Zero drop footwear features a level sole that maintains an even height from heel to toe, promoting a natural foot strike and encouraging proper posture. High drop shoes have an elevated heel relative to the forefoot, which can reduce calf strain and provide added cushioning for activities like running on hard surfaces. Choosing between zero drop and high drop depends on individual biomechanics, running style, and comfort preferences.
Table of Comparison
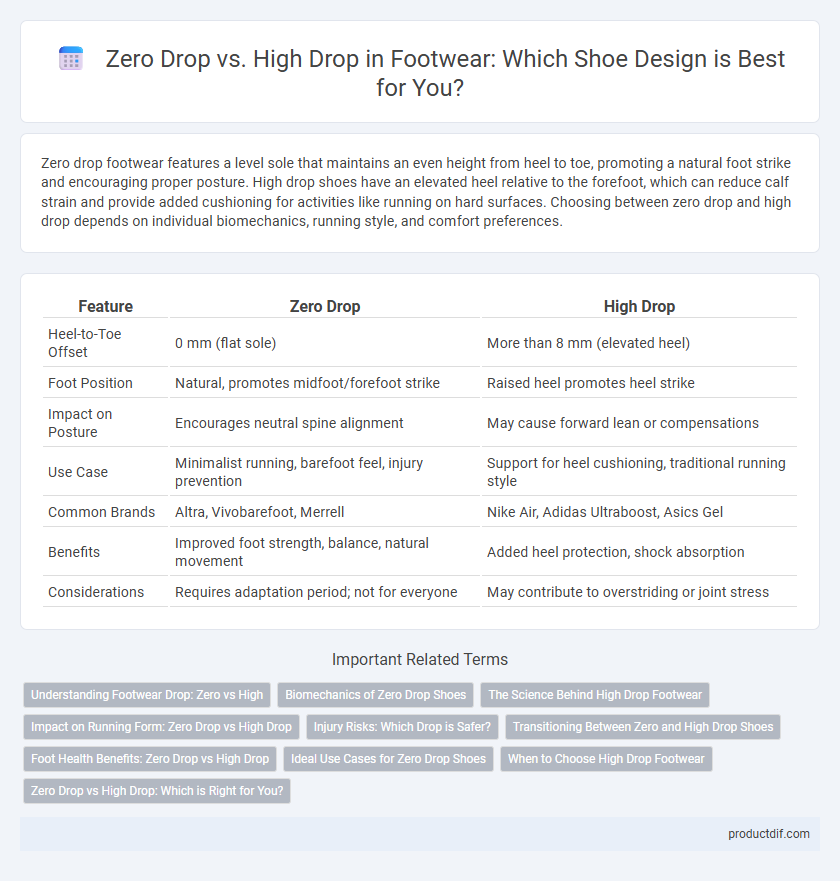
| Feature | Zero Drop | High Drop |
|---|---|---|
| Heel-to-Toe Offset | 0 mm (flat sole) | More than 8 mm (elevated heel) |
| Foot Position | Natural, promotes midfoot/forefoot strike | Raised heel promotes heel strike |
| Impact on Posture | Encourages neutral spine alignment | May cause forward lean or compensations |
| Use Case | Minimalist running, barefoot feel, injury prevention | Support for heel cushioning, traditional running style |
| Common Brands | Altra, Vivobarefoot, Merrell | Nike Air, Adidas Ultraboost, Asics Gel |
| Benefits | Improved foot strength, balance, natural movement | Added heel protection, shock absorption |
| Considerations | Requires adaptation period; not for everyone | May contribute to overstriding or joint stress |
Understanding Footwear Drop: Zero vs High
Footwear drop refers to the height difference between the heel and the forefoot of a shoe, influencing foot posture and running mechanics. Zero drop shoes promote a natural, flat stance encouraging midfoot or forefoot striking, while high drop shoes feature a raised heel that often leads to heel striking and increased calf strain. Understanding these differences helps runners select footwear that aligns with their biomechanics and comfort preferences.
