Rigid core flooring offers superior durability and water resistance, making it ideal for homes with pets that may cause spills or accidents. Flexible core flooring provides enhanced comfort and noise reduction, which benefits both pets and owners by creating a quieter, softer surface. Choosing between rigid core and flexible core flooring depends on balancing durability needs with comfort preferences in pet-friendly environments.
Table of Comparison
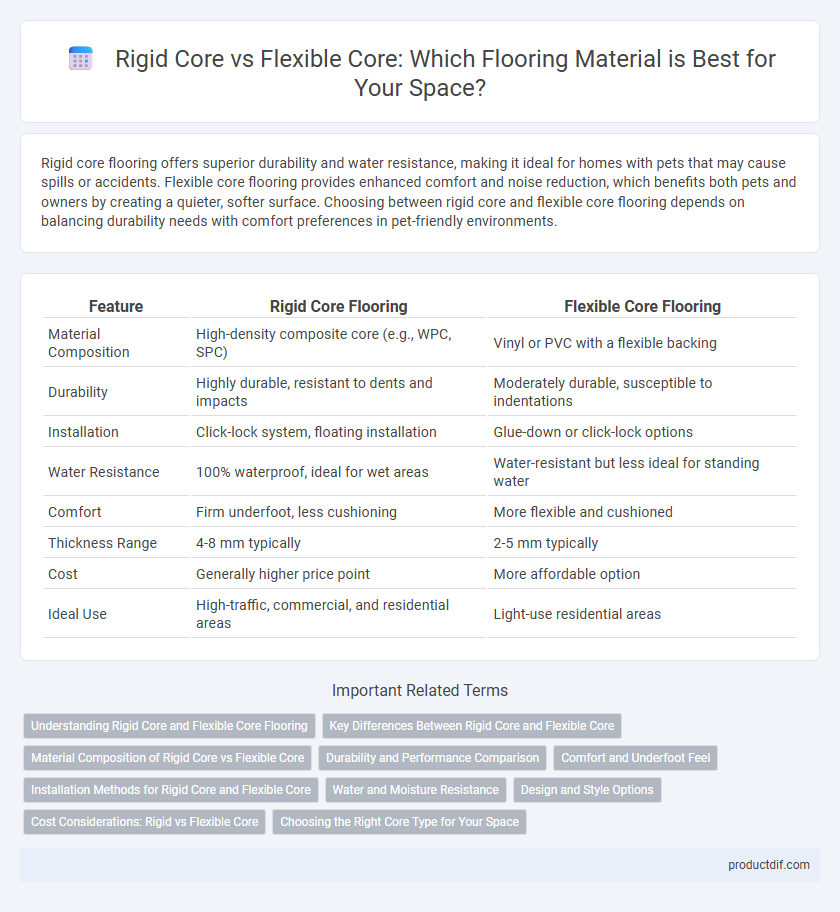
| Feature | Rigid Core Flooring | Flexible Core Flooring |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | High-density composite core (e.g., WPC, SPC) | Vinyl or PVC with a flexible backing |
| Durability | Highly durable, resistant to dents and impacts | Moderately durable, susceptible to indentations |
| Installation | Click-lock system, floating installation | Glue-down or click-lock options |
| Water Resistance | 100% waterproof, ideal for wet areas | Water-resistant but less ideal for standing water |
| Comfort | Firm underfoot, less cushioning | More flexible and cushioned |
| Thickness Range | 4-8 mm typically | 2-5 mm typically |
| Cost | Generally higher price point | More affordable option |
| Ideal Use | High-traffic, commercial, and residential areas | Light-use residential areas |
Understanding Rigid Core and Flexible Core Flooring
Rigid core flooring consists of a composite core made from materials like stone plastic composite (SPC) or wood plastic composite (WPC), offering enhanced durability, water resistance, and dimensional stability ideal for high-traffic or moisture-prone areas. Flexible core flooring is typically crafted from vinyl or similar soft materials, providing superior comfort underfoot, easier installation with click-lock or glue-down methods, and greater flexibility over uneven subfloors. Choosing between rigid core and flexible core depends on factors like durability needs, installation environment, and desired flooring comfort and resilience.
