Barefoot shoes offer a minimalist design that promotes natural foot movement and improved posture, contrasting with traditional sneakers, which often provide more cushioning and support but can restrict foot flexibility. The thin soles of barefoot shoes enhance sensory feedback from the ground, encouraging a more natural gait. While traditional sneakers may be preferred for high-impact activities, barefoot shoes support foot strength and balance for everyday wear.
Table of Comparison
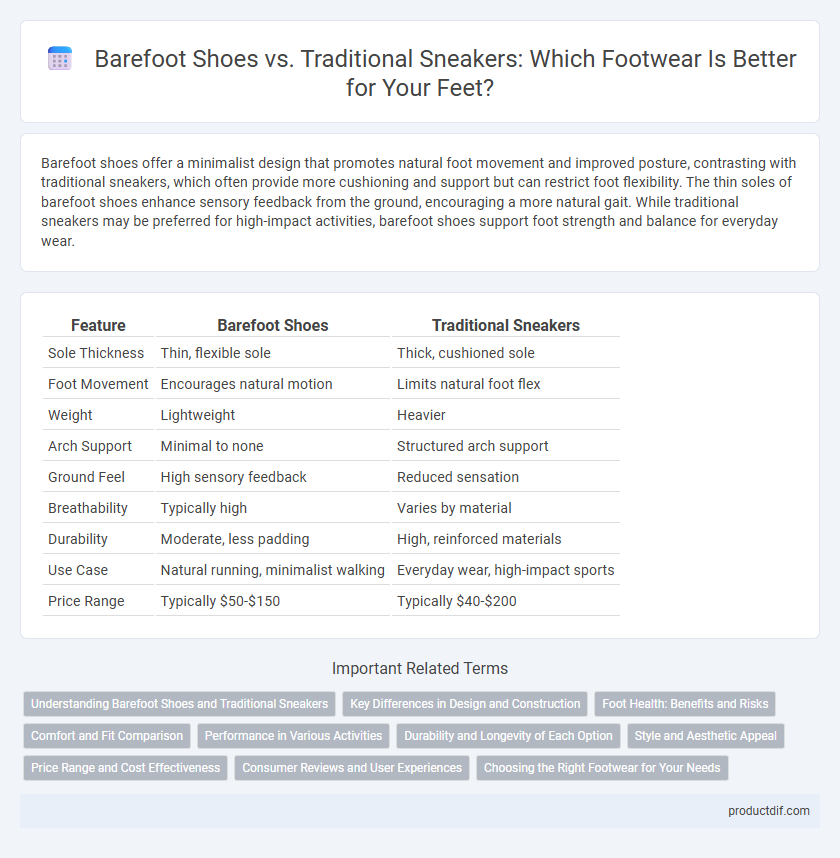
| Feature | Barefoot Shoes | Traditional Sneakers |
|---|---|---|
| Sole Thickness | Thin, flexible sole | Thick, cushioned sole |
| Foot Movement | Encourages natural motion | Limits natural foot flex |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier |
| Arch Support | Minimal to none | Structured arch support |
| Ground Feel | High sensory feedback | Reduced sensation |
| Breathability | Typically high | Varies by material |
| Durability | Moderate, less padding | High, reinforced materials |
| Use Case | Natural running, minimalist walking | Everyday wear, high-impact sports |
| Price Range | Typically $50-$150 | Typically $40-$200 |
Understanding Barefoot Shoes and Traditional Sneakers
Barefoot shoes prioritize natural foot movement by featuring minimal cushioning, thin soles, and a lightweight design that promotes proprioception and strengthens foot muscles. Traditional sneakers often include thicker soles, extensive padding, and structured support to absorb impact and provide stability during various activities. Understanding these differences helps consumers choose footwear that aligns with their comfort preferences, foot health goals, and athletic needs.
