Physical exfoliants use abrasive particles to manually remove dead skin cells, providing immediate smoothness but sometimes causing irritation on sensitive skin. Chemical exfoliants rely on ingredients like alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs) or beta hydroxy acids (BHAs) to dissolve dead skin cells gently and improve skin texture over time. Choosing between physical and chemical exfoliants depends on skin type, sensitivity, and desired exfoliation intensity.
Table of Comparison
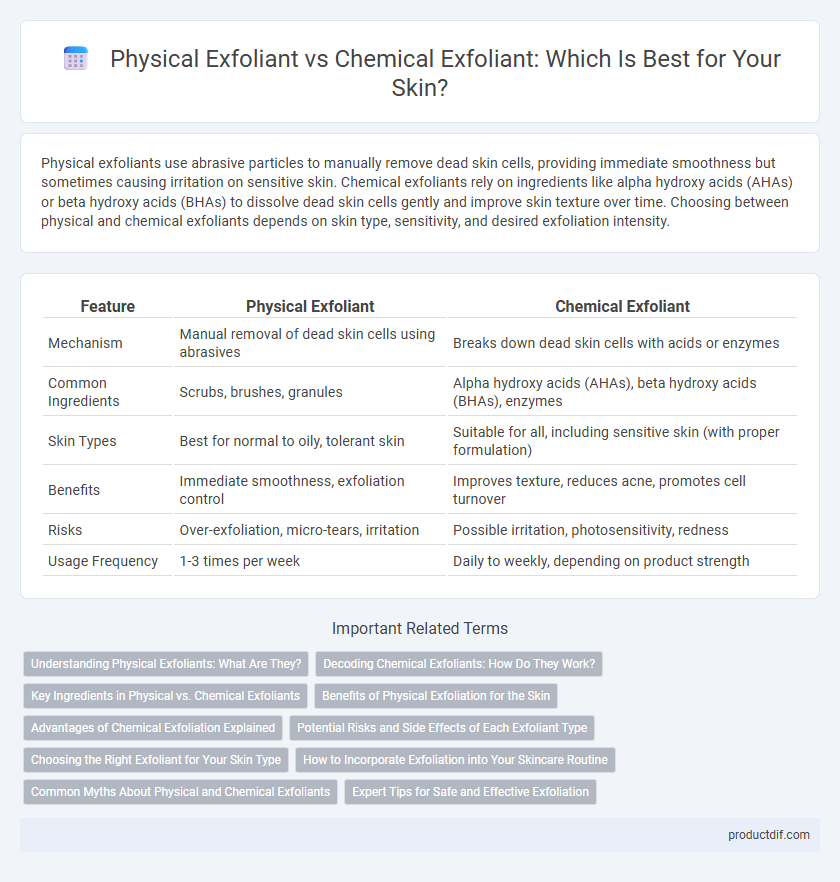
| Feature | Physical Exfoliant | Chemical Exfoliant |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanism | Manual removal of dead skin cells using abrasives | Breaks down dead skin cells with acids or enzymes |
| Common Ingredients | Scrubs, brushes, granules | Alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs), beta hydroxy acids (BHAs), enzymes |
| Skin Types | Best for normal to oily, tolerant skin | Suitable for all, including sensitive skin (with proper formulation) |
| Benefits | Immediate smoothness, exfoliation control | Improves texture, reduces acne, promotes cell turnover |
| Risks | Over-exfoliation, micro-tears, irritation | Possible irritation, photosensitivity, redness |
| Usage Frequency | 1-3 times per week | Daily to weekly, depending on product strength |
Understanding Physical Exfoliants: What Are They?
Physical exfoliants are skincare products that use abrasive particles or textured surfaces to manually remove dead skin cells from the surface of the skin. Common ingredients in physical exfoliants include natural elements like crushed walnut shells, sugar, salt, and synthetic microbeads, designed to smooth rough texture and enhance skin radiance. These exfoliants provide immediate results but require gentle application to avoid microtears and irritation, especially on sensitive skin types.
Decoding Chemical Exfoliants: How Do They Work?
Chemical exfoliants work by dissolving dead skin cells through active ingredients like alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs) and beta hydroxy acids (BHAs), which penetrate the skin's surface to promote cell turnover. AHAs such as glycolic acid target the skin's outer layer to improve texture and radiance, while BHAs like salicylic acid penetrate pores to reduce oil and prevent breakouts. This mechanism contrasts with physical exfoliants that manually scrub the skin, making chemical exfoliants a more precise and often gentler option for renewing skin.
