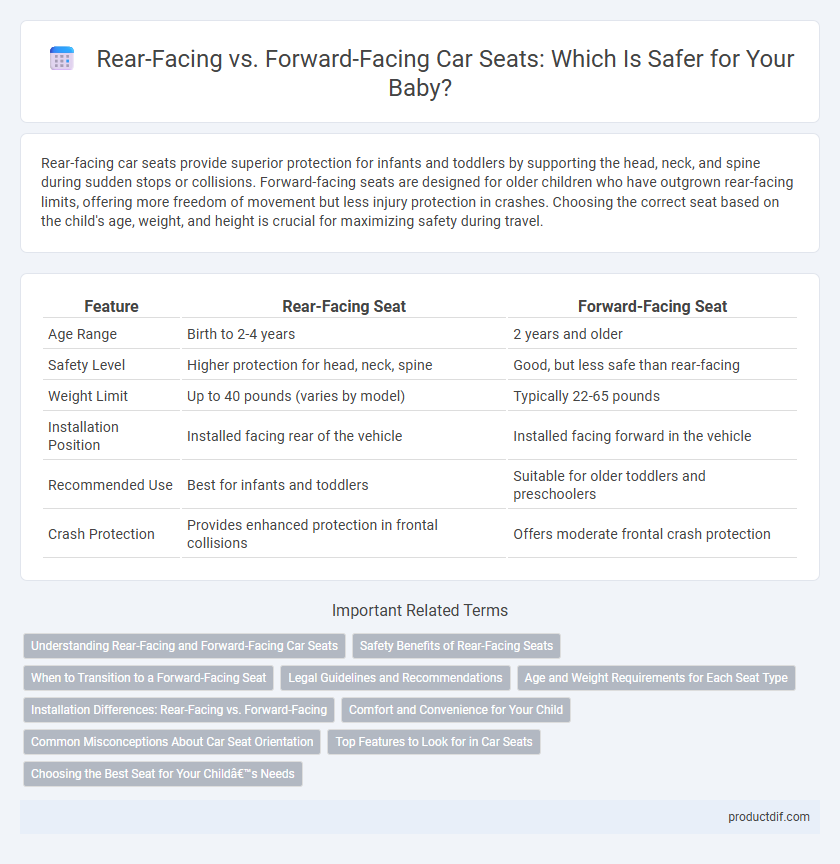
Rear-facing car seats provide superior protection for infants and toddlers by supporting the head, neck, and spine during sudden stops or collisions. Forward-facing seats are designed for older children who have outgrown rear-facing limits, offering more freedom of movement but less injury protection in crashes. Choosing the correct seat based on the child's age, weight, and height is crucial for maximizing safety during travel.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Rear-Facing Seat | Forward-Facing Seat |
|---|---|---|
| Age Range | Birth to 2-4 years | 2 years and older |
| Safety Level | Higher protection for head, neck, spine | Good, but less safe than rear-facing |
| Weight Limit | Up to 40 pounds (varies by model) | Typically 22-65 pounds |
| Installation Position | Installed facing rear of the vehicle | Installed facing forward in the vehicle |
| Recommended Use | Best for infants and toddlers | Suitable for older toddlers and preschoolers |
| Crash Protection | Provides enhanced protection in frontal collisions | Offers moderate frontal crash protection |
Understanding Rear-Facing and Forward-Facing Car Seats
Rear-facing car seats are designed to support an infant's head, neck, and spine in the event of a collision by distributing crash forces evenly across the back of the seat. Forward-facing car seats, equipped with harnesses, secure toddlers who meet height and weight requirements, offering protection by restraining upper body movement during impact. Understanding manufacturer guidelines and safety standards, such as those from the American Academy of Pediatrics and NHTSA, is essential for selecting the appropriate seat based on a child's age, weight, and developmental stage.
