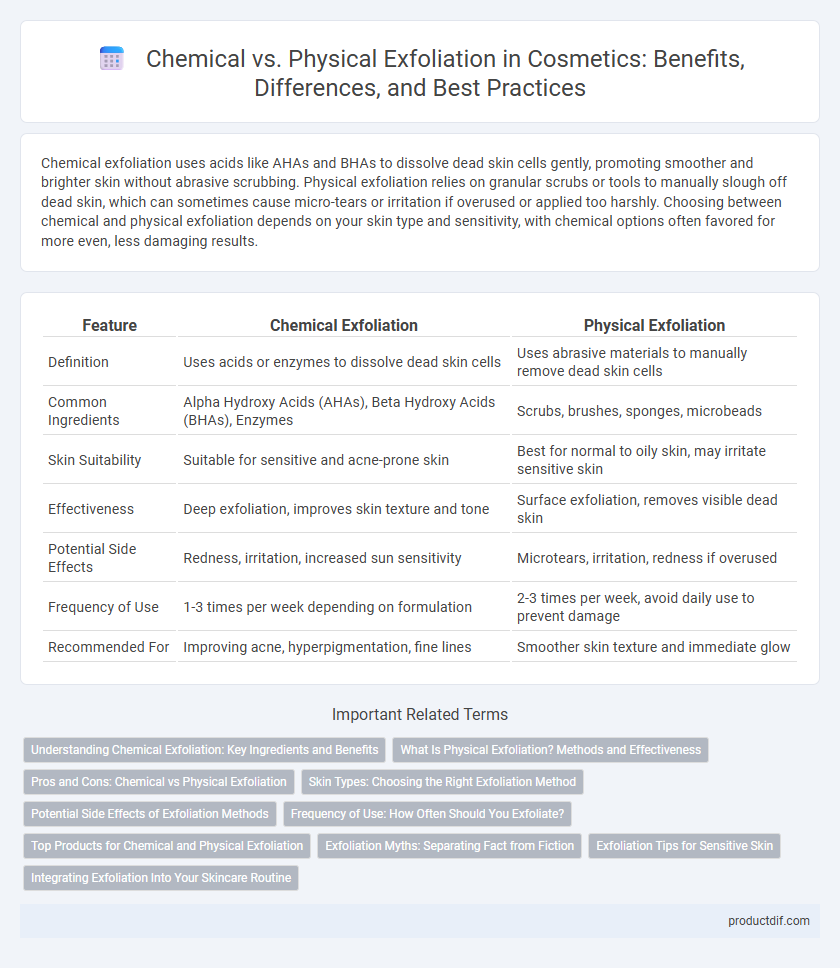
Chemical exfoliation uses acids like AHAs and BHAs to dissolve dead skin cells gently, promoting smoother and brighter skin without abrasive scrubbing. Physical exfoliation relies on granular scrubs or tools to manually slough off dead skin, which can sometimes cause micro-tears or irritation if overused or applied too harshly. Choosing between chemical and physical exfoliation depends on your skin type and sensitivity, with chemical options often favored for more even, less damaging results.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Chemical Exfoliation | Physical Exfoliation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Uses acids or enzymes to dissolve dead skin cells | Uses abrasive materials to manually remove dead skin cells |
| Common Ingredients | Alpha Hydroxy Acids (AHAs), Beta Hydroxy Acids (BHAs), Enzymes | Scrubs, brushes, sponges, microbeads |
| Skin Suitability | Suitable for sensitive and acne-prone skin | Best for normal to oily skin, may irritate sensitive skin |
| Effectiveness | Deep exfoliation, improves skin texture and tone | Surface exfoliation, removes visible dead skin |
| Potential Side Effects | Redness, irritation, increased sun sensitivity | Microtears, irritation, redness if overused |
| Frequency of Use | 1-3 times per week depending on formulation | 2-3 times per week, avoid daily use to prevent damage |
| Recommended For | Improving acne, hyperpigmentation, fine lines | Smoother skin texture and immediate glow |
Understanding Chemical Exfoliation: Key Ingredients and Benefits
Chemical exfoliation utilizes active ingredients such as alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs), beta hydroxy acids (BHAs), and enzymes to dissolve dead skin cells gently and promote cell turnover. AHAs like glycolic acid target surface layers for improved texture and brightness, while BHAs such as salicylic acid penetrate pores to reduce acne and control oil. Benefits include smoother skin, reduced hyperpigmentation, and enhanced absorption of skincare products without the mechanical irritation associated with physical exfoliants.
