A Dutch oven offers excellent heat retention and versatility, making it ideal for slow-cooking, braising, and baking tasks in the kitchen. In contrast, a stockpot features a large volume with tall, straight sides suited for boiling and simmering large quantities of liquids such as soups and stocks. Choosing between them depends on cooking style and recipe requirements, with the Dutch oven excelling in even heat distribution and the stockpot providing ample space for liquids.
Table of Comparison
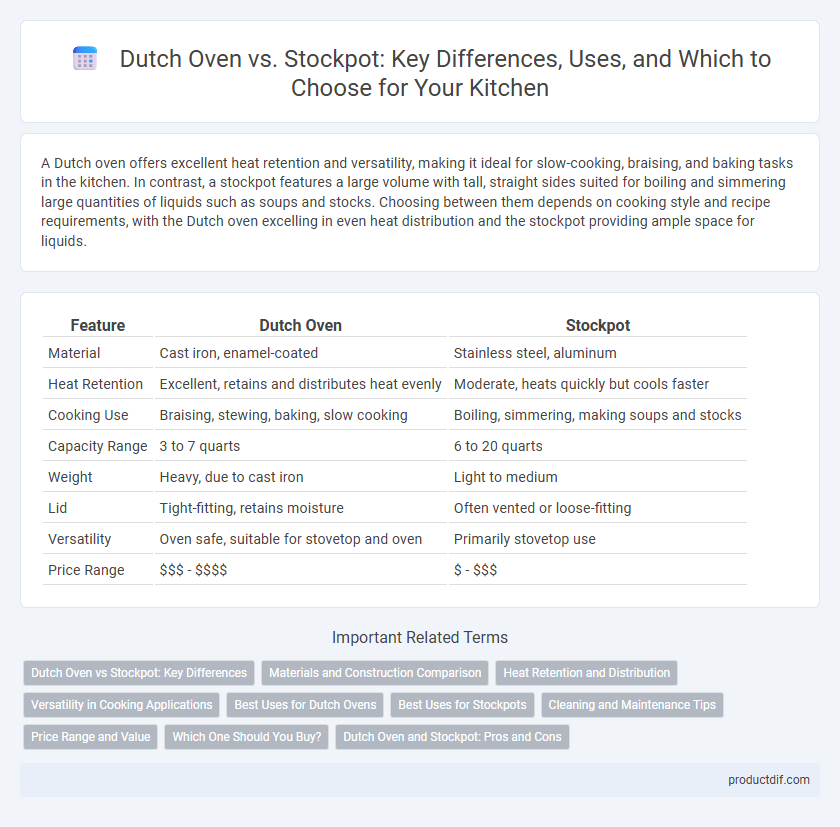
| Feature | Dutch Oven | Stockpot |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Cast iron, enamel-coated | Stainless steel, aluminum |
| Heat Retention | Excellent, retains and distributes heat evenly | Moderate, heats quickly but cools faster |
| Cooking Use | Braising, stewing, baking, slow cooking | Boiling, simmering, making soups and stocks |
| Capacity Range | 3 to 7 quarts | 6 to 20 quarts |
| Weight | Heavy, due to cast iron | Light to medium |
| Lid | Tight-fitting, retains moisture | Often vented or loose-fitting |
| Versatility | Oven safe, suitable for stovetop and oven | Primarily stovetop use |
| Price Range | $$$ - $$$$ | $ - $$$ |
Dutch Oven vs Stockpot: Key Differences
Dutch ovens are typically made of cast iron with an enamel coating, providing excellent heat retention and even cooking, while stockpots are usually stainless steel or aluminum for quick heating and are designed for large liquid volumes. Dutch ovens excel in slow-cooking, braising, and baking due to their thick walls and tight-fitting lids, whereas stockpots are ideal for boiling, simmering, and making large batches of soups or stocks. The weight and heat distribution of Dutch ovens differ significantly from the lighter, more heat-responsive stockpots, influencing cooking techniques and energy efficiency.
