Antibacterial products specifically target bacteria, killing or inhibiting their growth to reduce harmful bacterial presence on surfaces. Antimicrobial products offer a broader spectrum of protection by targeting a wide range of microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and mold. Choosing between antibacterial and antimicrobial cleaners depends on the types of pathogens you want to eliminate for a safer, more hygienic environment.
Table of Comparison
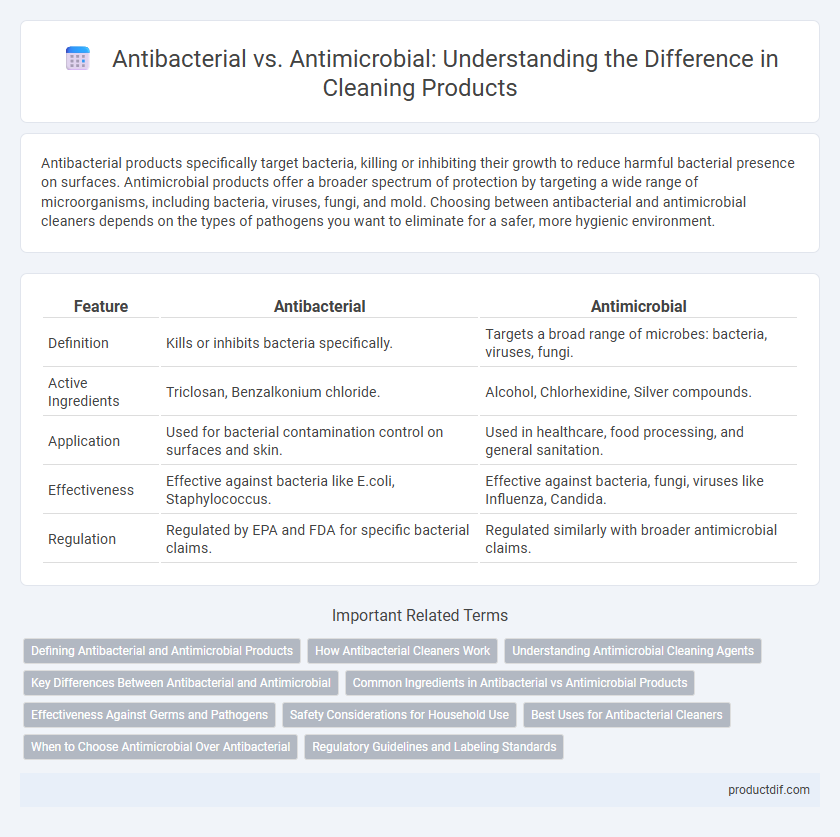
| Feature | Antibacterial | Antimicrobial |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Kills or inhibits bacteria specifically. | Targets a broad range of microbes: bacteria, viruses, fungi. |
| Active Ingredients | Triclosan, Benzalkonium chloride. | Alcohol, Chlorhexidine, Silver compounds. |
| Application | Used for bacterial contamination control on surfaces and skin. | Used in healthcare, food processing, and general sanitation. |
| Effectiveness | Effective against bacteria like E.coli, Staphylococcus. | Effective against bacteria, fungi, viruses like Influenza, Candida. |
| Regulation | Regulated by EPA and FDA for specific bacterial claims. | Regulated similarly with broader antimicrobial claims. |
Defining Antibacterial and Antimicrobial Products
Antibacterial products are specially formulated to eliminate or inhibit the growth of bacteria, targeting specific bacterial strains to reduce infection risk and contamination. Antimicrobial products exhibit a broader spectrum of activity, effectively combating bacteria, viruses, fungi, and other microorganisms to enhance overall hygiene and surface safety. Understanding these distinctions helps in selecting the appropriate product for specific cleaning needs and microbial threats.