Safety Benefits of Rear-Facing Seats
Rear-facing car seats provide superior protection by supporting an infant's head, neck, and spine in the event of a collision, reducing the risk of serious injury. Studies from the American Academy of Pediatrics show that rear-facing seats decrease the likelihood of fatal injury by 71% compared to forward-facing seats. Optimal safety is achieved when children remain rear-facing as long as possible, typically until at least age 2 or until they exceed the maximum height and weight limits of the seat.
When to Transition to a Forward-Facing Seat
Transition to a forward-facing seat typically occurs when a child reaches the height or weight limits specified by the rear-facing car seat manufacturer, usually around age 2 to 4 years. Safety experts like the American Academy of Pediatrics recommend keeping children rear-facing as long as possible, ideally until at least age 2, to provide better protection for the head, neck, and spine in a crash. Parents should verify the car seat's specifications and local safety regulations before making the transition for optimal child safety.
Legal Guidelines and Recommendations
Legal guidelines mandate that infants and toddlers remain in rear-facing car seats until at least age 2 or until they exceed the manufacturer's height and weight limits. Forward-facing seats are recommended only after a child outgrows the rear-facing limits, typically allowing for enhanced safety during car travel. Many safety organizations emphasize extended rear-facing use, citing reduced risk of severe injury in collisions compared to early transition to forward-facing seats.
Age and Weight Requirements for Each Seat Type
Rear-facing car seats are recommended for infants and toddlers from birth up to around 2 to 4 years old, typically supporting weights from 5 to 40 pounds depending on the model. Forward-facing seats are designed for older toddlers and preschoolers who have outgrown the rear-facing limits, usually accommodating children aged 2 to 7 years with weight ranges between 20 to 65 pounds. Following manufacturer guidelines and local safety laws ensures the proper transition from rear-facing to forward-facing seats, maximizing child protection during travel.
Installation Differences: Rear-Facing vs. Forward-Facing
Rear-facing seats are installed using a reclined position with a strict angle to support the baby's head and neck, often secured with a seat belt or LATCH system, ensuring maximum safety in the event of a crash. Forward-facing seats use a more upright installation and typically include a top tether strap along with the LATCH system or seat belt for added stability and reduced forward movement during impact. Proper installation techniques vary by vehicle and seat model, making adherence to manufacturer guidelines critical for both rear-facing and forward-facing seats.
Comfort and Convenience for Your Child
Rear-facing car seats provide superior comfort and support by distributing impact forces evenly across the child's back and neck, making them ideal for infants and toddlers. Forward-facing seats offer enhanced convenience by allowing easier access to buckle and adjust straps, which benefits older children who require more independence during travel. Selecting the appropriate seat depends on balancing comfort needs with practical features such as ease of installation, adjustability, and the child's growth stage.
Common Misconceptions About Car Seat Orientation
Many parents mistakenly believe forward-facing seats provide better safety once a child reaches a certain age, but rear-facing seats significantly reduce the risk of severe injury by better supporting the head, neck, and spine during collisions. The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends keeping toddlers in rear-facing seats until at least age 2 or until they reach the seat's height and weight limits. Misunderstandings about comfort and convenience often lead to premature transition, compromising child safety in car travel.
Top Features to Look for in Car Seats
Top features to look for in baby car seats include robust side-impact protection, adjustable harness systems for secure and comfortable fit, and energy-absorbing foam to reduce crash forces. Rear-facing seats offer enhanced head and neck support critical for infants and toddlers, while forward-facing seats often include higher weight limits and integrated cup holders for older children. Ensuring ease of installation with LATCH compatibility and clear recline indicators enhances safety and convenience during travel.
Choosing the Best Seat for Your Child’s Needs
Choosing the best car seat for your child involves understanding the safety benefits of rear-facing seats, which provide superior protection for infants and toddlers by supporting their head, neck, and spine during sudden stops. Forward-facing seats are suitable for older children who have outgrown rear-facing limits, offering harness systems designed to keep them secure while accommodating their growing size. Always select a seat based on your child's age, weight, and height, adhering to manufacturer guidelines and safety regulations to ensure optimal protection.
Rear-Facing Seat vs Forward-Facing Seat Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com