantly reduce maintenance costs and improve the overall durability of the lighting system.
Cost Implications of Integrated and External Drivers
Integrated drivers generally reduce installation costs by minimizing wiring and simplifying fixture design, leading to lower labor expenses. External drivers may increase upfront costs due to separate housing and additional components but offer easier maintenance and replacement, potentially lowering long-term expenses. Evaluating total cost of ownership involves balancing initial investment against maintenance and energy efficiency benefits for both driver types.
Choosing the Right Driver Type for Your Lighting Project
Choosing the right driver type for your lighting project depends on factors like installation space, maintenance access, and system efficiency. Integrated drivers simplify installation by being built into the lighting fixture, reducing wiring complexity and improving compactness. External drivers offer easier maintenance and heat management, making them ideal for larger or more customizable lighting setups requiring higher power or flexibility.
Integrated driver vs external driver Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com