How Antibacterial Cleaners Work
Antibacterial cleaners target and eliminate bacteria by disrupting their cell walls or interfering with essential enzymes, effectively preventing bacterial growth and reproduction. These products contain active ingredients such as triclosan, benzalkonium chloride, or alcohol-based compounds that kill or inhibit harmful bacteria on surfaces. Unlike broad-spectrum antimicrobial cleaners, antibacterial cleaners specifically focus on bacteria, making them ideal for sanitizing kitchens, bathrooms, and other high-contact areas prone to bacterial contamination.
Understanding Antimicrobial Cleaning Agents
Antimicrobial cleaning agents target a broad spectrum of microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and spores, while antibacterial products specifically eliminate bacteria. Understanding the difference enhances effective disinfection strategies in healthcare, food processing, and household environments. Selecting the appropriate antimicrobial agent ensures comprehensive surface hygiene and reduces the risk of cross-contamination.
Key Differences Between Antibacterial and Antimicrobial
Antibacterial products specifically target bacteria, aiming to kill or inhibit their growth, while antimicrobial products have a broader spectrum, effective against bacteria, viruses, fungi, and sometimes protozoa. Antibacterial agents often contain ingredients like triclosan or benzalkonium chloride, whereas antimicrobials may include compounds such as alcohol, hydrogen peroxide, or silver ions. Understanding these differences helps in selecting the appropriate cleaning product based on the desired microbial protection.
Common Ingredients in Antibacterial vs Antimicrobial Products
Antibacterial products frequently contain active ingredients such as triclosan, benzalkonium chloride, and chlorhexidine, which specifically target and kill bacteria. Antimicrobial products often include a broader range of agents like alcohol, hydrogen peroxide, and silver ions, effective against bacteria, viruses, fungi, and other microbes. Understanding these ingredient differences helps consumers select appropriate cleaning products for targeted disinfection and infection control.
Effectiveness Against Germs and Pathogens
Antibacterial products specifically target bacteria, effectively eliminating or inhibiting their growth to reduce the risk of bacterial infections. Antimicrobial agents have a broader spectrum, working against bacteria, viruses, fungi, and other pathogens, offering comprehensive protection in various cleaning scenarios. Choosing between antibacterial and antimicrobial cleaning products depends on the specific environment and the range of germs or pathogens that require control for optimal hygiene.
Safety Considerations for Household Use
Antibacterial cleaners specifically target bacteria, while antimicrobial products are effective against a broader range of microorganisms, including fungi and viruses. When selecting household cleaning products, consider the potential for skin irritation and respiratory sensitivity, especially in households with children or pets. Opting for EPA-registered agents with clear safety labels ensures effective germ control without compromising indoor air quality or user health.
Best Uses for Antibacterial Cleaners
Antibacterial cleaners target specific bacteria, making them ideal for high-touch surfaces prone to bacterial contamination, such as kitchen counters, bathroom fixtures, and cutting boards. These products are especially effective in healthcare settings and food preparation areas where controlling bacterial spread is crucial for preventing infections. While antimicrobial cleaners have a broader spectrum against various microbes, antibacterial formulations provide focused efficiency against bacteria, optimizing disinfection in environments where bacterial pathogens pose the greatest risk.
When to Choose Antimicrobial Over Antibacterial
Antimicrobial cleaning products target a broader spectrum of microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and molds, making them ideal for environments requiring comprehensive disinfection such as hospitals and food processing areas. Antibacterial products specifically eliminate bacteria but may not be effective against other pathogens, limiting their use in high-risk or multi-contaminant settings. Choose antimicrobial cleaners when diverse microbial threats pose a health risk or when preventing the spread of infection from various sources is critical.
Regulatory Guidelines and Labeling Standards
Antibacterial and antimicrobial cleaning products are regulated under distinct guidelines that define allowable claims and active ingredients to ensure consumer safety. Regulatory authorities such as the EPA in the United States enforce labeling standards that require clear identification of the product's efficacy against specific bacteria or a broader range of microbes, including viruses and fungi. Accurate labeling must comply with these standards to avoid misleading consumers and to meet legal requirements for product registration and marketing.
Antibacterial vs Antimicrobial Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com