Plant-derived surfactants offer eco-friendly cleaning power by breaking down dirt and oils using renewable resources, making them biodegradable and less toxic to aquatic life. In contrast, petroleum-derived surfactants, sourced from non-renewable fossil fuels, tend to persist in the environment and may cause pollution and health risks. Choosing plant-derived surfactants in pet cleaning products ensures safer use for pets and reduces environmental impact.
Table of Comparison
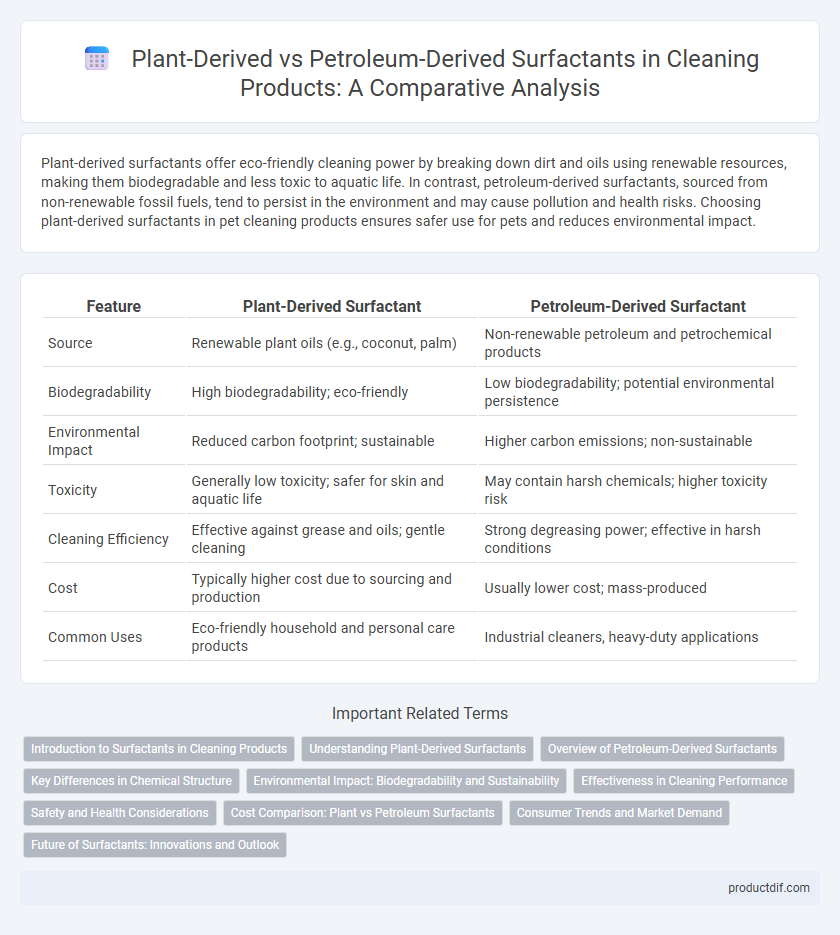
| Feature | Plant-Derived Surfactant | Petroleum-Derived Surfactant |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Renewable plant oils (e.g., coconut, palm) | Non-renewable petroleum and petrochemical products |
| Biodegradability | High biodegradability; eco-friendly | Low biodegradability; potential environmental persistence |
| Environmental Impact | Reduced carbon footprint; sustainable | Higher carbon emissions; non-sustainable |
| Toxicity | Generally low toxicity; safer for skin and aquatic life | May contain harsh chemicals; higher toxicity risk |
| Cleaning Efficiency | Effective against grease and oils; gentle cleaning | Strong degreasing power; effective in harsh conditions |
| Cost | Typically higher cost due to sourcing and production | Usually lower cost; mass-produced |
| Common Uses | Eco-friendly household and personal care products | Industrial cleaners, heavy-duty applications |
Introduction to Surfactants in Cleaning Products
Plant-derived surfactants in cleaning products offer biodegradable and renewable alternatives to traditional petroleum-derived surfactants, reducing environmental impact. These natural surfactants enhance dirt and grease removal through effective emulsification while maintaining skin compatibility and lower toxicity. Increasing consumer demand for eco-friendly formulations drives innovation in plant-based surfactant technologies within the cleaning industry.