What Is Physical Exfoliation? Methods and Effectiveness
Physical exfoliation involves the manual removal of dead skin cells using abrasive materials such as scrubs, brushes, or exfoliating gloves to enhance skin texture and promote cell renewal. Common methods include using sugar or salt scrubs, microdermabrasion devices, and exfoliating pads, which mechanically slough off the outer skin layer. This technique effectively improves skin smoothness and brightness but should be used cautiously to avoid irritation, especially for sensitive or acne-prone skin types.
Pros and Cons: Chemical vs Physical Exfoliation
Chemical exfoliation uses acids like AHAs and BHAs to dissolve dead skin cells, offering deeper, more even exfoliation and improved skin texture but may cause irritation or sensitivity in sensitive skin types. Physical exfoliation, with scrubs or brushes, provides immediate smoothness through manual removal but can be abrasive and cause micro-tears or inflammation if overused. Choosing between chemical and physical exfoliation depends on skin type, sensitivity, and desired results, balancing effectiveness against potential irritation.
Skin Types: Choosing the Right Exfoliation Method
Chemical exfoliation uses acids like AHAs and BHAs to dissolve dead skin cells, making it ideal for sensitive or acne-prone skin due to its gentle, even exfoliation. Physical exfoliation involves scrubs or brushes that manually remove dead skin but may cause irritation on sensitive or dry skin types. Oily and combination skin often benefit from chemical exfoliants for unclogging pores, while normal skin can tolerate physical exfoliation for smoother texture.
Potential Side Effects of Exfoliation Methods
Chemical exfoliation, using acids like AHAs or BHAs, can cause irritation, redness, and increased sensitivity, especially for sensitive skin types or when overused. Physical exfoliation, involving scrubs or brushes, may lead to microtears, inflammation, and worsening of acne or rosacea due to abrasive action. Choosing the right exfoliation method and frequency is essential to minimize side effects and maintain skin barrier health.
Frequency of Use: How Often Should You Exfoliate?
Chemical exfoliation using AHAs or BHAs can typically be performed 2-3 times per week, depending on skin sensitivity and product concentration, promoting cell turnover and improving texture without physical abrasion. Physical exfoliation, involving scrubs or brushes, is best limited to 1-2 times weekly to prevent micro-tears and irritation, especially on sensitive or acne-prone skin. Consistent exfoliation frequency tailored to skin type enhances results while maintaining skin barrier integrity and preventing over-exfoliation.
Top Products for Chemical and Physical Exfoliation
Top products for chemical exfoliation include alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs) like glycolic acid serums and beta hydroxy acids (BHAs) such as salicylic acid toners, which effectively remove dead skin cells by dissolving the bonds between them. Leading physical exfoliants feature gentle scrubs with ingredients like jojoba beads and rice bran powder, designed to manually slough off surface debris without damaging skin. Both types of exfoliants are essential in skincare routines, with chemical exfoliants often preferred for deeper penetration and physical exfoliants for immediate texture refinement.
Exfoliation Myths: Separating Fact from Fiction
Chemical exfoliation uses acids like AHAs and BHAs to dissolve dead skin cells gently, while physical exfoliation relies on abrasive particles or tools to manually slough off dead skin. A common myth claims physical exfoliation is always harsher, but when used correctly, it can be just as effective and safe as chemical methods. Understanding skin type compatibility and proper exfoliation frequency is key to debunking the misconception that one method universally outperforms the other.
Exfoliation Tips for Sensitive Skin
For sensitive skin, chemical exfoliation using alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs) like lactic acid is preferred due to its gentle, controlled removal of dead skin cells without abrasive friction. Physical exfoliation with fine particles or soft brushes can cause microtears and irritation, making it less suitable for delicate skin types. Incorporating products with soothing ingredients such as aloe vera or chamomile alongside chemical exfoliants enhances skin tolerance and minimizes redness.
Integrating Exfoliation Into Your Skincare Routine
Integrating exfoliation into your skincare routine requires understanding the benefits of chemical versus physical exfoliation, where chemical exfoliants like AHAs and BHAs dissolve dead skin cells for a smoother texture, while physical exfoliants use granular particles to manually slough off dead skin. For sensitive or acne-prone skin, chemical exfoliation offers a gentler yet effective option, promoting cell turnover without irritation. Optimal results come from balancing exfoliation frequency and selecting the exfoliant type based on skin type and specific concerns to maintain healthy, radiant skin.
Chemical Exfoliation vs Physical Exfoliation Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com