Resin casting involves pouring liquid resin directly into a mold to create detailed, durable shapes ideal for jewelry and decorative items. Mold pouring typically refers to transferring materials like plaster or silicone into a mold, often used for prototypes or larger craft projects. Choosing resin casting over mold pouring enhances clarity and strength, making it preferable for fine, transparent, or intricate designs.
Table of Comparison
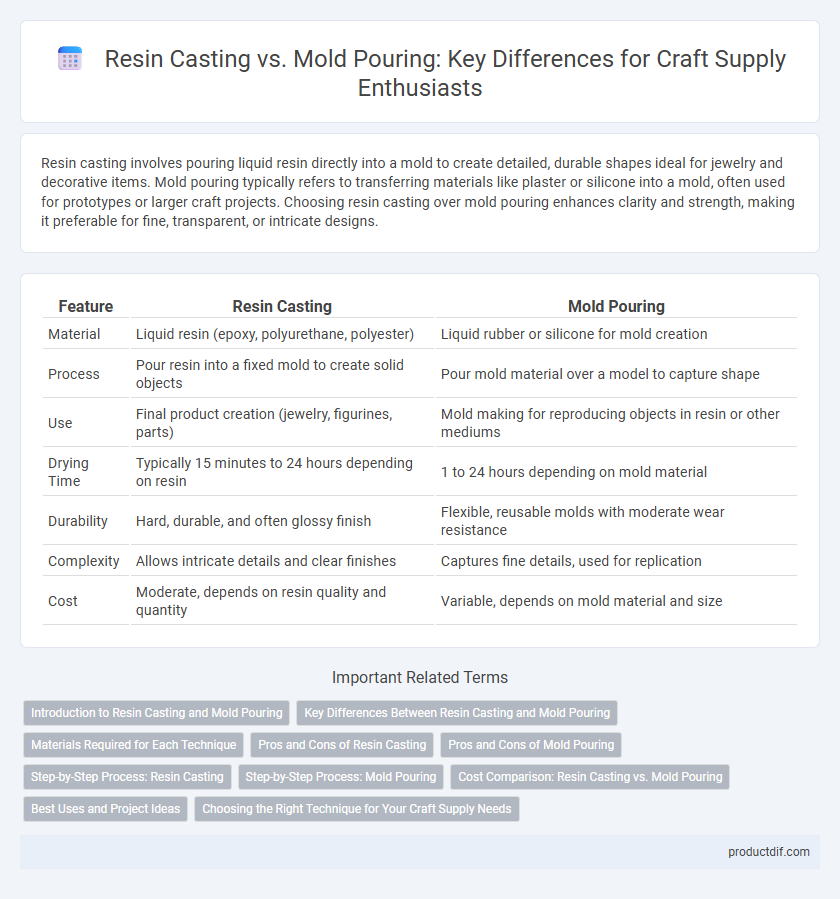
| Feature | Resin Casting | Mold Pouring |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Liquid resin (epoxy, polyurethane, polyester) | Liquid rubber or silicone for mold creation |
| Process | Pour resin into a fixed mold to create solid objects | Pour mold material over a model to capture shape |
| Use | Final product creation (jewelry, figurines, parts) | Mold making for reproducing objects in resin or other mediums |
| Drying Time | Typically 15 minutes to 24 hours depending on resin | 1 to 24 hours depending on mold material |
| Durability | Hard, durable, and often glossy finish | Flexible, reusable molds with moderate wear resistance |
| Complexity | Allows intricate details and clear finishes | Captures fine details, used for replication |
| Cost | Moderate, depends on resin quality and quantity | Variable, depends on mold material and size |
Introduction to Resin Casting and Mold Pouring
Resin casting involves pouring liquid resin into a rigid mold to create detailed and durable craft pieces, allowing for high precision and complex shapes. Mold pouring utilizes flexible molds, often silicone, to shape materials like resin or plaster, providing easy demolding and capturing fine textures. Both techniques are essential in craft supply for producing custom jewelry, figurines, and decorative items with varying levels of detail and finish.