Key Differences in Design and Construction
Barefoot shoes feature a minimalist design with thin, flexible soles that promote natural foot movement and ground feel, while traditional sneakers typically have thicker, cushioned soles engineered for shock absorption and arch support. The construction of barefoot footwear emphasizes lightweight materials and a wide toe box to enhance toe splay and balance, contrasting with the structured, often heavier build of sneakers designed for stability and performance. Key differences also include the absence of elevated heels in barefoot shoes, which aims to encourage a natural gait, whereas traditional sneakers usually incorporate heel lifts to optimize running mechanics.
Foot Health: Benefits and Risks
Barefoot shoes promote natural foot mechanics by allowing toes to splay and muscles to strengthen, which can enhance foot health and reduce injury risk associated with rigid traditional sneakers. Traditional sneakers often provide excessive cushioning and arch support that may weaken foot muscles over time and contribute to improper gait. However, barefoot shoes carry risks such as insufficient protection on rough terrain and a potential adjustment period causing initial discomfort or injury.
Comfort and Fit Comparison
Barefoot shoes provide a closer-to-natural foot movement with a minimalistic design that enhances comfort by allowing toes to spread and feet to flex freely, reducing pressure points common in traditional sneakers. Traditional sneakers often offer more cushioning and arch support, which can be beneficial for those requiring extra stability but may compromise natural foot biomechanics and lead to discomfort over prolonged wear. Comfort and fit preferences vary based on individual foot shape and activity type, making barefoot shoes ideal for those seeking enhanced proprioception and flexibility while traditional sneakers suit users needing structured support.
Performance in Various Activities
Barefoot shoes enhance proprioception and natural foot movement, boosting agility and balance during activities like running and hiking. Traditional sneakers provide greater cushioning and arch support, beneficial for high-impact sports and extended wear. Performance outcomes vary based on activity type, foot anatomy, and individual preferences, making footwear selection crucial for optimal results.
Durability and Longevity of Each Option
Barefoot shoes typically feature minimalist designs with flexible soles made from thin rubber or synthetic materials, which may wear out faster compared to the thicker, multi-layered soles of traditional sneakers engineered for prolonged use. Traditional sneakers often incorporate reinforced stitching, durable materials such as leather or mesh, and advanced cushioning technologies that enhance their longevity and resistance to daily wear and tear. While barefoot shoes promote natural foot movement and can last well with proper care, traditional sneakers generally offer superior durability for high-impact activities and extended usage periods.
Style and Aesthetic Appeal
Barefoot shoes emphasize a minimalist design with a sleek, low-profile silhouette that closely mimics natural foot movement, appealing to those who prioritize functional style and an understated aesthetic. Traditional sneakers often showcase bold branding, varied colorways, and structured designs that cater to diverse fashion trends and streetwear culture. The choice between barefoot shoes and traditional sneakers hinges on individual preferences for subtle elegance versus expressive, trend-driven styles.
Price Range and Cost Effectiveness
Barefoot shoes typically range from $70 to $150, offering long-term benefits such as improved foot strength and natural gait, which can reduce injury-related costs. Traditional sneakers usually cost between $50 and $120 but may require more frequent replacement due to conventional cushioning technology wearing out faster. Investing in barefoot shoes can be more cost-effective over time by promoting foot health and durability compared to the often shorter lifespan and limited biomechanical support of traditional sneakers.
Consumer Reviews and User Experiences
Consumer reviews highlight that barefoot shoes promote natural foot movement and enhance proprioception, with users reporting improved balance and reduced foot pain over time. Traditional sneakers receive praise for cushioning and arch support, appealing to those seeking immediate comfort and shock absorption. User experiences often reveal a transitional period when switching to barefoot shoes, requiring adaptation to less padding but leading to greater foot strength and flexibility.
Choosing the Right Footwear for Your Needs
Barefoot shoes promote natural foot movement and strengthen foot muscles by mimicking a barefoot experience, making them ideal for those seeking increased proprioception and minimalist design. Traditional sneakers offer enhanced cushioning, arch support, and stability, catering to high-impact activities or individuals with specific foot conditions. Selecting the right footwear depends on your activity type, foot biomechanics, and comfort preferences to ensure optimal performance and injury prevention.
Barefoot shoes vs Traditional sneakers Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com