Convection ovens use a fan to circulate hot air, ensuring faster and more even cooking compared to conventional ovens, which rely on radiant heat from the top and bottom. This airflow technology helps bake and roast food with crispier textures while reducing cooking times. Conventional ovens are ideal for recipes requiring slow and consistent heat, making them suitable for baking bread or casseroles where gentle cooking is preferred.
Table of Comparison
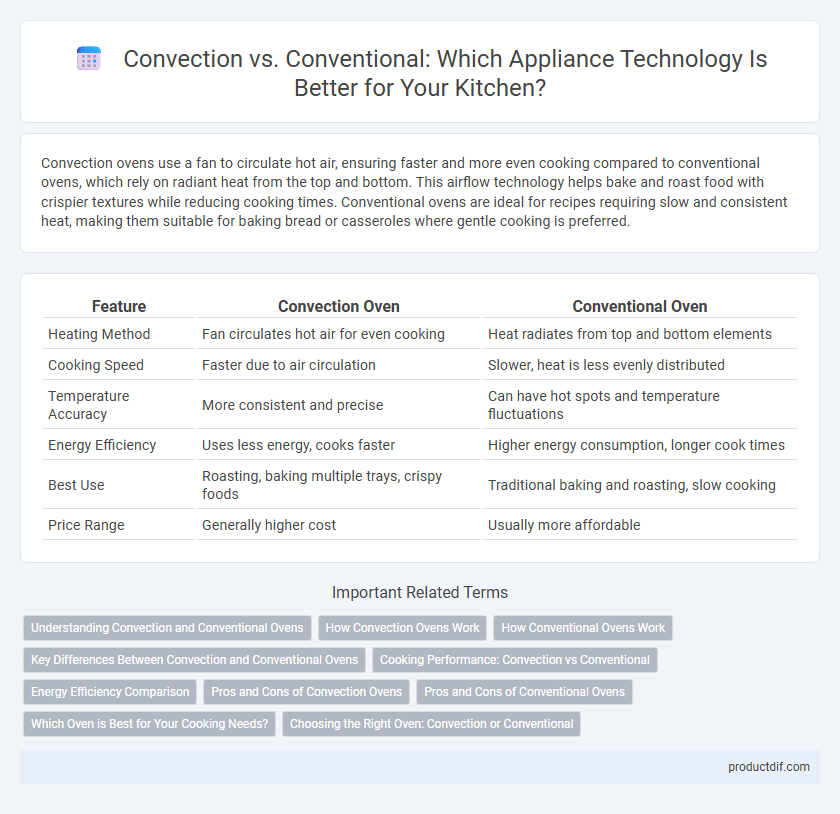
| Feature | Convection Oven | Conventional Oven |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Fan circulates hot air for even cooking | Heat radiates from top and bottom elements |
| Cooking Speed | Faster due to air circulation | Slower, heat is less evenly distributed |
| Temperature Accuracy | More consistent and precise | Can have hot spots and temperature fluctuations |
| Energy Efficiency | Uses less energy, cooks faster | Higher energy consumption, longer cook times |
| Best Use | Roasting, baking multiple trays, crispy foods | Traditional baking and roasting, slow cooking |
| Price Range | Generally higher cost | Usually more affordable |
Understanding Convection and Conventional Ovens
Convection ovens use a fan to circulate hot air, ensuring even cooking and reducing cooking time by up to 25%, while conventional ovens rely on radiant heat from the top and bottom heating elements. This airflow in convection ovens promotes consistent temperature distribution, ideal for roasting and baking delicate pastries. Conventional ovens offer more predictable cooking results for recipes requiring a gentler, slower cooking process without airflow disturbance.
How Convection Ovens Work
Convection ovens use a built-in fan and exhaust system to circulate hot air evenly around the food, promoting faster and more uniform cooking compared to conventional ovens. This airflow helps maintain a consistent temperature, reducing cooking times and preventing hot spots. The efficient heat distribution in convection ovens enhances browning and crisping, making them ideal for roasting and baking.
How Conventional Ovens Work
Conventional ovens use radiant heat from coils located at the top and bottom of the oven cavity, creating a static cooking environment ideal for baking and roasting. Heat distribution is slower and less even compared to convection ovens, often requiring longer cooking times and periodic food rotation for uniform results. The design relies on natural air circulation within the oven, making it effective for recipes that benefit from dry heat and slower cooking processes.
Key Differences Between Convection and Conventional Ovens
Convection ovens utilize a built-in fan and exhaust system to circulate hot air, promoting even cooking and reducing cooking time by up to 25% compared to conventional ovens. Conventional ovens rely on stationary heating elements that create uneven heat distribution, which may result in longer cooking times and less consistent browning. The energy efficiency of convection ovens often surpasses that of conventional models, making them ideal for roasting, baking, and dehydrating with precision.
Cooking Performance: Convection vs Conventional
Convection ovens use a fan to circulate hot air, resulting in faster and more even cooking compared to conventional ovens that rely on radiant heat from elements. This airflow promotes superior browning and crispiness, making convection ideal for roasting and baking tasks requiring consistent temperature distribution. Conventional ovens excel in recipes sensitive to drying out, as their gentler heat provides a more controlled cooking environment without airflow disturbances.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
Convection ovens use fans to circulate hot air, resulting in faster cooking times and lower energy consumption compared to conventional ovens that rely solely on radiant heat. Energy efficiency ratings for convection models often show a 20-30% reduction in electricity use, making them more cost-effective for frequent baking or roasting. Choosing convection appliances reduces overall energy bills and carbon footprints due to more uniform heat distribution and quicker cooking cycles.
Pros and Cons of Convection Ovens
Convection ovens use a fan to circulate hot air, resulting in faster and more even cooking compared to conventional ovens. This method reduces cooking times by up to 25% and provides superior browning and crisping, making it ideal for roasting and baking. However, convection ovens can be more expensive and may require recipe adjustments due to their intense heat distribution.
Pros and Cons of Conventional Ovens
Conventional ovens provide consistent heating through stationary heating elements, making them ideal for recipes requiring slow, even cooking like roasts and baked casseroles. They are typically more affordable and easier to maintain compared to convection ovens but may result in uneven cooking due to hot spots and longer cooking times. The lack of a fan means conventional ovens can struggle with browning and crisping, which can be a downside for baking pastries or achieving a perfect crust.
Which Oven is Best for Your Cooking Needs?
Convection ovens use a fan to circulate hot air, ensuring even cooking and faster baking times, making them ideal for roasting meats and baking pastries. Conventional ovens rely on static heat from top and bottom elements, offering consistent results for traditional recipes and slow-cooking dishes. Selecting the best oven depends on your cooking style--choose convection for efficiency and crisp textures, or conventional for classic, steady heat performance.
Choosing the Right Oven: Convection or Conventional
Convection ovens use a fan to circulate hot air, providing faster and more even cooking compared to conventional ovens that rely on radiant heat from the top and bottom. For baking delicate pastries or roasting meats evenly, convection ovens offer superior results by reducing cooking time and preventing hot spots. Conventional ovens are ideal for recipes requiring slower, gentler heat such as casseroles and baked goods that rise slowly, making the choice dependent on specific cooking needs.
Convection vs Conventional Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com