Materials and Construction Comparison
Dutch ovens are typically made from cast iron, often coated with an enamel finish that enhances heat retention and prevents rusting, providing superior even heating ideal for slow cooking and braising. Stockpots are commonly constructed from stainless steel or aluminum, materials chosen for their lightweight properties and rapid heat conduction, making them suitable for boiling and large-volume cooking. The thicker walls and heavy lids of Dutch ovens contribute to moisture retention, whereas stockpots prioritize capacity with thinner walls and vented lids for efficient evaporation.
Heat Retention and Distribution
Dutch ovens excel in heat retention due to their thick cast iron construction, allowing even cooking over long periods without temperature fluctuations. Stockpots, typically made from stainless steel or aluminum, offer rapid heat distribution but lose heat more quickly, making them ideal for boiling or simmering large volumes. The superior heat retention of Dutch ovens enhances slow-cooking and braising, while stockpots provide efficiency in tasks requiring fast, consistent heating.
Versatility in Cooking Applications
Dutch ovens excel in versatile cooking applications, offering excellent heat retention for slow-cooking, braising, and baking. Stockpots are ideal for boiling, steaming, and preparing large batches of soups or stocks due to their tall, spacious design. Both kitchenware pieces serve distinct purposes, with Dutch ovens providing multi-functional use and stockpots optimized for large-volume liquid-based cooking.
Best Uses for Dutch Ovens
Dutch ovens excel at slow-cooking, braising, and baking due to their thick, heavy walls and excellent heat retention, making them ideal for stews, roasts, and artisan bread. Their tight-fitting lids trap moisture effectively, enhancing flavors in recipes that require long simmering or slow roasting. Unlike stockpots, Dutch ovens can be used both on stovetops and in ovens, offering versatile cooking options for dishes benefiting from even, consistent heat.
Best Uses for Stockpots
Stockpots excel at cooking large quantities of liquids, making them ideal for soups, stews, boiling pasta, and preparing stocks or broths. Their tall, straight sides and large capacity enable even heat distribution and efficient evaporation, essential for reducing sauces or simmering ingredients over extended periods. Stockpots made of stainless steel or aluminum offer durability and quick heating, suitable for versatile kitchen tasks requiring consistent temperature control.
Cleaning and Maintenance Tips
Dutch ovens require careful cleaning to maintain their enamel coating, avoiding abrasive scrubbers and using warm, soapy water to prevent damage. Stockpots, often made of stainless steel, can withstand more rigorous scrubbing and are typically dishwasher-safe, making maintenance easier. Regular seasoning of cast iron Dutch ovens enhances their durability, while stockpots benefit from immediate drying to prevent water spots and rust.
Price Range and Value
Dutch ovens typically range from $50 to $300, offering excellent heat retention and versatility for slow cooking and baking, making them a valuable investment for home chefs. Stockpots vary between $30 and $150, providing a more affordable option ideal for boiling and large batch cooking but with less heat retention compared to Dutch ovens. Considering durability and multi-purpose use, Dutch ovens generally offer better long-term value despite a higher initial price.
Which One Should You Buy?
A Dutch oven excels in slow-cooking, braising, and baking thanks to its heavy cast iron construction with an enamel coating, ensuring even heat distribution and retention. A stockpot, typically made from stainless steel or aluminum, is ideal for boiling large quantities of water, making soups, and cooking pasta efficiently. Choose a Dutch oven for versatile, long-duration cooking tasks and a stockpot for high-volume boiling and simmering needs.
Dutch Oven and Stockpot: Pros and Cons
Dutch ovens offer excellent heat retention and versatility, making them ideal for slow-cooking, braising, and baking; their heavy cast iron build ensures even cooking but can be cumbersome and requires maintenance to prevent rust. Stockpots provide large capacity and are perfect for boiling, steaming, and making soups or stocks; they are usually lightweight and easy to handle but lack the heat retention and searing capabilities of Dutch ovens. Choosing between a Dutch oven and a stockpot depends on cooking needs, with Dutch ovens excelling in versatility and heat retention, while stockpots suit high-volume boiling and faster cooking tasks.
Dutch oven vs Stockpot Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com