Downlight fixtures direct illumination downward, creating focused, task-oriented lighting ideal for kitchens and workspaces. Uplight fixtures cast light upward, enhancing ambient lighting and highlighting architectural features or ceilings for a softer, more diffused effect. Choosing between downlight and uplight depends on the desired mood and functionality of the pet lighting environment.
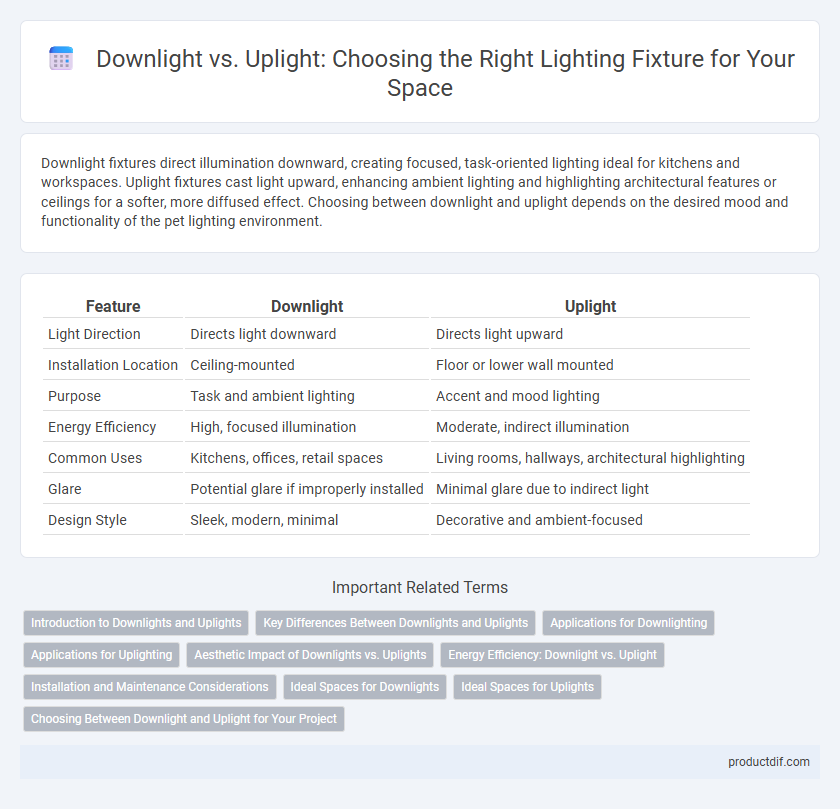
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Downlight | Uplight |
|---|---|---|
| Light Direction | Directs light downward | Directs light upward |
| Installation Location | Ceiling-mounted | Floor or lower wall mounted |
| Purpose | Task and ambient lighting | Accent and mood lighting |
| Energy Efficiency | High, focused illumination | Moderate, indirect illumination |
| Common Uses | Kitchens, offices, retail spaces | Living rooms, hallways, architectural highlighting |
| Glare | Potential glare if improperly installed | Minimal glare due to indirect light |
| Design Style | Sleek, modern, minimal | Decorative and ambient-focused |
Introduction to Downlights and Uplights
Downlights are recessed lighting fixtures installed into ceilings that provide focused, downward illumination ideal for task lighting and creating ambient spaces. Uplights emit light upward toward ceilings or walls, enhancing room ambiance and highlighting architectural features by producing indirect, soft illumination. Both lighting types serve complementary roles in interior design, balancing functionality and aesthetic appeal through strategic placement and light direction.
Key Differences Between Downlights and Uplights
Downlights direct light downward, ideal for task lighting and creating focused illumination in areas like kitchens or hallways. Uplights cast light upward, enhancing ambient lighting and highlighting architectural features or ceilings. The primary differences lie in their light direction, application purpose, and impact on room ambiance.
Applications for Downlighting
Downlighting is ideal for general ambient lighting in residential and commercial spaces, providing uniform illumination and reducing shadows by directing light downward. Common applications include kitchen counters, hallways, offices, and retail stores where focused light enhances visibility and aesthetics. Downlights are also favored for their ability to create a clean, unobtrusive ceiling appearance while effectively highlighting task areas and architectural features.
Applications for Uplighting
Uplighting is commonly used to highlight architectural features, such as columns, textured walls, and trees, creating dramatic vertical illumination that enhances spatial depth. It is ideal for accentuating artwork, decorative elements, and outdoor landscaping, providing ambient lighting that adds atmosphere without glare. This technique is frequently employed in hospitality, retail, and residential settings to create inviting, visually dynamic environments.
Aesthetic Impact of Downlights vs. Uplights
Downlights create a sleek, modern aesthetic by casting focused light downward that highlights specific areas without visual clutter. Uplights produce a softer, ambient glow by reflecting light off ceilings and walls, enhancing room spaciousness and architectural features. Combining both fixtures can balance direct illumination with atmospheric ambiance, elevating overall interior design.
Energy Efficiency: Downlight vs. Uplight
Downlights typically offer higher energy efficiency by directing light downward in a focused manner, reducing wasted illumination and lowering electricity consumption. Uplights tend to consume more energy as they disperse light over broader areas, requiring higher wattage to achieve comparable brightness levels. Choosing downlights can result in significant energy savings, especially in commercial and residential settings where targeted illumination is essential.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Downlight fixtures require recessed installation into ceilings, which often involves cutting precise openings and ensuring proper insulation clearance to prevent heat buildup. Uplight fixtures can be surface-mounted or installed at floor level, generally allowing easier access for bulb replacement and cleaning. Maintenance for downlights may necessitate ceiling access panels or specialized tools, while uplights offer simpler upkeep due to their accessible positioning.
Ideal Spaces for Downlights
Downlights are ideal for kitchens, hallways, and living rooms where focused, direct lighting is needed for tasks and ambiance. Their recessed design provides an unobtrusive light source that enhances ceiling height and creates a streamlined look. Suitable for spaces requiring even illumination without glare, downlights complement modern interiors by emphasizing functionality and minimalist aesthetics.
Ideal Spaces for Uplights
Uplights are ideal for creating ambient and accent lighting in living rooms, hallways, and dining areas, where indirect light enhances the atmosphere without causing glare. They are commonly used to highlight architectural features, such as textured walls or crown molding, by casting light upwards and emphasizing vertical surfaces. Uplights also work well in bedrooms and lounges to provide soft, diffused illumination that promotes relaxation and visual comfort.
Choosing Between Downlight and Uplight for Your Project
Downlights provide focused illumination directed downward, ideal for task lighting and highlighting specific areas, while uplights create ambient lighting by casting light upward, enhancing ceilings and walls. When choosing between downlight and uplight for your project, consider the room's purpose, ceiling height, and desired mood; downlights suit kitchens and workspaces, whereas uplights are effective in living rooms and hallways for soft, indirect lighting. Energy efficiency, fixture placement, and compatibility with dimmers also influence the decision to achieve optimal lighting performance and aesthetic appeal.
Downlight vs Uplight Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com