Understanding Plant-Derived Surfactants
Plant-derived surfactants, sourced from renewable materials such as coconut oil, corn, and sugar, offer biodegradable and eco-friendly alternatives to petroleum-derived surfactants known for their synthetic origin and environmental persistence. These bio-based surfactants feature superior skin compatibility and lower toxicity, making them ideal for sustainable cleaning products that reduce ecological impact. Their molecular structure promotes effective foaming and emulsification while ensuring faster degradation in wastewater treatment systems, supporting greener cleaning solutions.
Overview of Petroleum-Derived Surfactants
Petroleum-derived surfactants, commonly used in many cleaning products, are synthesized from non-renewable fossil fuels such as crude oil and natural gas. These surfactants offer strong cleaning power and affordability but often pose environmental challenges due to their slow biodegradability and potential toxicity. Their widespread use contributes to pollution and resource depletion, driving increased interest in more sustainable, plant-derived alternatives.
Key Differences in Chemical Structure
Plant-derived surfactants are primarily composed of natural molecules such as fatty acid esters and sugars, featuring biodegradable and renewable chemical structures that enhance environmental compatibility. Petroleum-derived surfactants consist mainly of synthetic hydrocarbons and petrochemical compounds with more complex, non-biodegradable molecular frameworks derived from fossil fuels. These fundamental chemical structure differences influence their biodegradability, toxicity, and overall sustainability in cleaning product formulations.
Environmental Impact: Biodegradability and Sustainability
Plant-derived surfactants exhibit higher biodegradability rates and lower toxicity, promoting environmental sustainability by reducing persistent pollution and ecological harm. Petroleum-derived surfactants, sourced from non-renewable fossil fuels, contribute to long-term environmental degradation due to their slower breakdown and accumulation in ecosystems. Choosing plant-based options supports sustainable resource use and minimizes carbon footprint, aligning with eco-friendly cleaning product goals.
Effectiveness in Cleaning Performance
Plant-derived surfactants exhibit superior biodegradability and lower toxicity, contributing to environmentally friendly cleaning performance without compromising effectiveness. Petroleum-derived surfactants often provide stronger grease-cutting power due to their synthetic nature, resulting in faster soil removal in heavy-duty cleaning tasks. Efficiency in cleaning performance depends on the formulation balance, with plant-based surfactants being optimal for sensitive surfaces and petroleum-based surfactants excelling in industrial-strength applications.
Safety and Health Considerations
Plant-derived surfactants offer enhanced safety and health benefits due to their biodegradability and lower toxicity compared to petroleum-derived surfactants, which can contain harmful chemicals and pose environmental risks. These natural surfactants reduce skin irritation and allergic reactions, making them suitable for sensitive skin and household use. Choosing plant-based surfactants supports safer indoor air quality and reduces long-term health hazards associated with synthetic chemical exposure.
Cost Comparison: Plant vs Petroleum Surfactants
Plant-derived surfactants typically incur higher production costs due to the extraction and processing of renewable raw materials such as coconut oil, palm oil, and corn. Petroleum-derived surfactants benefit from extensive refining infrastructure and lower raw material expenses, resulting in a generally lower cost per unit for manufacturers. However, fluctuations in petroleum prices and growing environmental regulations may influence long-term cost stability, positioning plant-based surfactants as increasingly competitive in sustainable cleaning product markets.
Consumer Trends and Market Demand
Plant-derived surfactants are gaining significant traction in the cleaning product industry due to increasing consumer demand for sustainable and eco-friendly ingredients. Market data shows a rising preference among environmentally conscious consumers for biodegradable, non-toxic surfactants sourced from renewable resources like coconut or palm oil. In contrast, petroleum-derived surfactants face declining demand amid growing concerns over environmental pollution and fossil fuel dependency, prompting manufacturers to shift toward greener alternatives.
Future of Surfactants: Innovations and Outlook
Plant-derived surfactants are gaining prominence due to their biodegradability, lower toxicity, and renewable sourcing, which align with global sustainability goals and regulatory trends pushing for greener alternatives. Innovations in biotechnology enable the development of more efficient, cost-effective plant-based surfactants with enhanced performance, such as improved foaming and emulsifying properties, surpassing traditional petroleum-derived options. The future outlook predicts increased adoption of bio-based surfactants driven by consumer demand for eco-friendly cleaning products and advances in enzymatic synthesis and microbial fermentation technologies.
Plant-derived surfactant vs Petroleum-derived surfactant Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com