Cast iron cookware offers superior heat retention and even cooking, making it ideal for slow-cooked meals and searing, while its natural non-stick seasoning improves with use. Stainless steel provides excellent durability, resistance to rust and corrosion, and is perfect for high-heat cooking and acidic foods without reacting or altering flavors. Choosing between cast iron and stainless steel depends on your cooking style, maintenance preference, and desired performance in the kitchen.
Table of Comparison
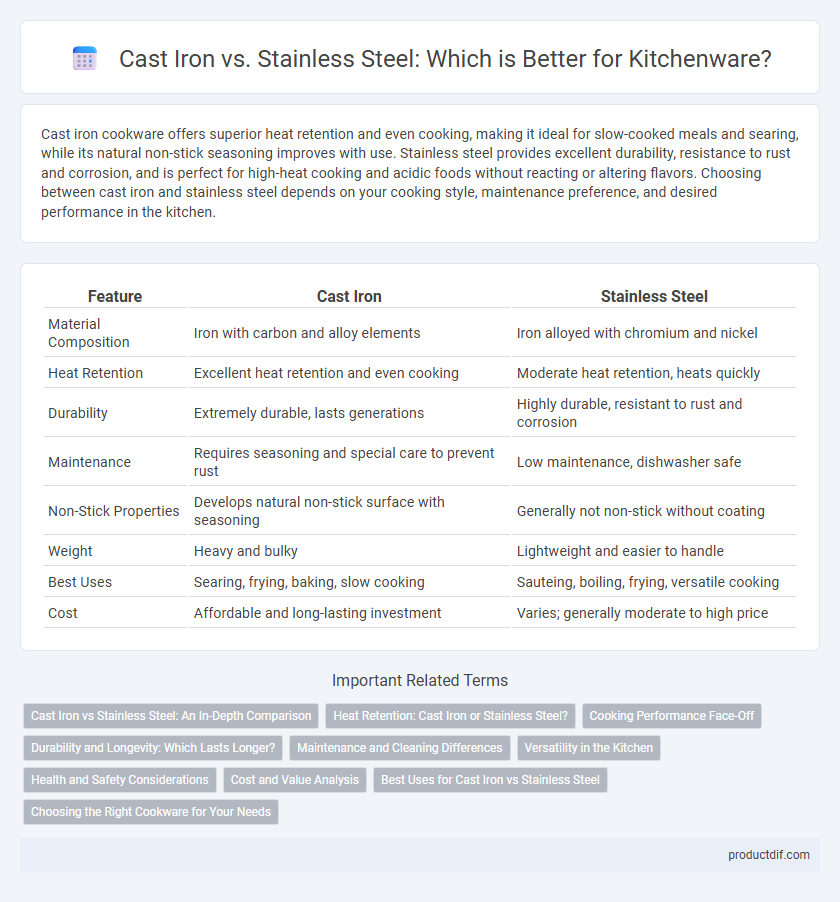
| Feature | Cast Iron | Stainless Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Iron with carbon and alloy elements | Iron alloyed with chromium and nickel |
| Heat Retention | Excellent heat retention and even cooking | Moderate heat retention, heats quickly |
| Durability | Extremely durable, lasts generations | Highly durable, resistant to rust and corrosion |
| Maintenance | Requires seasoning and special care to prevent rust | Low maintenance, dishwasher safe |
| Non-Stick Properties | Develops natural non-stick surface with seasoning | Generally not non-stick without coating |
| Weight | Heavy and bulky | Lightweight and easier to handle |
| Best Uses | Searing, frying, baking, slow cooking | Sauteing, boiling, frying, versatile cooking |
| Cost | Affordable and long-lasting investment | Varies; generally moderate to high price |
Cast Iron vs Stainless Steel: An In-Depth Comparison
Cast iron offers superior heat retention and even cooking ideal for searing and slow-cooking, while stainless steel provides excellent durability, resistance to corrosion, and a non-reactive surface suitable for acidic dishes. Cast iron requires regular seasoning to maintain its non-stick properties and prevent rust, whereas stainless steel demands less maintenance and is dishwasher safe. The choice between cast iron and stainless steel depends on cooking style, maintenance preference, and desired cookware longevity.
