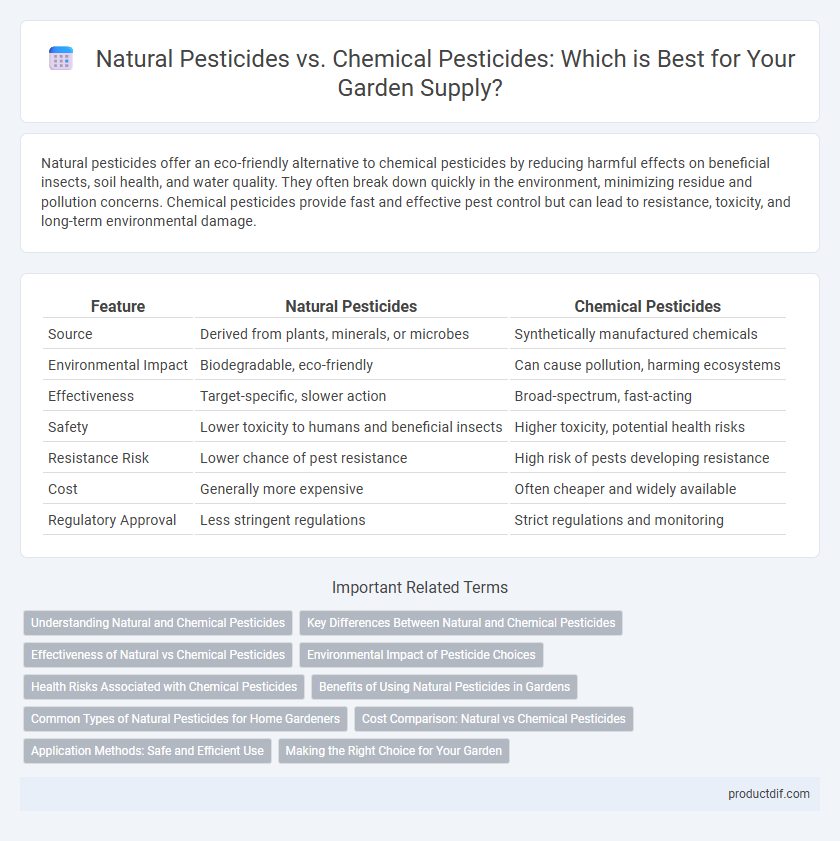
Natural pesticides offer an eco-friendly alternative to chemical pesticides by reducing harmful effects on beneficial insects, soil health, and water quality. They often break down quickly in the environment, minimizing residue and pollution concerns. Chemical pesticides provide fast and effective pest control but can lead to resistance, toxicity, and long-term environmental damage.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Natural Pesticides | Chemical Pesticides |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Derived from plants, minerals, or microbes | Synthetically manufactured chemicals |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, eco-friendly | Can cause pollution, harming ecosystems |
| Effectiveness | Target-specific, slower action | Broad-spectrum, fast-acting |
| Safety | Lower toxicity to humans and beneficial insects | Higher toxicity, potential health risks |
| Resistance Risk | Lower chance of pest resistance | High risk of pests developing resistance |
| Cost | Generally more expensive | Often cheaper and widely available |
| Regulatory Approval | Less stringent regulations | Strict regulations and monitoring |
Understanding Natural and Chemical Pesticides
Natural pesticides, derived from plant extracts, minerals, or microorganisms, offer eco-friendly pest control with minimal impact on beneficial insects and soil health. Chemical pesticides, synthesized through industrial processes, provide rapid and broad-spectrum pest elimination but may lead to environmental contamination and resistance in pests. Understanding the sources, mechanisms, and environmental effects of both pesticide types is essential for sustainable garden management.
