Induction cooktops offer precise temperature control and faster heating compared to gas stoves, making them energy-efficient and safer for kitchenware pet owners. Gas stoves provide visual flame control and compatibility with a wide range of cookware but tend to consume more energy and pose a higher risk of accidental burns. Choosing between the two depends on kitchen preferences, energy considerations, and the type of cookware used with your kitchenware pet setup.
Table of Comparison
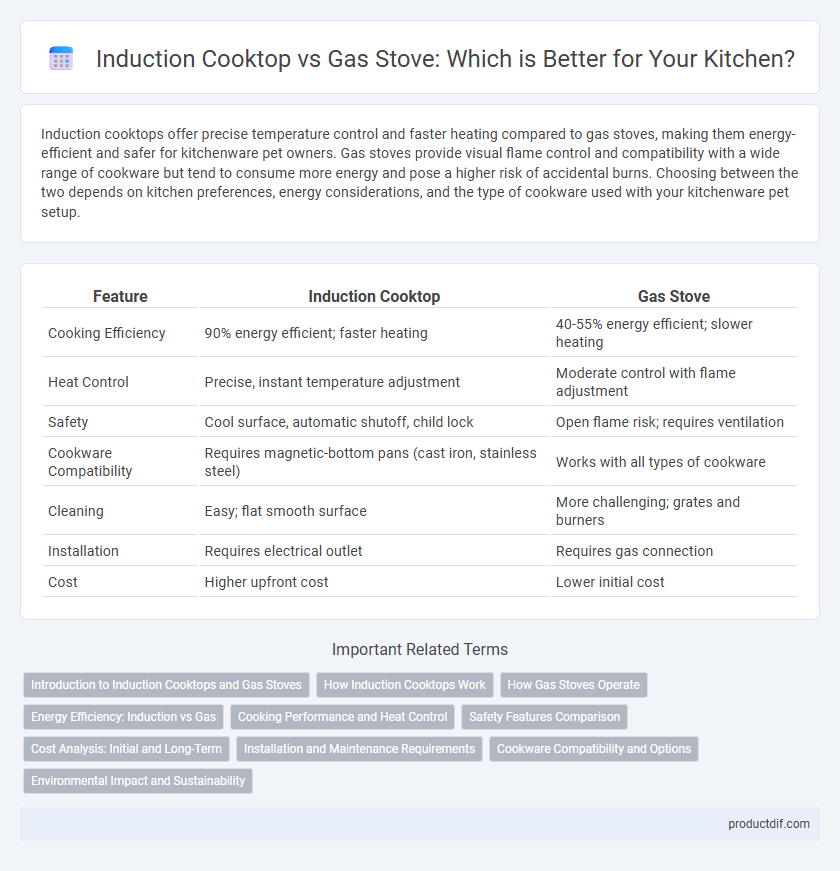
| Feature | Induction Cooktop | Gas Stove |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Efficiency | 90% energy efficient; faster heating | 40-55% energy efficient; slower heating |
| Heat Control | Precise, instant temperature adjustment | Moderate control with flame adjustment |
| Safety | Cool surface, automatic shutoff, child lock | Open flame risk; requires ventilation |
| Cookware Compatibility | Requires magnetic-bottom pans (cast iron, stainless steel) | Works with all types of cookware |
| Cleaning | Easy; flat smooth surface | More challenging; grates and burners |
| Installation | Requires electrical outlet | Requires gas connection |
| Cost | Higher upfront cost | Lower initial cost |
Introduction to Induction Cooktops and Gas Stoves
Induction cooktops utilize electromagnetic fields to directly heat pots and pans, offering rapid temperature control and energy efficiency compared to traditional gas stoves. Gas stoves provide visible flames and precise manual control, favored in professional kitchens for their responsiveness and compatibility with all cookware types. Both cooking technologies cater to different culinary preferences, with induction emphasizing safety and speed, while gas prioritizes tactile control and versatility.
How Induction Cooktops Work
Induction cooktops use electromagnetic fields to directly heat pots and pans made of ferrous metals, providing rapid and precise temperature control. Unlike gas stoves that transfer heat through flames, induction technology heats cookware efficiently by inducing electric currents, resulting in faster cooking times and energy savings. This method ensures safer operation with a cool-to-touch surface and minimizes heat loss in the kitchen environment.
How Gas Stoves Operate
Gas stoves operate by igniting natural gas or propane through burners, producing an open flame that directly heats cookware for immediate temperature control. The combustion process involves mixing gas with air to create a consistent flame, enabling precise cooking adjustments favored by professional chefs. This direct heat transfer method offers high responsiveness but may result in uneven heat distribution compared to induction cooktops.
Energy Efficiency: Induction vs Gas
Induction cooktops convert up to 90% of energy directly into heat, making them significantly more energy-efficient than gas stoves, which typically convert only about 40-55% of fuel energy into cooking heat. Gas stoves release a large portion of energy as heat into the surrounding environment, leading to energy loss and higher utility costs. Energy efficiency of induction cooktops also aligns with eco-friendly kitchen trends, reducing carbon footprint compared to fossil fuel-dependent gas stoves.
Cooking Performance and Heat Control
Induction cooktops offer precise heat control through electromagnetic technology, enabling rapid temperature adjustments and consistent cooking performance. Gas stoves provide visible flame control, preferred by chefs for immediate heat changes and versatility with various cookware types. Both options deliver effective cooking performance, but induction excels in energy efficiency and safety while gas stoves maintain traditional tactile heat management.
Safety Features Comparison
Induction cooktops offer enhanced safety by using electromagnetic fields to heat only compatible cookware, significantly reducing burn risks and eliminating open flames. Gas stoves pose higher fire hazards due to exposed flames and potential gas leaks, requiring careful monitoring and proper ventilation. Induction cooktops include automatic shut-off and child lock features, whereas gas stoves generally lack these advanced safety mechanisms.
Cost Analysis: Initial and Long-Term
Induction cooktops typically have a higher initial purchase price, ranging from $300 to $1,200, compared to gas stoves, which cost between $200 and $800. Long-term energy savings are notable with induction cooktops, as they convert around 90% of electricity to heat, whereas gas stoves convert only about 40-55% of fuel energy, leading to higher utility bills. Maintenance costs for gas stoves can be greater due to parts like burners and gas lines needing regular servicing, while induction cooktops generally require less upkeep but may incur higher repair costs for electronic components.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Induction cooktops require a smooth, flat surface for installation and need compatible magnetic cookware, making the setup moderately technical but space-efficient. Gas stoves demand a gas line connection and proper ventilation, involving more complex installation and higher safety considerations. Maintenance of induction cooktops is simpler due to their flat surface, while gas stoves require regular cleaning of burners and inspection of gas lines for leaks.
Cookware Compatibility and Options
Induction cooktops require cookware with magnetic properties, such as cast iron or stainless steel, to function efficiently, limiting options compared to gas stoves which accommodate a broader range including aluminum, copper, and non-magnetic pans. Gas stoves offer superior versatility for different cookware materials and shapes due to direct flame heating, while induction cooktops provide precise temperature control but depend heavily on the cookware's magnetic compatibility. Choosing between these depends on the existing cookware collection and the willingness to invest in induction-compatible pots and pans.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Induction cooktops offer superior energy efficiency, converting approximately 90% of energy into heat compared to about 40-55% for gas stoves, significantly reducing carbon emissions. Gas stoves release methane, a potent greenhouse gas, contributing to indoor air pollution and environmental degradation. Transitioning to induction technology supports sustainable kitchen practices by minimizing fossil fuel dependency and promoting cleaner energy usage.
Induction Cooktop vs Gas Stove Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com