Key Differences Between Rigid Core and Flexible Core
Rigid core flooring features a solid, dense core made from materials like stone plastic composite (SPC) or wood plastic composite (WPC), providing enhanced durability, moisture resistance, and dimensional stability. Flexible core flooring, typically constructed with vinyl wrapped around felt or foam backing, offers greater flexibility, softer underfoot feel, and easier installation over uneven subfloors. Key differences include rigidity impacting water resistance and stability versus comfort and adaptability to irregular surfaces.
Material Composition of Rigid Core vs Flexible Core
Rigid Core flooring consists primarily of high-density materials like limestone composite, PVC, and WPC (Wood Plastic Composite), providing enhanced durability, water resistance, and dimensional stability. Flexible Core flooring, often made of thinner vinyl layers combined with fabric or foam backing, offers greater elasticity and comfort underfoot but is less resilient to heavy impact and moisture. These compositional differences influence performance characteristics, making Rigid Core ideal for high-traffic or moisture-prone areas, while Flexible Core suits residential spaces seeking softer flooring options.
Durability and Performance Comparison
Rigid core flooring offers superior durability with enhanced resistance to dents, scratches, and moisture, making it ideal for high-traffic areas and moisture-prone environments. Flexible core flooring provides better shock absorption and sound insulation but may be more susceptible to wear and tear over time. Performance-wise, rigid core flooring maintains its structural integrity longer, while flexible core flooring excels in comfort and ease of installation.
Comfort and Underfoot Feel
Rigid Core flooring offers exceptional durability with a firm underfoot feel, providing a solid, stable surface ideal for high-traffic areas. Flexible Core flooring enhances comfort through its softer, more cushioned texture that reduces fatigue during prolonged standing. Both materials impact the overall comfort of a space, with Flexible Core prioritizing softness and Rigid Core emphasizing structural support.
Installation Methods for Rigid Core and Flexible Core
Rigid core flooring typically features a click-lock installation system, allowing planks to snap together securely without the need for glue or nails, making it ideal for DIY projects and quick installations. Flexible core flooring often relies on a glue-down or loose-lay method, providing enhanced adaptability on uneven subfloors but generally requiring more professional installation for best results. Both installation methods are designed to optimize durability and stability based on the core composition, with rigid core offering more straightforward assembly and flexible core accommodating challenging surfaces.
Water and Moisture Resistance
Rigid core flooring, often made from materials such as WPC (Wood Plastic Composite) or SPC (Stone Plastic Composite), provides superior water and moisture resistance due to its dense core and waterproof top layer, making it ideal for areas prone to humidity like kitchens and bathrooms. Flexible core flooring, primarily composed of vinyl or laminate, offers moderate moisture resistance but may suffer damage or warping in prolonged exposure to water. Choosing rigid core flooring ensures better durability and longevity in wet environments, reducing maintenance costs and the risk of mold or mildew growth.
Design and Style Options
Rigid core flooring offers a variety of realistic wood and stone textures with enhanced durability, making it ideal for modern, high-traffic spaces seeking a sleek, contemporary aesthetic. Flexible core flooring provides greater versatility in design with options like intricate patterns, diverse colors, and softer textures that suit residential settings aiming for comfort and warmth. Both core types support extensive customization, but rigid core excels in mimicking natural materials while flexible core emphasizes creative expression through adaptable styles.
Cost Considerations: Rigid vs Flexible Core
Rigid core flooring generally has a higher upfront cost due to its durable construction and enhanced stability, making it a long-term investment for high-traffic areas. Flexible core flooring tends to be more budget-friendly initially, offering a softer feel and easier installation but may require earlier replacement in heavy-use environments. Evaluating cost considerations involves balancing initial expenses with expected durability and maintenance requirements for each flooring type.
Choosing the Right Core Type for Your Space
Rigid core flooring features a dense, high-density core made from materials like limestone composite or wood plastic composite, offering superior stability and water resistance ideal for high-traffic or moisture-prone areas. Flexible core flooring, often constructed with layers of vinyl and fiberglass, provides enhanced comfort underfoot and better sound absorption, making it suitable for residential spaces or areas requiring softer flooring. Selecting the right core type depends on factors such as room usage, moisture levels, and desired durability, ensuring optimal performance and longevity for your flooring investment.
Rigid Core vs Flexible Core Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com