Flash pasteurization rapidly heats beverages to destroy pathogens while preserving flavor, making it ideal for products needing refrigeration. Aseptic processing sterilizes both product and packaging separately before filling, enabling shelf-stable beverages without preservatives. Choosing between methods depends on desired shelf life, flavor retention, and storage requirements.
Table of Comparison
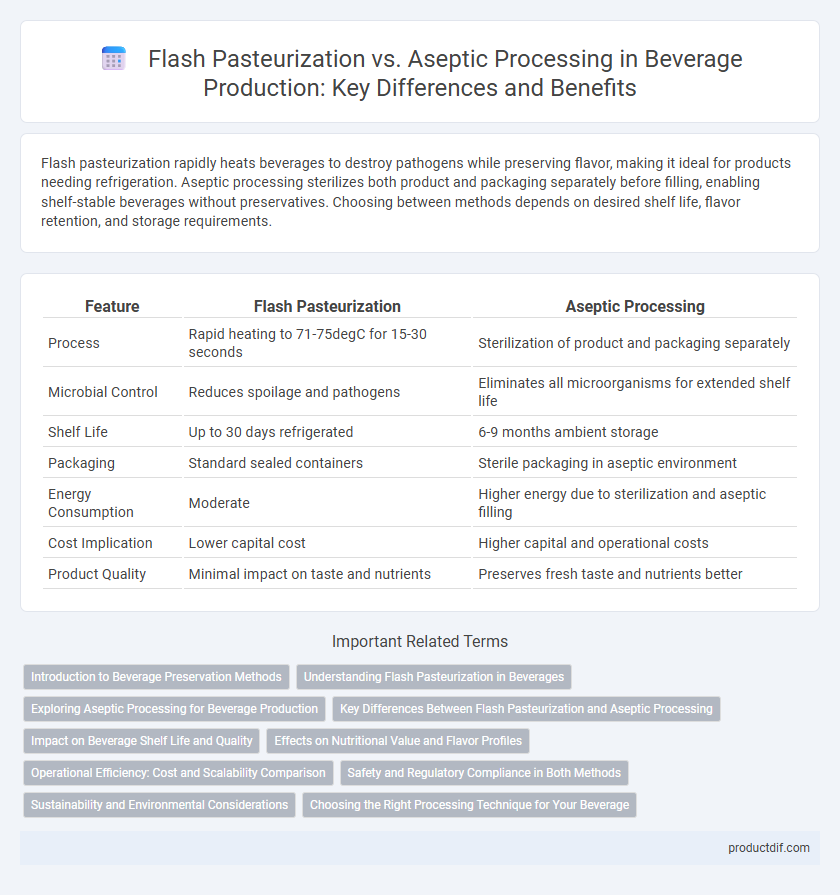
| Feature | Flash Pasteurization | Aseptic Processing |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Rapid heating to 71-75degC for 15-30 seconds | Sterilization of product and packaging separately |
| Microbial Control | Reduces spoilage and pathogens | Eliminates all microorganisms for extended shelf life |
| Shelf Life | Up to 30 days refrigerated | 6-9 months ambient storage |
| Packaging | Standard sealed containers | Sterile packaging in aseptic environment |
| Energy Consumption | Moderate | Higher energy due to sterilization and aseptic filling |
| Cost Implication | Lower capital cost | Higher capital and operational costs |
| Product Quality | Minimal impact on taste and nutrients | Preserves fresh taste and nutrients better |
Introduction to Beverage Preservation Methods
Flash pasteurization rapidly heats beverages to 71.5degC for 15-30 seconds, effectively reducing microbial load while preserving flavor and nutrients. Aseptic processing sterilizes both the beverage and packaging separately before filling in a sterile environment, extending shelf life without refrigeration. Both methods are essential for ensuring safety and quality in juice, dairy, and other liquid products.
