Chemical peels use acids to dissolve dead skin cells and stimulate collagen production, offering deeper skin renewal compared to physical exfoliation. Physical exfoliation involves manually scrubbing the skin with abrasive particles to remove surface dead cells, which may cause irritation or microtears if overused. Choosing between chemical peels and physical exfoliation depends on skin type, sensitivity, and desired results for smoother, brighter skin.
Table of Comparison
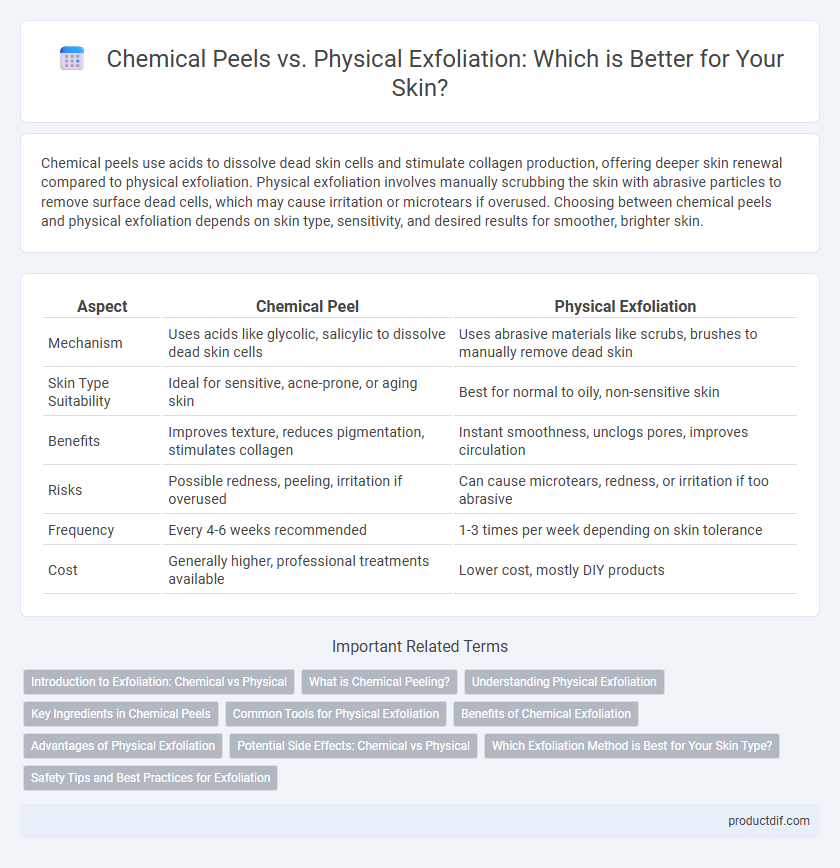
| Aspect | Chemical Peel | Physical Exfoliation |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanism | Uses acids like glycolic, salicylic to dissolve dead skin cells | Uses abrasive materials like scrubs, brushes to manually remove dead skin |
| Skin Type Suitability | Ideal for sensitive, acne-prone, or aging skin | Best for normal to oily, non-sensitive skin |
| Benefits | Improves texture, reduces pigmentation, stimulates collagen | Instant smoothness, unclogs pores, improves circulation |
| Risks | Possible redness, peeling, irritation if overused | Can cause microtears, redness, or irritation if too abrasive |
| Frequency | Every 4-6 weeks recommended | 1-3 times per week depending on skin tolerance |
| Cost | Generally higher, professional treatments available | Lower cost, mostly DIY products |
Introduction to Exfoliation: Chemical vs Physical
Exfoliation involves removing dead skin cells to reveal a smoother, brighter complexion, achieved through chemical or physical methods. Chemical peels use acids like alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs) and beta hydroxy acids (BHAs) to dissolve bonds between dead cells, promoting cell turnover without abrasion. Physical exfoliation employs mechanical methods such as scrubs or brushes to manually slough off the skin surface, providing immediate texture improvement but with a higher risk of irritation for sensitive skin.
What is Chemical Peeling?
Chemical peeling involves applying a solution containing acids such as glycolic, salicylic, or lactic acid to the skin, which induces controlled exfoliation by dissolving the bonds between dead skin cells. This process promotes cell turnover, improves skin texture, reduces hyperpigmentation, and stimulates collagen production for a rejuvenated appearance. Unlike physical exfoliation, chemical peels penetrate deeper layers of the skin, offering more effective treatment for acne scars, fine lines, and uneven tone.