Key Ingredients in Physical vs. Chemical Exfoliants
Physical exfoliants contain key ingredients such as microbeads, sugar, salt, and crushed nutshells that manually buff away dead skin cells through abrasion. Chemical exfoliants rely on active ingredients like alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs) including glycolic acid and lactic acid, beta hydroxy acids (BHAs) like salicylic acid, and enzymes from fruits to dissolve dead skin cells and promote cell turnover. Choosing between physical or chemical exfoliants depends on skin sensitivity and desired exfoliation depth, with chemical exfoliants offering deeper, more uniform results.
Benefits of Physical Exfoliation for the Skin
Physical exfoliation effectively removes dead skin cells through manual abrasion, promoting smoother and brighter skin texture. It enhances circulation and supports faster cell turnover, resulting in a refreshed and rejuvenated complexion. Regular use of physical exfoliants helps unclog pores, reduce the occurrence of acne, and improves the absorption of skincare products.
Advantages of Chemical Exfoliation Explained
Chemical exfoliants, such as alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs) and beta hydroxy acids (BHAs), penetrate the skin to dissolve dead skin cells gently and promote cell turnover without abrasion. They offer advantages like improved texture, reduced acne, and enhanced absorption of skincare products, making them suitable for sensitive skin types. Unlike physical exfoliants, chemical exfoliants provide more even exfoliation and long-term benefits by stimulating collagen production and evening out skin tone.
Potential Risks and Side Effects of Each Exfoliant Type
Physical exfoliants, composed of abrasive particles like crushed walnut shells or microbeads, can cause micro-tears and irritation, especially on sensitive or acne-prone skin, leading to redness and inflammation. Chemical exfoliants, utilizing acids such as alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs) or beta hydroxy acids (BHAs), may cause irritation, increased photosensitivity, and allergic reactions if overused or applied improperly. Both exfoliant types require cautious use tailored to individual skin types to minimize risks such as barrier disruption and heightened sensitivity.
Choosing the Right Exfoliant for Your Skin Type
Physical exfoliants use granular particles or brushes to manually slough off dead skin cells, making them ideal for normal to oily skin types that tolerate texture without irritation. Chemical exfoliants utilize ingredients like alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs) or beta hydroxy acids (BHAs) to dissolve dead skin cells and are preferred for sensitive or dry skin due to their gentle, controlled action. Selecting the right exfoliant depends on your skin's sensitivity, texture, and specific concerns, ensuring effective renewal without causing irritation or damage.
How to Incorporate Exfoliation into Your Skincare Routine
Incorporate physical exfoliants into your skincare routine by using them 1-2 times per week to gently slough off dead skin cells, focusing on areas prone to dryness or dullness while avoiding over-exfoliation to prevent irritation. Chemical exfoliants containing AHAs, BHAs, or PHAs can be applied 2-3 times weekly, allowing for deeper cellular turnover and improved skin texture, with gradual introduction to monitor sensitivity. Always follow exfoliation with a hydrating serum and broad-spectrum sunscreen to protect the newly revealed skin and maintain barrier health.
Common Myths About Physical and Chemical Exfoliants
Physical exfoliants are often mistaken for being harsher on the skin, yet many contain gentle natural ingredients like jojoba beads that effectively remove dead skin without irritation. Chemical exfoliants, such as AHAs and BHAs, are commonly believed to cause excessive dryness, but when used properly, they promote cell turnover and improve skin texture without damaging the skin barrier. Misconceptions also include the idea that physical exfoliation is better for sensitive skin, while chemical exfoliation is only for oily or acne-prone types, even though tailored formulations exist for all skin types.
Expert Tips for Safe and Effective Exfoliation
Physical exfoliants use granular particles or tools to manually remove dead skin cells, while chemical exfoliants rely on acids like AHAs and BHAs to dissolve cellular bonds for smoother skin. Experts recommend patch testing chemical exfoliants to avoid irritation and using physical exfoliants no more than twice weekly to prevent microtears and inflammation. Combining gentle physical scrubs with low-concentration chemical exfoliants can optimize exfoliation benefits while maintaining skin barrier integrity.
Physical Exfoliant vs Chemical Exfoliant Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com