Biomechanics of Zero Drop Shoes
Zero drop shoes promote a natural foot strike by maintaining the heel and forefoot at the same level, reducing strain on the Achilles tendon and calf muscles. This biomechanical alignment encourages a midfoot or forefoot landing, enhancing shock absorption and improving posture during walking or running. Research indicates that zero drop footwear can help prevent injuries related to overstriding and promote a more efficient gait cycle.
The Science Behind High Drop Footwear
High drop footwear features a significant heel-to-toe elevation difference, typically ranging from 8mm to 12mm, influencing foot strike patterns and load distribution during running or walking. This elevated heel promotes a heel-first landing, reducing strain on the Achilles tendon and calf muscles by altering ankle dorsiflexion and plantarflexion mechanics. Biomechanical studies reveal that high drop shoes can potentially mitigate injury risks for runners with tight calf muscles or Achilles tendinopathies by modifying ground reaction forces and running kinematics.
Impact on Running Form: Zero Drop vs High Drop
Zero drop footwear promotes a natural running form by encouraging a midfoot or forefoot strike, which can reduce impact forces on joints and improve balance. High drop shoes, featuring a significant heel-to-toe offset, often lead to a heel-striking pattern that increases impact load and may strain knees and hips over time. Runners transitioning from high drop to zero drop shoes should gradually adapt to changes in running biomechanics to prevent injury.
Injury Risks: Which Drop is Safer?
Zero drop footwear, with a heel-to-toe height difference of 0mm, promotes a more natural foot strike and can reduce the risk of certain injuries like plantar fasciitis and Achilles tendonitis by encouraging midfoot or forefoot landing. High drop shoes, typically featuring a 10-12mm heel-to-toe offset, provide extra heel cushioning and support, which may help prevent heel-related injuries and offer better shock absorption for heel strikers. Injury risk varies based on individual biomechanics and transition periods, making gradual adjustment to zero drop shoes essential to avoid calf strain and stress fractures.
Transitioning Between Zero and High Drop Shoes
Transitioning between zero drop and high drop shoes requires careful adaptation to avoid injury and discomfort. Gradually increasing mileage in the new footwear over several weeks allows the Achilles tendon and calf muscles to strengthen and adjust to altered heel-to-toe offsets. Consistent stretching and incorporating foot strengthening exercises support a smoother transition while maintaining natural gait mechanics.
Foot Health Benefits: Zero Drop vs High Drop
Zero drop shoes promote natural foot alignment by maintaining the heel and forefoot at equal heights, reducing strain on the Achilles tendon and encouraging a more natural gait. High drop shoes elevate the heel relative to the forefoot, which can alleviate pressure on the calf muscles but may contribute to altered posture and increased risk of plantar fasciitis. Choosing zero drop footwear supports foot strength and mobility, while high drop options may benefit those with specific muscle tightness or heel pain.
Ideal Use Cases for Zero Drop Shoes
Zero drop shoes promote a natural foot strike by maintaining equal heel-to-toe height, ideal for running and walking on flat, even surfaces where natural gait and posture are prioritized. They benefit athletes seeking to strengthen foot muscles, improve balance, and reduce impact forces during activities such as trail running, minimalist training, and daily casual wear. Zero drop footwear suits individuals aiming to transition from traditional high drop shoes while minimizing injury risk and enhancing proprioception.
When to Choose High Drop Footwear
High drop footwear, typically featuring a heel-to-toe offset of 8mm or more, is ideal for runners or walkers who experience Achilles tendon tightness or calf muscle strain, as it reduces stress on these areas. Individuals recovering from heel pain conditions like plantar fasciitis may also benefit from high drop shoes to alleviate pressure during movement. Athletes transitioning from traditional running shoes with significant heel cushioning often find high drop footwear provides enhanced comfort and injury prevention.
Zero Drop vs High Drop: Which is Right for You?
Zero drop shoes feature a heel and forefoot at the same level, promoting a natural gait and reducing heel strike impact, ideal for runners seeking a minimalist, barefoot-like experience. High drop shoes raise the heel significantly above the forefoot, offering enhanced cushioning and support, beneficial for heel strikers and those with calf tightness or injury concerns. Choosing between zero drop and high drop depends on your running style, injury history, and personal comfort preferences to ensure optimal performance and injury prevention.
Zero drop vs High drop Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com