Self-publishing offers authors full creative control and higher royalty rates, allowing for faster market entry and personalized marketing strategies. Traditional publishing provides professional editorial support, broader distribution channels, and established industry credibility that can enhance an author's reach and reputation. Choosing between self-publishing and traditional publishing depends on the author's goals, resources, and willingness to manage different aspects of the publishing process.
Table of Comparison
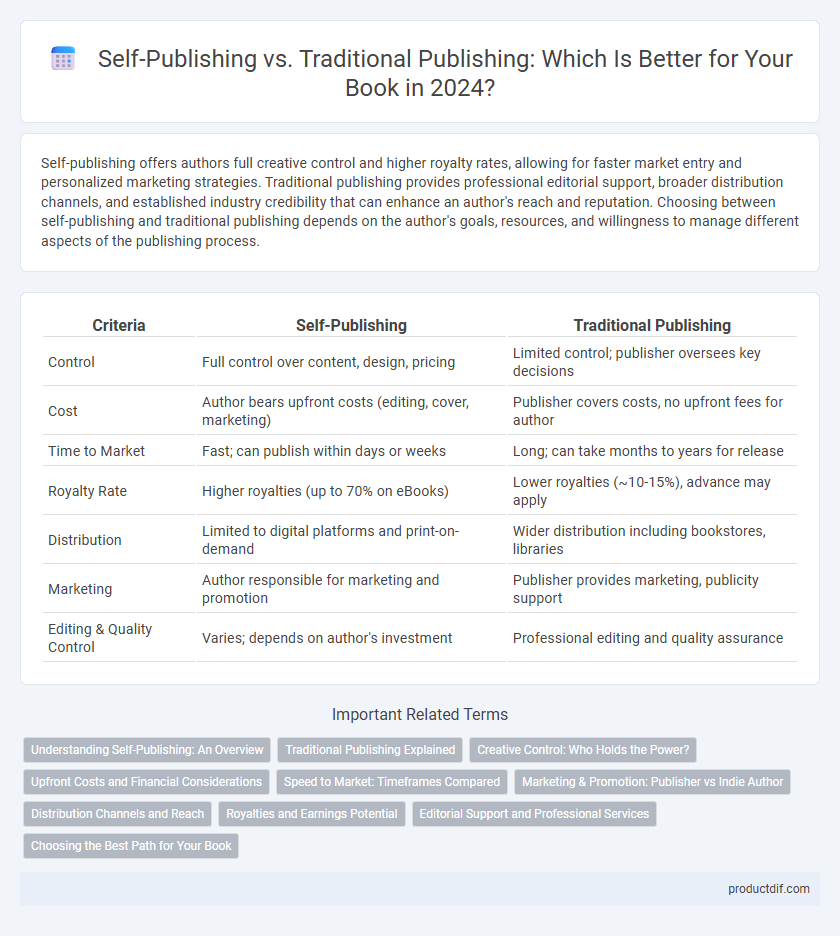
| Criteria | Self-Publishing | Traditional Publishing |
|---|---|---|
| Control | Full control over content, design, pricing | Limited control; publisher oversees key decisions |
| Cost | Author bears upfront costs (editing, cover, marketing) | Publisher covers costs, no upfront fees for author |
| Time to Market | Fast; can publish within days or weeks | Long; can take months to years for release |
| Royalty Rate | Higher royalties (up to 70% on eBooks) | Lower royalties (~10-15%), advance may apply |
| Distribution | Limited to digital platforms and print-on-demand | Wider distribution including bookstores, libraries |
| Marketing | Author responsible for marketing and promotion | Publisher provides marketing, publicity support |
| Editing & Quality Control | Varies; depends on author's investment | Professional editing and quality assurance |
Understanding Self-Publishing: An Overview
Self-publishing empowers authors to maintain full creative control and retain higher royalty percentages compared to traditional publishing. Platforms like Amazon Kindle Direct Publishing and IngramSpark offer accessible distribution channels, making it easier for authors to reach global audiences. Understanding marketing strategies, cover design, and formatting is crucial for success in the self-publishing landscape.
Traditional Publishing Explained
Traditional publishing involves established publishing houses that manage the entire process from editing and design to distribution and marketing. This model offers authors professional support, access to wide distribution channels, and potential advances against royalties. However, it often requires authors to relinquish some creative control and endure a lengthy approval and publication timeline.
Creative Control: Who Holds the Power?
Self-publishing grants authors full creative control over content, cover design, and marketing decisions, allowing for complete artistic freedom. Traditional publishing involves editorial oversight, with publishers influencing title selection, cover art, and sometimes content adjustments to meet market demands. The power dynamic in creative control heavily favors authors in self-publishing, whereas traditional publishing prioritizes marketability guided by publishing houses.
Upfront Costs and Financial Considerations
Self-publishing requires authors to cover upfront costs such as editing, cover design, and marketing, which can range from a few hundred to several thousand dollars depending on the quality of services. Traditional publishing typically offers advance payments to authors, offsetting initial expenses, but royalties are lower and earned only after recouping those advances. Financial considerations include evaluating initial investment risks in self-publishing against potentially slower, but less costly, traditional publishing revenue streams.
Speed to Market: Timeframes Compared
Self-publishing offers authors a significantly faster speed to market, often allowing books to be published within days or weeks after finalizing the manuscript. Traditional publishing typically involves longer timeframes, ranging from six months to over a year due to editing, design, and marketing processes. This time disparity impacts an author's ability to quickly capitalize on market trends and reader demand.
Marketing & Promotion: Publisher vs Indie Author
Traditional publishers leverage established marketing teams, industry connections, and extensive distribution channels to maximize book visibility and sales. Indie authors face the challenge of building their marketing strategies from scratch, often relying on social media, email lists, and grassroots campaigns to reach target audiences. Success in indie publishing depends heavily on an author's ability to engage readers directly and create personalized promotional content.
Distribution Channels and Reach
Self-publishing offers authors direct control over distribution channels, enabling access to global platforms like Amazon Kindle Direct Publishing and Smashwords, which provide immediate reach to diverse audiences. Traditional publishing utilizes established networks with bookstores, libraries, and wholesalers, ensuring broader physical presence and often more extensive marketing support. Despite slower process times, traditional methods typically achieve wider mainstream distribution, while self-publishing excels in digital reach and niche market penetration.
Royalties and Earnings Potential
Self-publishing offers authors higher royalty rates, typically ranging from 35% to 70%, allowing for greater earnings potential per book sold compared to traditional publishing, where royalties often fall between 5% and 15%. Traditional publishers provide advances and handle marketing and distribution, but authors may earn less over time due to lower royalty percentages and shared rights. Authors choosing self-publishing retain full control over pricing and rights, maximizing income opportunities through multiple sales channels and expanded formats.
Editorial Support and Professional Services
Editorial support in traditional publishing includes comprehensive professional editing, proofreading, and developmental guidance provided by experienced publishing houses, ensuring a polished final manuscript. Self-publishing authors often must seek and fund their own editorial services independently, such as freelance editors or proofreaders, which can vary widely in quality and cost. Professional services in traditional publishing also encompass cover design, marketing, and distribution handled by the publisher, whereas self-published authors typically manage or outsource these services themselves.
Choosing the Best Path for Your Book
Self-publishing offers authors complete creative control and higher royalty rates, making it ideal for those seeking independence and faster market entry. Traditional publishing provides extensive editorial support, professional marketing, and wider distribution channels, which benefit authors aiming for credibility and broad audience reach. Evaluating factors such as budget, timeline, target audience, and personal goals helps determine the best publishing route for a successful book launch.
Self-Publishing vs Traditional Publishing Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com