Understanding Flash Pasteurization in Beverages
Flash pasteurization rapidly heats beverages to approximately 71.5degC for 15-30 seconds, effectively reducing pathogenic microorganisms while preserving flavor and nutritional quality. This method is widely used in juice and dairy industries due to its balance of safety and sensory retention compared to traditional pasteurization. Major companies utilize flash pasteurization to extend shelf life without the need for preservatives, ensuring product freshness and consumer safety.
Exploring Aseptic Processing for Beverage Production
Aseptic processing in beverage production ensures extended shelf life and preserves flavor by sterilizing both the product and packaging separately before filling under sterile conditions. This method reduces thermal degradation compared to flash pasteurization, maintaining nutrient integrity and sensory qualities. Its efficacy in beverage safety and quality control makes aseptic processing a preferred choice for juices, dairy drinks, and ready-to-drink products.
Key Differences Between Flash Pasteurization and Aseptic Processing
Flash pasteurization involves heating beverages to 71.7degC (161degF) for at least 15 seconds to eliminate pathogens while preserving flavor, whereas aseptic processing sterilizes both the product and packaging separately before filling under sterile conditions. Flash pasteurization is typically used for products with shorter shelf life and refrigeration requirements, while aseptic processing extends shelf life for ambient storage without preservatives. The key difference lies in the temperature and method of sterilization, impacting product preservation, shelf stability, and packaging.
Impact on Beverage Shelf Life and Quality
Flash pasteurization rapidly heats beverages to eliminate pathogens, preserving fresh flavor while extending shelf life to several weeks under refrigeration. Aseptic processing sterilizes both product and packaging separately before filling, enabling shelf-stable beverages with extended shelf life of up to several months without refrigeration. Flash pasteurization maintains sensory qualities better in fresh juices, whereas aseptic processing suits shelf-stable milk or juice concentrates requiring longer storage.
Effects on Nutritional Value and Flavor Profiles
Flash pasteurization preserves more natural flavor and retains a higher content of heat-sensitive vitamins like vitamin C compared to traditional pasteurization, but it may result in slight nutrient loss due to brief exposure to high temperatures. Aseptic processing extends shelf life by sterilizing both the product and packaging separately, leading to minimal flavor changes and better preservation of nutrients such as antioxidants and phenolic compounds. Both methods optimize safety and shelf stability, yet flash pasteurization often better maintains fresh taste while aseptic processing excels in long-term nutrient retention.
Operational Efficiency: Cost and Scalability Comparison
Flash pasteurization offers lower upfront equipment costs and simpler operation, making it more cost-effective for small to medium beverage production volumes. Aseptic processing involves higher initial investment but enables greater scalability and extended shelf life without refrigeration, reducing long-term operational expenses. The choice between flash pasteurization and aseptic processing depends on production scale, budget constraints, and desired shelf stability for beverages.
Safety and Regulatory Compliance in Both Methods
Flash pasteurization ensures beverage safety by rapidly heating products to eliminate pathogens, meeting stringent FDA and USDA regulations for microbial control. Aseptic processing sterilizes both the beverage and packaging separately before filling in a sterile environment, complying with global standards such as FDA 21 CFR Part 113 and EU Directive 2009/54/EC. Both methods offer robust microbial safety, but aseptic processing often provides longer shelf life without preservatives, aligning with regulatory demands for minimally processed beverages.
Sustainability and Environmental Considerations
Flash pasteurization consumes less energy due to shorter heating times compared to aseptic processing, reducing the overall carbon footprint. Aseptic processing requires sterile packaging materials and complex machinery, increasing resource consumption and waste production. Sustainable beverage production favors flash pasteurization for its lower water usage and decreased environmental impact in energy-intensive operations.
Choosing the Right Processing Technique for Your Beverage
Flash pasteurization preserves flavor and nutritional quality by rapidly heating beverages to a high temperature for a short time, making it ideal for juice and dairy products requiring fresh taste retention. Aseptic processing offers extended shelf life by sterilizing both the product and packaging separately before filling, suited for beverages needing long-term storage without refrigeration. Selecting the right technique depends on factors like product type, desired shelf life, flavor profile, and packaging compatibility to ensure optimal quality and safety.
Flash Pasteurization vs Aseptic Processing Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com