Key Differences Between Resin Casting and Mold Pouring
Resin casting involves injecting or pouring liquid resin into a rigid mold, solidifying into detailed, durable shapes ideal for jewelry and small decorative items, while mold pouring typically uses flexible molds and is suited for materials like plaster or silicone, emphasizing ease of release and replication. Resin casting requires precise mixing ratios and curing times to achieve optimal results, whereas mold pouring often allows more variation in materials and quicker setting times depending on the substance used. The key differences lie in material compatibility, mold type, and the level of detail each method can capture, making resin casting preferable for fine-detail projects and mold pouring better for bulk, simpler forms.
Materials Required for Each Technique
Resin casting requires liquid resin, hardener, mixing cups, and stirring sticks, while mold pouring primarily involves silicone or latex molds and casting materials like plaster or resin. Each technique demands precise preparation tools such as gloves and measuring devices for accurate resin-to-hardener ratios or mold filling. Material choice impacts curing time, finish quality, and the flexibility of the final craft product.
Pros and Cons of Resin Casting
Resin casting offers high detail accuracy and durability, making it ideal for intricate craft projects and custom jewelry, but it requires careful mixing and curing times, which can be time-consuming and prone to errors if not handled properly. The material's strength and finish quality create a polished, professional look, though resin chemicals may pose health risks without adequate ventilation and protective gear. While resin casting allows for multiple reproductions from a single mold, it generally involves higher costs and more specialized equipment compared to simpler mold pouring methods.
Pros and Cons of Mold Pouring
Mold pouring offers the advantage of creating detailed and consistent shapes, making it ideal for mass production of resin crafts. However, it requires precise mold preparation and can result in air bubbles or uneven surfaces if not carefully managed. The process can also be time-consuming due to curing times and potential mold wear, impacting overall efficiency in craft supply projects.
Step-by-Step Process: Resin Casting
Resin casting involves mixing two components, resin and hardener, in precise ratios before pouring the mixture into a silicone mold to cure. The process requires meticulous preparation of the mold, degassing the resin to remove bubbles, and allowing adequate curing time, typically ranging from several hours to days depending on resin type. This technique offers high detail reproduction and durability, making it ideal for intricate crafts and jewelry creation.
Step-by-Step Process: Mold Pouring
Mold pouring involves carefully mixing resin components before slowly pouring the mixture into a pre-prepared mold to avoid air bubbles, ensuring a clean and detailed cast. The process requires precise temperature control and timing to allow proper curing, typically ranging from several hours to overnight depending on resin type. After curing, the mold is gently removed to reveal the final resin casting, ready for sanding, painting, or additional finishing.
Cost Comparison: Resin Casting vs. Mold Pouring
Resin casting generally incurs higher initial material costs due to specialized resins and pigments, but offers greater precision and durability for intricate designs. Mold pouring often reduces upfront expenses by utilizing reusable molds and more affordable base materials, making it cost-effective for large-volume production. Evaluating long-term output and project scale is essential to determine the most economical choice between resin casting and mold pouring.
Best Uses and Project Ideas
Resin casting offers precision and durability, making it ideal for detailed jewelry, intricate figurines, and custom molds requiring high clarity and strength. Mold pouring suits larger projects like garden ornaments, soap bars, or concrete replicas due to its ease in handling bulk materials and ability to fill complex shapes. Choosing between resin casting and mold pouring depends on project scale and desired finish, with resin excelling in fine detail and mold pouring in volume production.
Choosing the Right Technique for Your Craft Supply Needs
Resin casting offers precise detail and durability, ideal for small, intricate craft projects requiring high-quality finishes. Mold pouring suits larger or repetitive designs, providing cost-effective production and consistent shapes with less manual effort. Selecting the right technique depends on project complexity, volume, and desired texture to maximize efficiency and craftsmanship.
Resin casting vs Mold pouring Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com