Understanding Physical Exfoliation
Physical exfoliation involves the mechanical removal of dead skin cells using abrasive materials such as scrubs, brushes, or exfoliating gloves. This method helps to improve skin texture and promote cell turnover by physically sloughing off surface impurities. Unlike chemical peels, physical exfoliation provides immediate results but can cause irritation if overused or applied too harshly on sensitive skin.
Key Ingredients in Chemical Peels
Chemical peels rely on key active ingredients such as alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs) like glycolic acid and lactic acid, beta hydroxy acids (BHAs) such as salicylic acid, and trichloroacetic acid (TCA) to chemically exfoliate the skin by dissolving dead skin cells and promoting cell turnover. These ingredients penetrate deeply to target uneven texture, hyperpigmentation, and acne, producing more dramatic and longer-lasting results compared to physical exfoliation methods like scrubs or brushes. The controlled chemical action in peels reduces the risk of microtears commonly associated with physical exfoliants while enhancing collagen production for smoother, brighter skin.
Common Tools for Physical Exfoliation
Common tools for physical exfoliation include facial scrubs with fine abrasive particles, cleansing brushes, and exfoliating gloves, which mechanically remove dead skin cells to reveal smoother skin. Microdermabrasion devices use a combination of abrasive crystals and suction to deeply exfoliate and stimulate collagen production. These methods offer immediate texture improvement but require careful use to avoid skin irritation compared to chemical peels.
Benefits of Chemical Exfoliation
Chemical exfoliation uses acids like alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs) and beta hydroxy acids (BHAs) to deeply penetrate and dissolve dead skin cells, resulting in smoother texture and improved skin tone. This method promotes collagen production and enhances cell turnover, reducing fine lines, acne scars, and hyperpigmentation more effectively than physical scrubs. Unlike physical exfoliation, chemical peels minimize the risk of microtears and irritation, making them suitable for sensitive and acne-prone skin types.
Advantages of Physical Exfoliation
Physical exfoliation offers immediate removal of dead skin cells through gentle abrasion, enhancing skin texture and promoting a radiant complexion without the use of chemicals. It allows precise control over the exfoliation intensity, reducing the risk of irritation for sensitive skin types compared to chemical peels. Ingredients like jojoba beads, sugar, and apricot kernels provide natural exfoliation while stimulating circulation and supporting cell turnover for healthier skin.
Potential Side Effects: Chemical vs Physical
Chemical peels may cause redness, irritation, and peeling due to the acids penetrating the skin's surface, with a higher risk of hyperpigmentation or scarring if improperly applied. Physical exfoliation, using abrasive particles or tools, can lead to microtears, increased sensitivity, and inflammation, especially on sensitive or acne-prone skin. Both methods carry potential side effects, making it essential to choose based on skin type and consult a dermatologist for personalized recommendations.
Which Exfoliation Method is Best for Your Skin Type?
Chemical peels utilize acids like alpha-hydroxy acid (AHA) or beta-hydroxy acid (BHA) to dissolve dead skin cells, making them ideal for oily, acne-prone, or uneven skin types due to their ability to deeply penetrate pores and improve texture. Physical exfoliation, involving scrubs with granules or brushes, is better suited for resilient skin without inflammation, as overuse can cause microtears or irritation, especially in sensitive or rosacea-prone skin. Choosing the right exfoliation method depends on skin sensitivity, issues like acne or hyperpigmentation, and desired results, with chemical peels offering more controlled, customizable treatments and physical exfoliation providing immediate smoothing effects.
Safety Tips and Best Practices for Exfoliation
Chemical peel treatments involve the controlled application of acids like glycolic or salicylic acid to remove dead skin cells, promoting smoother skin, while physical exfoliation uses abrasive tools or scrubs to manually slough off the surface layer. To ensure safety during exfoliation, always perform a patch test before chemical peels, avoid over-exfoliating more than 2-3 times per week, and moisturize deeply after treatment to maintain the skin barrier. Avoid combining chemical peels with harsh physical exfoliants simultaneously to prevent irritation, and always apply broad-spectrum sunscreen daily to protect sensitized skin from UV damage.
Chemical Peel vs Physical Exfoliation Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com