Key Differences Between Natural and Chemical Pesticides
Natural pesticides are derived from plant extracts, minerals, or beneficial microorganisms, offering eco-friendly pest control with lower toxicity to humans and non-target animals. Chemical pesticides consist of synthetic compounds designed for rapid and broad-spectrum pest eradication but can pose environmental risks such as soil degradation and water contamination. The key differences lie in their origin, environmental impact, persistence in ecosystems, and potential health effects on gardeners and wildlife.
Effectiveness of Natural vs Chemical Pesticides
Natural pesticides, derived from plant extracts and organic materials, often provide targeted pest control with reduced environmental impact but may require more frequent applications due to lower residual activity. Chemical pesticides typically offer stronger, broad-spectrum pest eradication with longer-lasting residue, enhancing overall effectiveness for immediate pest suppression. However, chemical use poses risks of resistance development in pests and potential harm to beneficial organisms, necessitating careful management in garden supply strategies.
Environmental Impact of Pesticide Choices
Natural pesticides typically break down more quickly in the environment, reducing soil and water contamination compared to chemical pesticides, which often persist and accumulate, harming beneficial insects and aquatic life. Chemical pesticides can disrupt ecosystems by killing non-target species and reducing biodiversity, leading to long-term ecological imbalances. Choosing natural pesticides supports sustainable gardening by minimizing toxic residues, promoting healthier soil microbiomes, and protecting pollinator populations essential for plant reproduction.
Health Risks Associated with Chemical Pesticides
Chemical pesticides often contain toxic substances that can lead to serious health risks such as respiratory issues, skin irritation, and long-term neurological effects. Exposure to these synthetic chemicals has been linked to increased instances of cancer and hormonal imbalances in both adults and children. Natural pesticides, derived from plant extracts and biodegradable materials, offer a safer alternative by minimizing harmful residues and reducing environmental contamination.
Benefits of Using Natural Pesticides in Gardens
Natural pesticides enhance garden health by reducing harmful chemical residues, promoting safer environments for pollinators and beneficial insects. They biodegrade quickly, minimizing soil and water contamination while supporting sustainable gardening practices. Using natural pesticides also lowers the risk of pest resistance, leading to long-term effectiveness in pest management.
Common Types of Natural Pesticides for Home Gardeners
Common types of natural pesticides for home gardeners include neem oil, insecticidal soap, and diatomaceous earth, each targeting a range of garden pests while minimizing environmental impact. Neem oil acts as a repellent and disrupts insect growth, insecticidal soap effectively eliminates soft-bodied insects like aphids, and diatomaceous earth causes dehydration in crawling insects through its abrasive properties. These natural alternatives help maintain plant health and biodiversity by reducing reliance on synthetic chemicals often associated with soil and water contamination.
Cost Comparison: Natural vs Chemical Pesticides
Natural pesticides typically incur higher upfront costs due to organic ingredient sourcing and lower production scales, but they often reduce long-term expenses through improved soil health and reduced resistance development in pests. Chemical pesticides are generally cheaper per application and more widely available, yet frequent use can lead to increased costs from pest resistance management and environmental remediation. Evaluating total cost efficiency requires balancing immediate price differences with ecological impact and sustainability considerations in garden supply choices.
Application Methods: Safe and Efficient Use
Natural pesticides often require precise application techniques such as targeted spraying or soil incorporation to maximize their effectiveness while minimizing environmental impact. Chemical pesticides usually involve calibrated equipment and specific timing to ensure thorough coverage and optimal pest control without damaging plants. Employing proper application methods for both types enhances pest management efficiency and safety in garden supply practices.
Making the Right Choice for Your Garden
Natural pesticides offer eco-friendly pest control by using plant-based or biological ingredients that minimize harm to beneficial insects and soil health. Chemical pesticides provide faster, more potent results but can lead to pesticide resistance, environmental pollution, and potential health risks for humans and pets. Choosing the right pesticide depends on your garden's ecosystem, the specific pest problem, and your commitment to sustainable gardening practices.
Natural pesticides vs Chemical pesticides Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com