Heat Retention: Cast Iron or Stainless Steel?
Cast iron excels in heat retention due to its dense composition, allowing it to maintain consistent cooking temperatures for longer periods. Stainless steel heats up quickly but loses heat faster because of its lighter, thinner structure. For dishes requiring steady, even heat, cast iron offers superior thermal performance compared to stainless steel cookware.
Cooking Performance Face-Off
Cast iron offers superior heat retention and even cooking, making it ideal for searing and slow-cooking recipes. Stainless steel provides excellent heat conductivity and resists corrosion, delivering precise temperature control for sauteing and boiling. While cast iron requires seasoning to maintain its non-stick surface, stainless steel ensures durability and easy maintenance without seasoning.
Durability and Longevity: Which Lasts Longer?
Cast iron cookware offers exceptional durability due to its dense material and ability to withstand high heat, often lasting decades with proper care. Stainless steel is highly resistant to rust, corrosion, and warping, providing long-lasting performance and maintaining its appearance over time. Both materials excel in longevity, but cast iron requires seasoning to prevent rust, while stainless steel requires less maintenance and is more resistant to everyday wear.
Maintenance and Cleaning Differences
Cast iron cookware requires seasoning to maintain its non-stick surface and prevent rust, demanding regular oiling after each use, while stainless steel is more resistant to corrosion and can be cleaned with abrasive scrubbers without damage. Cast iron should never be soaked in water and should be dried immediately to avoid rust, whereas stainless steel is dishwasher-safe and tolerates prolonged exposure to water. Proper maintenance of cast iron extends its lifespan and cooking performance, while stainless steel offers convenience with minimal care requirements.
Versatility in the Kitchen
Cast iron offers exceptional heat retention and even cooking, making it ideal for searing, frying, and baking, while stainless steel excels in quick heating and is perfect for sauteing, boiling, and making sauces. Stainless steel cookware often features non-reactive surfaces suitable for acidic ingredients, whereas cast iron develops a natural non-stick patina over time with seasoning. Both materials complement a versatile kitchen by covering a broad range of cooking techniques and temperature demands.
Health and Safety Considerations
Cast iron cookware naturally increases dietary iron intake, benefiting those with iron deficiency but may pose risks for individuals with hemochromatosis due to excess iron absorption. Stainless steel is non-reactive and does not leach metals into food, making it safer for cooking acidic dishes and preventing potential contamination. Both materials require proper maintenance--cast iron needs seasoning to prevent rust and maintain a non-stick surface, while stainless steel demands thorough cleaning to avoid bacterial buildup in scratches.
Cost and Value Analysis
Cast iron cookware offers long-term value due to its durability and excellent heat retention, often priced lower upfront but requiring seasoning and maintenance. Stainless steel pans, typically more expensive initially, provide superior resistance to rust and corrosion, ensuring longevity with minimal upkeep. Evaluating cost-effectiveness depends on cooking style and care commitment, where cast iron appeals to budget-conscious users seeking versatility, while stainless steel suits those prioritizing low-maintenance and sleek aesthetics.
Best Uses for Cast Iron vs Stainless Steel
Cast iron excels in slow-cooking, searing, and frying due to its superior heat retention and even heating capabilities, making it ideal for dishes like stews, cornbread, and steaks. Stainless steel is best suited for high-temperature cooking and sauteing with acidic foods, as it resists corrosion and doesn't react, perfect for deglazing and preparing sauces. Choosing between cast iron and stainless steel depends on cooking style, with cast iron favored for durability and heat retention, while stainless steel offers versatility and ease of maintenance.
Choosing the Right Cookware for Your Needs
Cast iron offers superior heat retention and seasoning capabilities ideal for slow cooking and searing, while stainless steel provides excellent durability, corrosion resistance, and is preferred for tasks requiring quick temperature changes. Consider cast iron if you prioritize flavor development and non-stick properties over time, whereas stainless steel suits those seeking low-maintenance, versatile cookware for sauteing and boiling. Evaluating cooking style, maintenance preferences, and heat responsiveness ensures the selection of cookware tailored to specific culinary needs.
Cast Iron vs Stainless Steel Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com